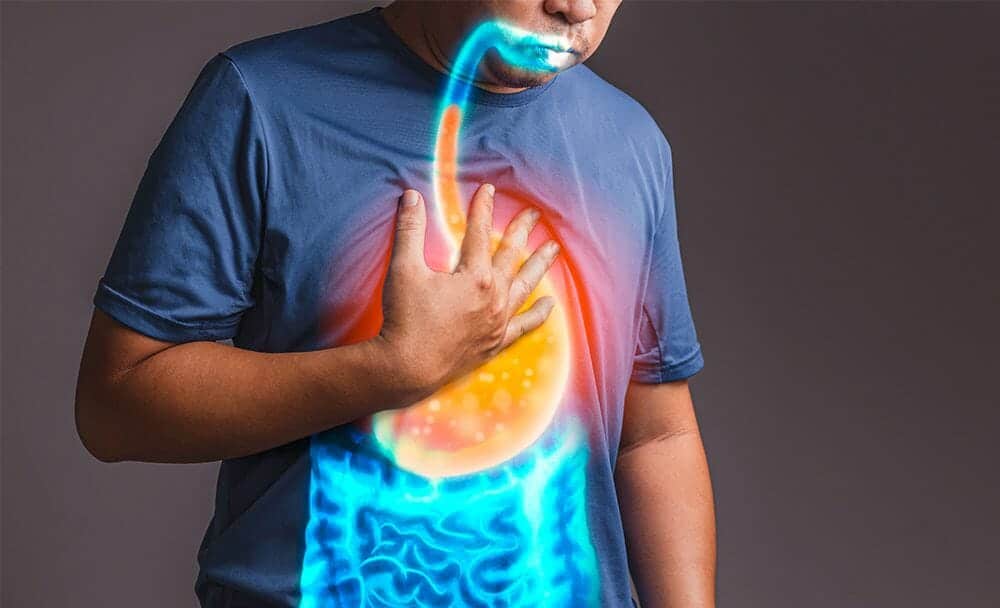
Gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD is a debilitating gastrointestinal condition that affects the digestive system. It occurs when stomach acid jumps up into the esophagus or food pipe, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Usually, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) acts as a barrier, preventing stomach acid from entering the esophagus. However, in individuals with GERD, the LES becomes weakened or relaxes abnormally, allowing acid and sometimes bile to move upwards, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. [1] Ayurveda, the ancient healing system, uses the term ‘Urdhawaga amlapitta’ to describe the condition of GERD
This article will explore what is gastroesophageal reflux disease, its causes, and treatment options.
Symptoms of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease can manifest with various symptoms, which may vary in severity from person to person. The most common gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms include:
- Heartburn (Hrit Kantha Daha in Ayurveda)
- Regurgitation and sour eructation (Amlika in Ayurveda)
- Dysphagia
- Stomach Pain, especially across the GI tract (Paridaha in Ayurveda)
- Chronic Cough
- Bloating and Belching
- Nausea
- Tooth Erosions [1]
Causes of GERD
The underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease causes are multifactorial and can be attributed to lifestyle, physiological, and anatomical factors. Some common causes include:
Hiatal Hernia:
A hiatal hernia significantly contributes to the development of Gastroesophageal reflux disease by weakening the Lower Esophageal Sphincter muscles, making it easier for stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus. [1]
Weak Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES):
The LES may be weak in some individuals, predisposing them to GERD. [1]
Obesity:
Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can increase pressure on the stomach, leading to Gastroesophageal reflux disease. [1]
Pregnancy:
The increased pressure on the abdomen during pregnancy can contribute to acid reflux. [1]
Excessive alcohol consumption and Smoking:
Tobacco use can weaken the LES and impair the protective mechanisms of the esophagus. [1]
Connective Tissue Disorders and Delayed Stomach Emptying:
Conditions that slow down gastric emptying can increase the risk of acid reflux. [1]
Medications:

Some medications, such as certain antidepressants, calcium channel blockers, and NSAIDs or aspirin, can relax the LES and contribute to Gastroesophageal reflux disease. [1]
Treatment of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease treatment aims to relieve symptoms, heal any damage to the esophagus, and prevent complications. The approach to managing Gastroesophageal reflux disease involves a combination of botanicals, lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter medications, prescription drugs, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Here are the various treatment options:
Botanicals:
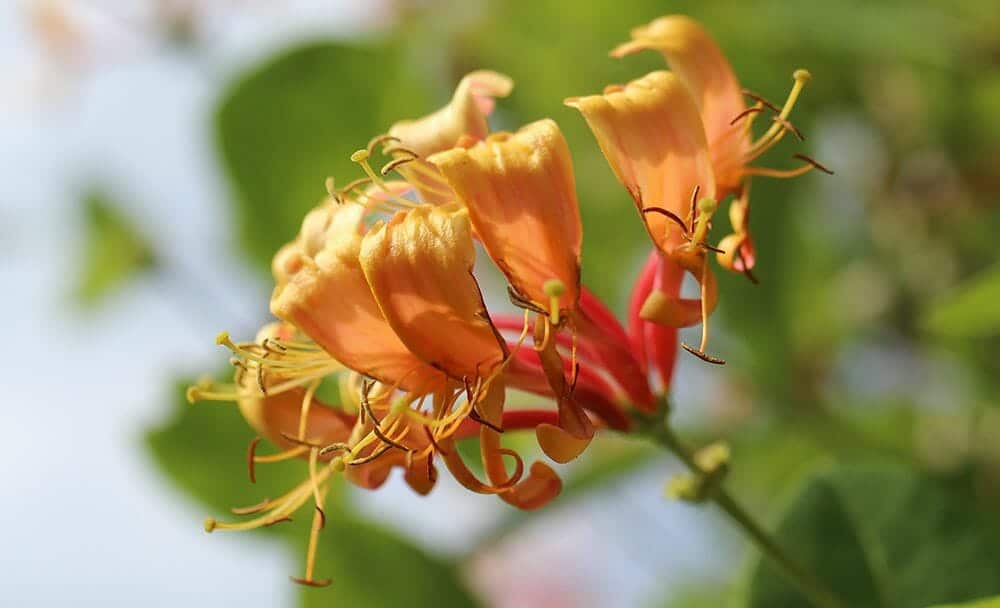

