This article is reviewed by an expert

The food you consume plays a crucial role in determining your health and well-being. In Ayurveda, food is considered medicine, and a balanced diet is one that provides all the necessary nutrients to maintain good health. [9]
This guide will help you understand the basics of a balanced diet and provide tips for creating one that suits your preferences.
What is a balanced diet?

According to Ayurveda, each person has a unique combination of three doshas – Vata, Pitta, and Kapha – that determine their physical, emotional, and mental characteristics. [8]A balanced diet must be one that is tailored to the needs of each person’s dosha and includes a variety of whole, freshly cooked foods. It is a holistic approach to nutrition that takes into account the unique needs of each individual. These foods include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. A healthy balanced diet chart contains fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and may include little to no processed food or sweetened beverages. A balanced diet should also provide enough calories to meet your daily energy needs. [1]
Why is a Balanced Diet Important?
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. A well-rounded diet provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support bodily functions, boost the immune system, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Excessive weight is widely acknowledged as a major risk factor for numerous health issues including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, steoarthritis, certain types of cancer, and gallbladder disease. While type 2 diabetes was
previously only observed in adults, it is now becoming increasingly prevalent in children and teenagers. Overweight and obesity are the primary culprits behind type 2 diabetes, accounting for 90% of all diagnosed cases.[12] A balanced diet can also improve mental health and cognitive function. [1]
Tips for creating a balanced diet for your health
Eat a variety of foods

Eating a variety of foods ensures that you get all the essential nutrients your body needs. Include different types of grains, vegetables and fruits in your diet.
The vegetable food group consists of dark green vegetables, red and orange vegetables, starchy vegetables(potatoes, beetroot, green peas, corn etc.) and legumes. [3] Each food group has unique nutrients that are beneficial for your health.
Focus on whole foods

Ayurveda emphasises the importance of fresh, whole foods that are minimally processed and free from additives and preservatives.
[10] Fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains(Ragi, jowar bajra, etc.), pulses and lentils(green gram, rajma,chickpeas, etc.), nuts(almonds, cashews, etc.), and seeds(pumkin, sesame, sunflower, etc.) should make up the bulk of your diet. They are rich in fibre, vitamins, and minerals. While it’s impossible to avoid processed foods entirely it is good practice to incorporate more whole foods into your diet. Include whole grains, fruits and vegetables in your meals. [4]
Choose healthy sources of protein
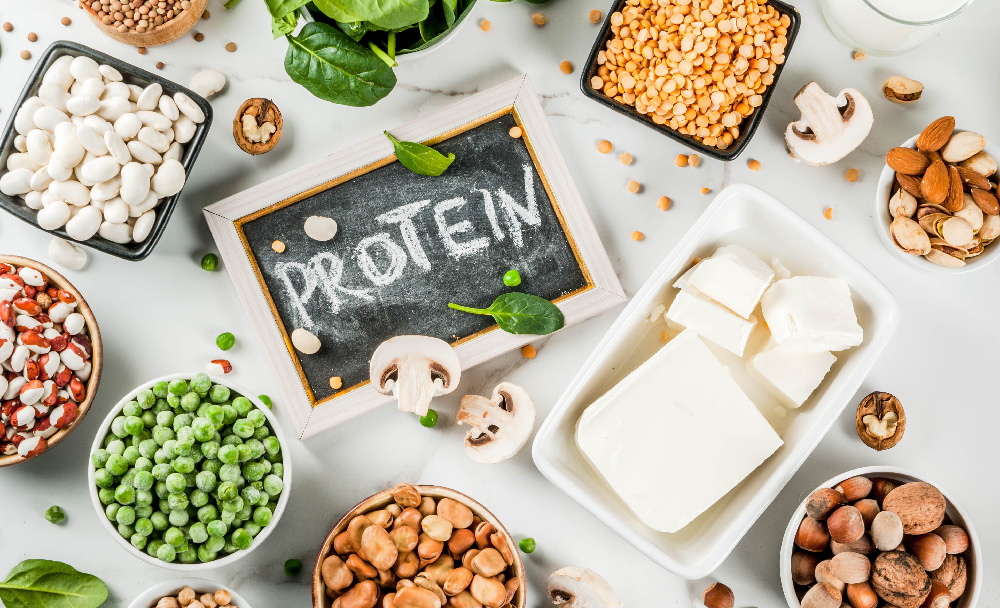

