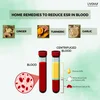
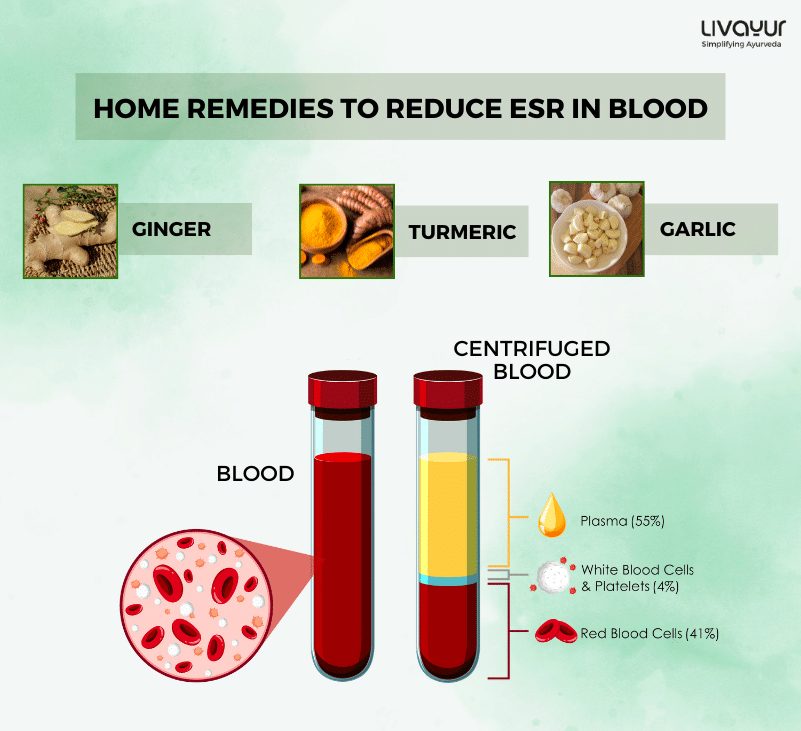
Peanut butter is a delicious and nutritious spread that can be enjoyed in many ways. It is made from ground peanuts and often includes added salt, sugar, and oils. Here are 15 amazing health benefits of peanut butter, supported by scientific research.
- A Good Source of Protein
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter is a good source of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body.
Secondary Benefit: A 2-tablespoon serving of peanut butter contains 7 grams of protein, which is more than the amount found in an egg [1].
- High in Healthy Fats
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter is high in healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Secondary Benefit: These fats have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and improved cholesterol levels [2].
- May Help with Weight Loss
Primary Benefit: Despite being high in calories, peanut butter may help with weight loss.
Secondary Benefit: This is because the high protein and fibre content can increase feelings of fullness and reduce appetite [3].
- May Improve Heart Health
Primary Benefit: The healthy fats in peanut butter may help improve heart health.
Secondary Benefit: One study found that consuming peanut butter at least 5 times per week was associated with a 21% lower risk of developing heart disease [4].
- May Reduce the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter may help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Secondary Benefit: Several studies have found that consuming peanuts and peanut butter can improve blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity [5].
- May Improve Brain Function
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains nutrients that may help improve brain function.
Secondary Benefit: The vitamin E, magnesium, and healthy fats found in peanut butter have been linked to improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline [6].
- May Boost Immune System
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains nutrients that may help boost the immune system.
Secondary Benefit: The high levels of vitamin E, vitamin B6, and zinc found in peanut butter have been shown to support immune function [7].
- May Improve Bone Health
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains nutrients that may help improve bone health.
Secondary Benefit: The magnesium, phosphorus, and protein found in peanut butter have been linked to improved bone density and a reduced risk of osteoporosis [8].
- May Reduce the Risk of Gallstones
Primary Benefit: Consuming peanut butter may help reduce the risk of gallstones.
Secondary Benefit: One study found that women who consumed at least 1 ounce of nuts or peanut butter per week had a lower risk of developing gallstones [9].
- May Improve Gut Health
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter may help improve gut health.
Secondary Benefit: The fibre and healthy fats found in peanut butter have been linked to improved digestive function and a reduced risk of gut-related diseases [10].
- May Reduce Inflammation
Primary Benefit: The healthy fats and antioxidants found in peanut butter may help reduce inflammation in the body.
Secondary Benefit: One study found that consuming peanuts and peanut butter was associated with lower levels of inflammatory markers in the blood [11].
- May Improve Sleep
Primary Benefit: The tryptophan found in peanut butter may help improve sleep.
Secondary Benefit: Tryptophan is an amino acid that can help produce serotonin and melatonin, which are important for regulating sleep [12].
- May Improve Skin Health
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains vitamin E, which can help maintain healthy skin.
Secondary Benefit: Peanut butter also contains resveratrol, which has been shown to have anti-ageing and skin-protecting properties [13].
- Reduces Inflammation
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains monounsaturated fats, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Secondary Benefit: Peanut butter also contains polyphenols and other antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress [14].
- Supports Immune System
Primary Benefit: Peanut butter contains several nutrients that are important for immune system function, such as vitamin E, magnesium, and zinc.
Secondary Benefit: Peanut butter also contains flavonoids and other compounds that can help support immune system health [15].
In conclusion, peanut butter is a delicious and nutritious food that offers a wide range of health benefits. From supporting heart health and reducing inflammation to promoting healthy skin and boosting energy, peanut butter is a versatile food that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. So next time you reach for a jar of peanut butter, remember all the amazing ways it can benefit your health.
References:
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170000/nutrients
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-fats-bad-and-good
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12468624/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/1720482
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4997299/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452159/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6266234/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452159/
- https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/133/11/3818S/4687940
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257681/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/92/2/454/4597602
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12421877/
- https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(13)02151-3/fulltext
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6083539/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3649729/