The flower of Lonicerae, commonly known as Chinese Honeysuckle and peppermint oil, offers some benefits by expediting the early phase of gastric emptying, increasing the relaxation time of the pyloric valve, and decreasing resting lower esophageal sphincter pressure. [2]
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes:
Avoiding trigger foods such as chocolates, spicy foods, citrus, and carbonated beverages, eating smaller meals, and avoiding meals at least 3 hours before bedtime can reduce symptoms.
- Weight Management:
Losing weight if overweight or obese can alleviate pressure on the stomach and improve Gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms.
- Sleep Management:
Practicing proper sleep hygiene has been demonstrated to positively reduce reflux episodes by suppressing transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs) during sleep.
- Elevating the Headrest of the Bed:
Raising the bed at the head by a few inches can prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus while sleeping
- Quitting Smoking:
Smoking cessation can improve LES function and overall health.
- Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine:
Reducing alcohol and caffeine intake can help alleviate symptoms. [1]
- Avoiding Tight-Fitting Clothing:
Wearing loose-fitting clothes can prevent excessive pressure on the abdomen
Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Antacids:
Antacids can neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief from heartburn.
- H2 Blockers:
Histamine-2 receptor antagonists {H2RAs) such as famotidine and cimetidine help reduce stomach acid production and offer longer-lasting relief.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
PPIs such as (omeprazole, lansoprazole, and esomeprazole are potent acid suppressants that can provide long-term relief by reducing acid production in the stomach. [1]
Prescription gastroesophageal reflux disease medication:
Stronger PPIs: Higher doses or more potent PPIs may be prescribed for individuals with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease. [1]
Prokinetics: These drugs (cisapride, metoclopramide) help improve stomach emptying, reducing the risk of reflux. [2]
Surgical Interventions:
Nissen Fundoplication: [1] In this laparoscopic procedure, the stomach’s upper portion is wrapped around the LES to strengthen it and prevent reflux. [2]
Endoscopic Treatments:
- MSA: Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation (MSA) is an effective therapeutic option and a minimally invasive surgical procedure that helps strengthen the function of LES and prevent acid moving upward in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. [1]
- Stretta Procedure: Radiofrequency energy is used to strengthen the LES and reduce reflux. [3]
- Endoscopic Suturing: Suturing the LES can help tighten it and prevent reflux. [3]
FAQs
What are the best Ayurvedic gastroesophageal reflux disease home remedies?
Various herbs can be used for gastroesophageal reflux disease self-care, such as:
Pippali or Long Pepper: This contains potent compounds that aid digestion and balance the Pitta doshas, alleviating heartburn.
Tulsi or Holy Basil: The leaves contain volatile oils with carminative properties that relieve flatulence, gas, and hyperacidity. [4]
Elaichi or Cardamom: This is rich in B vitamins and antioxidants, promoting healthy metabolism and smooth digestion. It can help reduce nausea, bloating, and bitter taste in the mouth associated with GERD. [4]
Ash Gourd: The nutritious green vegetable has a high water content and valuable phytonutrients such as terpenes and flavonoids. These components can significantly reduce acid levels in the gut and alleviate nausea, vomiting, and constipation. [4]
Aloe Vera or Ghrit Kumari: A versatile remedy for GERD, the gel from its leaves contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that neutralize stomach acids, heal peptic ulcers, and ease heartburn. [4]
If you are looking for some Ayurvedic tonic to help you manage the symptoms like heartburn, flatulence, bloating etc, you may consider taking the Zandu Pancharishta, an effective herbal tonic for improved digestion. 35 powerful Ayurvedic herbs in this tonic can treat the symptoms of GERD effectively. Visit Zanducare.com to place your order.
Is GERD a serious problem?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is characterized by experiencing reflux episodes more than twice a week. It is a more severe condition compared to GER (gastroesophageal reflux). Usually, medical professionals treat GERD using medications.
Can GERD be cured?
Yes, GERD is treatable. The primary approach to managing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease involves medication, effectively reducing stomach acid levels. If lifestyle modifications are insufficient, your doctor may recommend surgery as an alternative option.
Conclusion:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a prevalent and chronic condition affecting millions worldwide. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes of GERD are essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate management. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and over-the-counter medications can relieve mild cases. However, individuals with severe or refractory GERD may require prescription medications or surgical interventions.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is not medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References:
















I like this site so much, saved to my bookmarks.