lentils and pulses like cooked dal(4.5g/100g) are great sources of protein. These sources are also rich in fibre, which helps to keep you feeling full.
Limit your intake of processed foods
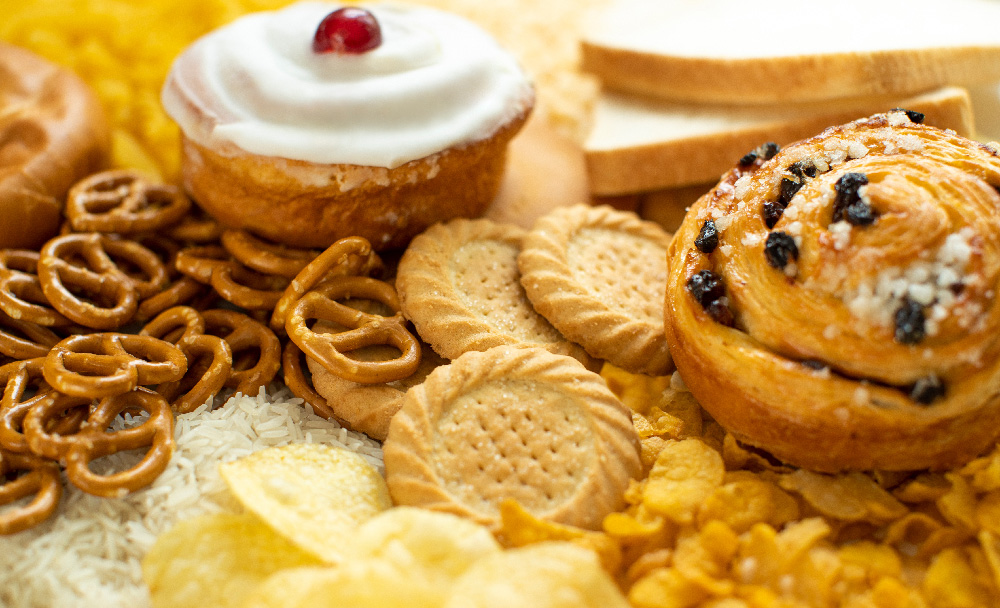

Processed foods are high in calories, sugar, and unhealthy fats. They are also low in nutrients. Limit your intake of processed foods such as sugary drinks, chips, cookies, and packaged snacks. Research has shown tha sweet fruit juices can contain up to 90g of sugar per kilogram which is much above the 25g per day limit prescribed by WHO. [4 ] [10] For instances where you can’t avoid consuming processed food products, read the nutritional labels to pick products which a lower amount of fat, salt and sugar content.[8]
Include healthy fats in your diet
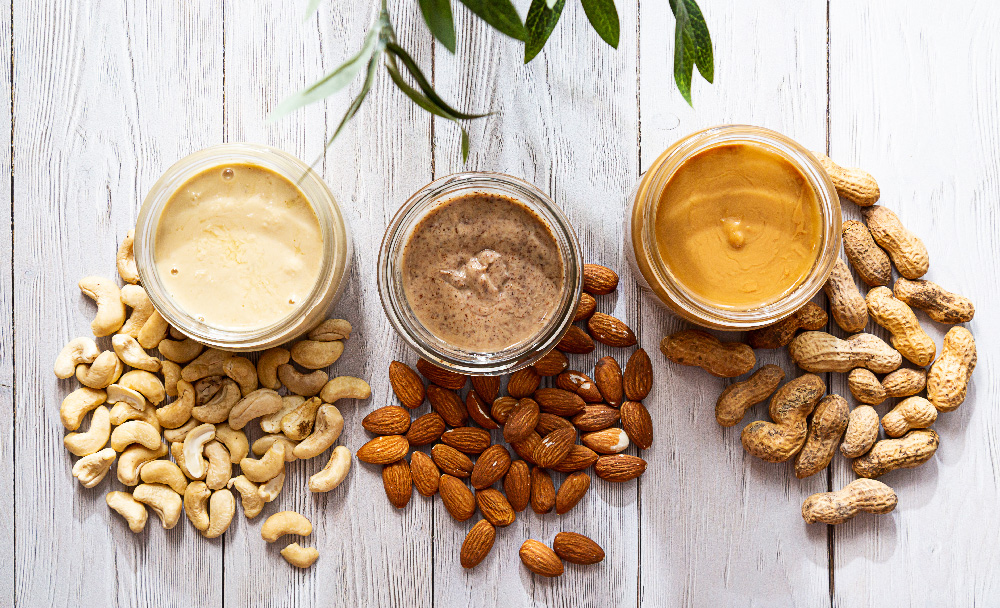

