Reviewed by Dr. Vipin Bihari Sharma

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the colon and rectum. It is a chronic condition that causes inflammation, ulcers, and bleeding in the lining of the large intestine. UC can cause a range of symptoms, including diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. It is a lifelong condition, and there is currently no cure. However, with the right treatment and management, many people with Ulcerative colitis can lead healthy, active lives. [1] In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and more of Ulcerative colitis.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
The symptoms of Ulcerative colitis can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Some people with UC may experience long periods of remission, during which they have no symptoms. The most common symptoms of Ulcerative colitis include:
Diarrhoea
This is the most common symptom of Ulcerative colitis, and it can range from mild to severe. It may be accompanied by blood, mucus, or pus in the stool. [1] [2]
Abdominal pain and cramping
People with Ulcerative colitis may experience abdominal pain and cramping, which can be mild or severe. [1] [2]
Rectal bleeding
Ulcerative colitis can cause bleeding from the rectum, which may be seen in the stool or on toilet paper. [1] [2]
Urgency
People with Ulcerative colitis may feel an urgent need to have a bowel movement, even if they have just had one. [1] [2]
Weight loss
Chronic diarrhoea and other symptoms of Ulcerative colitis can lead to weight loss. [1] [2]
Fatigue
Ulcerative colitis can cause fatigue, which may be due to anaemia or other factors. [1] [2]
Fever
Some people with Ulcerative colitis may experience a fever, which is often a sign of inflammation. [1] [2]
Joint pain
Ulcerative colitis can cause joint pain, which may be a sign of inflammation in the joints. [1] [2]
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of Ulcerative colitis is not yet known. However, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of Ulcerative colitis are more likely to develop the condition. Environmental factors that may play a role in the development of UC include:
Diet

Some studies have suggested that a diet high in fat and low in fibre may increase the risk of developing Ulcerative colitis. [1] [2]
Smoking
Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing Ulcerative colitis. [1] [2]
Stress

Stress may trigger or worsen symptoms of Ulcerative colitis in some people. [1] [2]
Infections
Some infections may trigger the development of Ulcerative colitis in some people. [1] [2]
Dosha Imbalance
According to Ayurveda, Ulcerative colitis is primarily a disease of the pitta dosha. Pitta represents the fire element in the body, and when it becomes imbalanced, it can lead to inflammation and irritation in the digestive tract, which can manifest as UC. [3]
Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis
To diagnose Ulcerative colitis, a doctor will perform a physical examination and may order several tests. These may include:
Blood tests
Blood tests can help to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. [4]
Stool sample
A stool sample can help to rule out infections that may cause similar symptoms. [4]
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is a procedure in which a long, flexible tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the rectum and colon. This allows the doctor to examine the lining of the colon and rectum for signs of inflammation, ulcers, or other abnormalities. [4]
Biopsy
During a colonoscopy, the doctor may take a small sample of tissue (biopsy) from the lining of the colon and rectum. This tissue can be examined under a microscope to confirm a diagnosis of Ulcerative colitis. [4]
Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
There is no cure for Ulcerative colitis, but treatment can help to manage symptoms and prevent complications. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and allow the lining of the colon and rectum to heal. Treatment options for Ulcerative colitis may include:
Medications
Several types of medications are available to treat Ulcerative colitis. These may include anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, antibiotics, and biologics. The choice of medication will depend on the severity of the disease, the symptoms, and the individual’s overall health. [5]
Surgery
Surgery may be necessary for people with severe Ulcerative colitis who do not respond to medication or who develop complications. Surgery may involve removing the colon and rectum (proctocolectomy) and creating an ileostomy, in which waste is eliminated through a stoma (a small opening) in the abdomen. [5]
Lifestyle changes
Certain lifestyle changes may help to manage symptoms of Ulcerative colitis. These may include eating a healthy, balanced diet, avoiding trigger foods, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, may also be helpful. [5]
Ayurvedic Remedies
The use of medicated drugs in Anuvasan Vasti and Pichha Vasti not only helps to reduce the symptoms and complications of the disease but also helps to prevent relapses or the recurrence of the disease. Additionally, remedies like Triphala can be used to promote digestive health and reduce inflammation in the colon. [3]
Complications of Ulcerative Colitis
If left untreated or poorly managed, Ulcerative colitis can lead to several complications. These may include:
Colorectal cancer
People with Ulcerative colitis have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. [6]
Toxic megacolon
This is a rare but life-threatening complication of Ulcerative colitis in which the colon becomes dilated and paralyzed. [6]
Perforation of the colon
In severe cases of Ulcerative colitis, the colon may become weakened and perforated, leading to infection and other complications. [6]
Anaemia
Chronic bleeding from the colon can lead to anaemia, a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. [6]
Osteoporosis
Long-term use of corticosteroids to treat Ulcerative colitis can lead to osteoporosis, a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle. [6]
Prevention of Ulcerative Colitis

