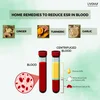
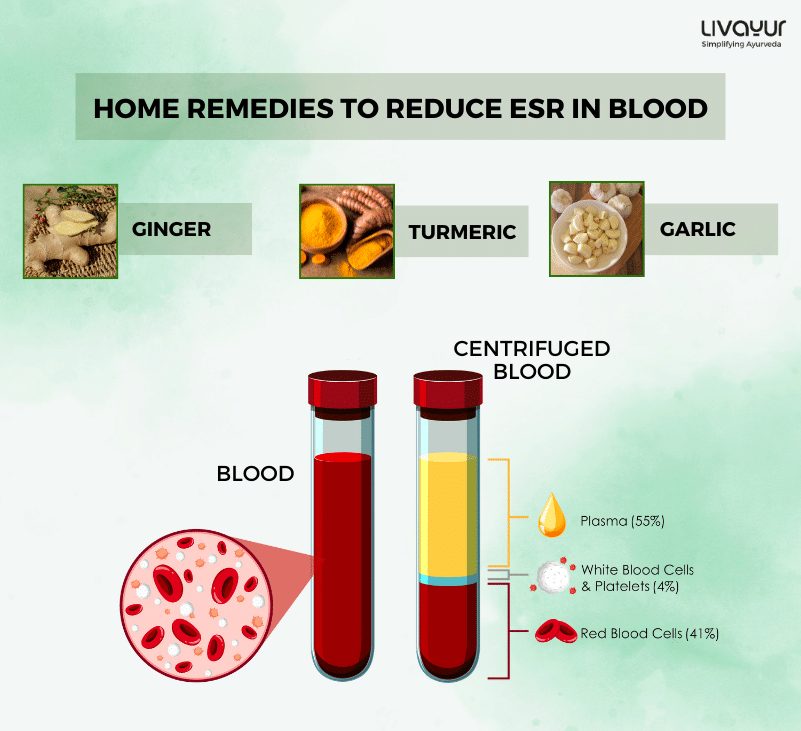
Coriander leaves, also known as cilantro or Dhaniya, have been an integral part of Ayurvedic medicine and culinary traditions for centuries. These vibrant green leaves not only add flavour and aroma to dishes but also offer a myriad of health benefits. From supporting digestion and detoxification to boosting immunity and heart health, coriander leaves have earned their place as a valuable herb in Ayurveda. In this article, we will explore 15 scientifically proven benefits of coriander leaves, delving into both their primary and secondary effects.
Coriander Leaves Benefits
- Digestive Support [1]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves possess carminative properties that help alleviate digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and indigestion.
Secondary Benefit: The essential oils present in coriander leaves stimulate digestive enzymes, promoting healthy digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Detoxification [2]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves exhibit detoxifying effects by aiding in the elimination of toxins and heavy metals from the body.
Secondary Benefit: The antioxidants present in coriander leaves protect against oxidative stress and support liver function, an essential organ for detoxification.
- Heart Health [3]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves contain compounds that help reduce cholesterol levels and lower blood pressure, supporting cardiovascular health.
Secondary Benefit: The presence of potassium in coriander leaves helps maintain a healthy heart rhythm and regulates blood pressure levels.
- Immune Boosting [4]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, which strengthen the immune system and protect against infections.
Secondary Benefit: The antimicrobial properties of coriander leaves help fight against harmful bacteria and viruses, enhancing overall immunity.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects [5]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves possess anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in the body.
Secondary Benefit: The presence of specific compounds in coriander leaves inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, alleviating inflammatory conditions.
- Skin Health [6]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves offer antibacterial and antifungal properties that help prevent skin infections and promote a healthy complexion.
Secondary Benefit: The antioxidants present in coriander leaves protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, delaying signs of ageing.

- Blood Sugar Regulation [7]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves may aid in regulating blood sugar levels due to their hypoglycemic effects.
Secondary Benefit: The fibre content in coriander leaves slows down the absorption of sugars, preventing sudden spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Bone Health [8]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves contain essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
Secondary Benefit: The presence of vitamin K in coriander leaves contributes to proper calcium absorption, supporting bone density.
- Anti-Anxiety and Sleep Aid [9]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves possess calming properties that help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
Secondary Benefit: The sedative effects of coriander leaves may aid in improving sleep quality and reducing insomnia symptoms.
- Anti-cancer Potential [10]
Primary Benefit: Certain compounds found in coriander leaves demonstrate anticancer properties, inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
Secondary Benefit: The antioxidants in coriander leaves help neutralize free radicals, reducing the risk of cellular damage and cancer development.
- Eye Health [11]
Primary Benefit: The presence of beta-carotene and vitamin C in coriander leaves supports vision health and protects against age-related macular degeneration.
Secondary Benefit: The antioxidant properties of coriander leaves help reduce oxidative stress in the eyes, maintaining their overall health.
- Anti-allergic Effects [12]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves exhibit anti-allergic properties, helping to alleviate symptoms of allergic reactions.
Secondary Benefit: The bioactive compounds in coriander leaves inhibit the release of histamine, reducing allergic responses.
- Respiratory Health [13]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves possess expectorant properties, facilitating the expulsion of mucus and relieving respiratory congestion.
Secondary Benefit: The presence of vitamin C in coriander leaves supports lung function and helps prevent respiratory infections.
- Hormonal Balance
Primary Benefit: Certain compounds found in coriander leaves may help regulate hormonal imbalances, particularly in women.
Secondary Benefit: Coriander leaves may aid in reducing menstrual cramps and supporting a regular menstrual cycle.
- Anti-microbial Properties [14]
Primary Benefit: Coriander leaves exhibit antimicrobial effects, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi.
Secondary Benefit: The essential oils in coriander leaves help protect against foodborne pathogens and promote food safety.
FAQs
Can coriander leaves help with weight loss?
Yes, coriander leaves are low in calories and high in fibre, which can promote feelings of fullness and support healthy weight management.
Are coriander leaves beneficial for skin health?
Yes, coriander leaves possess antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that can help reduce acne, improve skin texture, and provide a youthful glow.
Can coriander leave help with diabetes management?
Yes, coriander leaves have hypoglycemic properties that help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall diabetes management.
How can coriander leaves be incorporated into the diet?
Coriander leaves can be used as a garnish in salads, soups, curries, and other dishes. They can also be blended into chutneys or added to juices and smoothies for a refreshing flavour.
Conclusion
Coriander leaves, a potent Ayurvedic herb, offer an array of health benefits ranging from digestive support and detoxification to immune boosting and heart health promotion. Incorporating coriander leaves into your daily diet can be a delightful and beneficial addition to your wellness routine. However, it is important to remember that individual responses may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized advice.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.
References:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2221169115000647
- Ren H., Jia H., Endo H. and Hayashi T. (2009): Cadmium detoxification effect of chinese parsley Coriandrum sativum in liver and kidney of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish science 75:731-741.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19146935
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5618098/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5609694/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3891203/
- http://www.foodandnutritionjournal.org/volume11number1/nutritional-and-functional-quality-of-mustard-and-coriander-greens-at-different-phases-of-development/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3195130/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25148954/
- https://www.indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:mpijpri&volume=5&issue=2&article=001
- http://jtim.biosci.in/ojs/index.php/jtim/article/view/117
- http://journals.sjp.ac.lk/index.php/ait/article/view/5598
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15161192