Fats are essential for providing energy and absorbing vitamins. Newer research indicates that healthy fats are essential and advantageous for maintaining good health, despite past dietary recommendations advocating for low-fat diets. Choose healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats found in fried foods and baked goods. [2]
Watch your portion sizes

Eating too much of any food (even healthy food) can lead to weight gain. Consistently consuming larger quantities of food can result in changes to one’s perception of hunger and fullness. Consuming an amount of food that does not trigger the sensation of fullness may be perceived as inadequate or insufficient, leading to a continued feeling of hunger. [7] Use smaller plates and measure your food portions to avoid overeating.
Drink plenty of water

Water is essential for maintaining good health. It helps in carrying nutrients and oxygen to your cells, flushing bacteria from your bladder, aiding digestion, preventing constipation, normalizing blood pressure, cushioning joints, protecting organs and tissues, regulating body temperature, maintaining electrolyte (sodium) balance and much more. [6] According to Ayurveda it’s best to consume water(preferably warm or room temperature) during meals in small sips and to avoid drinking any immediately after a meal. Drink at least seven to eight glasses of water per day.
Here’s a sample meal plan for a balanced diet
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with almonds, raisins, and a sliced banana
- Snack: Nuts like almonds or Carrot sticks with hummus
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a mixed green salad
- Snack: Apple slices with peanut butter
- Dinner: Stir-fry vegetables with brown rice
Conclusion
Creating a balanced diet is all about making healthy food choices and including a variety of foods in your diet. A balanced diet provides all the essential nutrients that your body needs to function properly. By following the tips outlined in this guide and incorporating healthy foods into your meals, you can create a balanced diet that supports your health and well-being.
Disclaimer
This article is from a health and wellness perspective only and does not constitute medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a trained medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
Reference:
- World Health Organization, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (2004). Vitamin and mineral requirements in human nutrition (PDF) (2. ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-9241546126.
- “Fats and Cholesterol”. The Nutrition Source. The President and Fellows of Harvard College. 18 September 2012.
- Healthy Eating As You Age: Know Your Food Groups. 25 February 2022.
- “What Should I Eat?”. The Nutrition Source. Harvard School of Public Health. 18 September 2012.
- Protein for Life: Review of Optimal Protein Intake, Sustainable Dietary Sources and the Effect on Appetite in Ageing Adults. 16 March 2018.
- How much water should you drink? 15 May 2022.
- Portion control in weight management – one size plate doesn’t fit all. 17 June 2022.
- Understanding personality from Ayurvedic perspective for psychological assessment: A case. March 2011.
- Exploring Ayurvedic Knowledge on Food and Health for Providing Innovative Solutions to Contemporary Healthcare. March 2013.
- Ayurveda Based Dietary And Lifestyle Advocacy For Mental Health & Psychiatric Disorders(PDF), Ministry of AYUSH Govt of India, ISBN: 978-93-83864-50-8
- Ultra-processed foods and the nutrition transition: global, regional and national trends, food systems transformations and political economy drivers. 06 August 2020.
- Food Literacy: Bridging the Gap between Food, Nutrition and Well-Being, Sarah Colatruglio And Joyce Slater. 2014.