Currently, there is no known way to prevent Ulcerative colitis. However, some lifestyle changes may help to reduce the risk of developing the disease or managing symptoms. [7] These may include:
– Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is high in fibre and low in fat.
– Avoiding trigger foods that may worsen symptoms, such as dairy, caffeine, and alcohol.
– Quitting smoking, as smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing Ulcerative colitis.
– Getting regular exercise and managing stress through techniques such as yoga or meditation.
FAQs
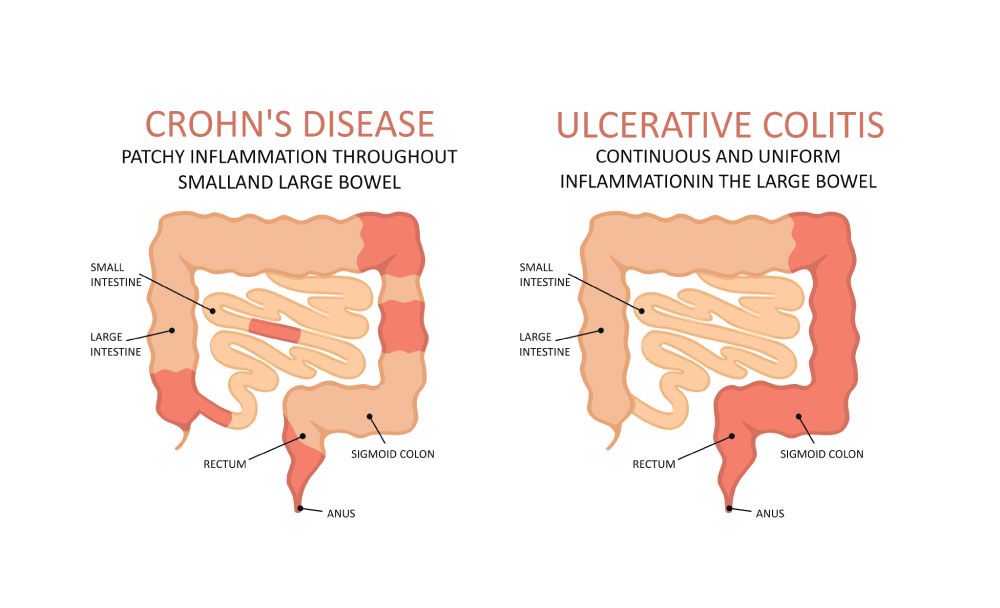
1. Is ulcerative colitis the same as Crohn’s disease?
No, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are two different types of inflammatory bowel disease. While ulcerative colitis affects only the colon and rectum, Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus.
2. Can ulcerative colitis be cured?
No, there is currently no cure for ulcerative colitis, but it can be managed with medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
3. Is ulcerative colitis hereditary?
While the exact cause of ulcerative colitis is not yet known, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Having a family history of ulcerative colitis or other inflammatory bowel diseases can increase the risk of developing the condition.
4. Can diet affect ulcerative colitis?
Yes, diet can play a role in managing symptoms of ulcerative colitis. Certain foods can trigger flare-ups, while others can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. A registered dietitian can help develop a personalized diet plan for individuals with ulcerative colitis.
5. Can stress cause ulcerative colitis?
Stress does not cause ulcerative colitis, but it can trigger flare-ups and worsen symptoms in individuals with the condition. Learning stress management techniques, such as meditation and relaxation exercises, can help reduce the impact of stress on ulcerative colitis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon that can cause a range of symptoms and complications. While the exact cause of the condition is not yet known, it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder with genetic and environmental factors contributing to its development. Diagnosing and managing ulcerative colitis requires a multidisciplinary approach, including medical treatment, nutritional therapy, surgery, and lifestyle changes. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with ulcerative colitis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Disclaimer: This article is from a modern medicine and general knowledge perspective only and does not constitute medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a trained medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References:
- Ulcerative Colitis – NIDDK (nih.gov)
- Ulcerative colitis – NHS (www.nhs.uk)
- Ayurvedic Management Of Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Study
- Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosis | Stanford Health Care
- Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis – NIDDK (nih.gov)
- Ulcerative colitis – Complications – NHS (www.nhs.uk)
- A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease – PMC (nih.gov)