This article is reviewed by an expert

Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys or the urinary tract. They can cause severe pain, blood in the urine, nausea, vomiting, and urinary problems. They can also lead to complications such as infection, obstruction, or kidney damage if not treated promptly. Understanding the causes and symptoms of kidney stones is important so that you can take steps to prevent the problem or to deal with it swiftly. This is important, considering that India has a kidney stone prevalence rate of 12 percent – meaning that 1 in 10 Indians experiences kidney stones. Prevalence rates are also higher in northern India at 15 percent 1.
Causes Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stone causes can vary as there are different types of stones, depending on their chemical composition. The most common types are 2:
- Calcium stones: These are usually made of calcium oxalate, but can also contain calcium phosphate or maleate. They can be influenced by diet, excess body weight, some medical conditions, and certain supplements and medications.
- Uric acid stones: These form when the urine is too acidic, which can be caused by gout, diabetes, obesity, or a diet high in purines (found in animal proteins).
- Struvite stones: These are associated with urinary tract infections (UTIs), as bacteria can produce ammonia that increases the pH of the urine and promotes the formation of these stones.
- Cystine stones: These are rare and occur in people with a genetic disorder called cystinuria, which causes excess cystine (an amino acid) to leak into the urine.
Some factors that can increase the risk of developing kidney stones are 3:
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can make the urine more concentrated and prone to crystallization.
- Family History: Having a relative who had kidney stones can increase your chances of having them too.
- Age & Sex: Kidney stones are more common in people between 20 and 50 years old, and more often in men than women.
- Diet: Eating foods high in oxalate, sodium, sugar, or animal protein can increase the risk of certain types of stones.
Kidney Stone Symptoms
Kidney stones can cause different symptoms depending on their size, location, and type. Some stones may not cause any symptoms at all, while others can cause severe pain and complications. Here are some of the possible symptoms of kidney stones 4.
Kidney Stone Early Symptoms
Some people may notice some early signs of kidney stones before they cause any pain. These signs may include:
- Cloudy, foul-smelling, or bloody urine
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Reduced amount of urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if there is an infection)

Common Kidney Stone Symptoms
Pain is perhaps the defining symptom of kidney stones and will only appear once the stone has grown or moved. The movement of a kidney stone into the ureter, the tube that connects the kidney to the bladder can cause sudden and severe pain. This pain comes and goes and also radiates from the back or side to the lower abdomen, groin, or genitals. The pain can also change in intensity or location as the stone moves along the urinary tract.
Although both men and women experience similar symptoms of kidney stones, there may be some differences due to the anatomy of their urinary tracts 5.
Kidney Stone Symptoms In Women
- Women are more likely to experience no symptoms from stone formation.
- Women may have more urinary tract infections (UTIs) associated with kidney stones, as they have a shorter urethra that is more prone to bacterial invasion.
Kidney Stone Symptoms In Men
- Men are more likely than women to develop calcium oxalate monohydrate stones and also experience more intense and severe pain according to some studies.
- Men may feel more pain in their testicles or penis as the stone passes through the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body.
Tips To Manage Kidney Stone Pain Symptoms
Kidney stone pain can be excruciating, but there are some effective home treatments and Ayurvedic medicines for kidney stones that can provide relief.
- Apply a heating pad or a hot pack to the affected area for quick relief from kidney stone pain. The heat helps to relax the muscles and may alleviate discomfort 6.
- Soaking in a warm bath can help relax the body and potentially reduce kidney stone pain. It may also provide overall comfort and relaxation 6.
- Light physical activity, such as walking or stretching, may help relieve pain by promoting blood flow and reducing muscle tension. Some activities may also help to dislodge and eliminate kidney stones 7.
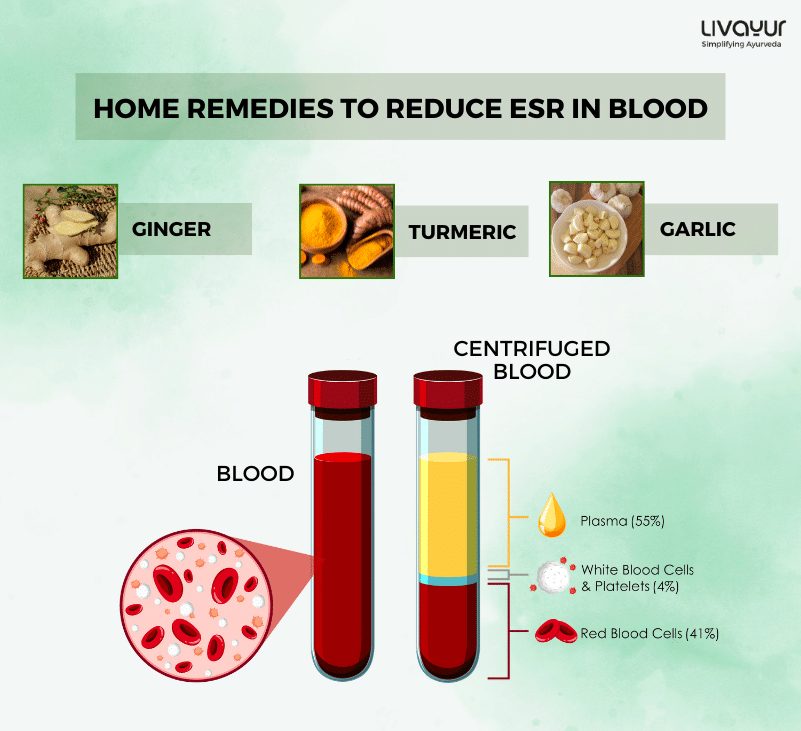
- Include household ingredients to prepare Tulsi tea, lemon juice or pomegranate juice as they are highly recommended in Ayurveda and can help with the breakdown and passage of some types of stones 8.
- Ayurvedic medicines containing herbs such as Punarnava, Kalonji, Prajmoda, Varuna and Gokhru are extremely effective at both treating kidney stones and reducing the risk of recurrence 9,10,11,12,13.
Conclusion
If you experience severe or worsening pain, fever, persistent vomiting, or any concerning symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and guide you through appropriate treatment options for kidney stones.
FAQs
How do you detect kidney stones?
The most effective method of diagnosis is with imaging tests, such as high-speed or dual energy computerized tomography (CT) as they can even detect tiny stones.
How long do kidney stones last?
The vast majority of tiny kidney stones (under 4 mm), will often cause no symptoms and pass on their own within a month. More than half of those between 4 to 6 mm pass without intervention in about 45 days. With stones larger than 6 mm, most require treatment and only some resolve without intervention but can last for a year.
What food causes kidney stones?
Processed foods and a diet that is not well balanced greatly increase the risk of kidney stones. Colas, fast foods and processed meats are the worst offenders.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.
References:
- https://www.cureus.com/articles/136289-risk-factors-of-incident-kidney-stones-in-indian-adults-a-hospital-based-cross-sectional-study#!/
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000135.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8499392/
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stones/symptoms-causes
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8497339/
- https://arkansasurology.com/kidney-stones-what-can-i-do-to-pass-one-at-home/
- https://brieflands.com/articles/asjsm-104372.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4374253/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.3109/13880209.2011.581671
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331775916_Efficacy_of_black_seed_Nigella_sativa_L_on_kidney_stone_dissolution_A_randomized_double-blind_placebo-controlled_clinical_trial
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5698599/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3221072/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3161431/