Dyslexia is a complex learning difference that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by reading, writing, and spelling difficulties. However, dyslexia is much more than struggling with words on a page.
This article delves into the meaning, symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options for dyslexia. It will shed light on this often-misunderstood condition. Whether you are seeking information for yourself or a loved one, let’s understand dyslexia and tips for navigating its challenges.
What is dyslexia meaning?
Dyslexia is a neurobiological condition affecting how people process and understand language. People with this condition can face difficulties in accurate and fluent reading and challenges in spelling and writing. However, dyslexia is not a reflection of intelligence or cognitive ability.
Individuals with dyslexia can have above-average intelligence and possess unique strengths in areas like creativity and problem-solving. Dyslexia involves difficulties in phonological processing, which is the ability to identify the individual sounds in words. This can make it challenging for individuals with dyslexia to decode words and recognize familiar words quickly. As a result, reading can be laborious and accompanied by errors. [1]
What are dyslexia symptoms?
The signs and symptoms of dyslexia can vary. Each individual with the condition will have unique strengths and weaknesses. Let’s explore some common symptoms observed in different age groups: [1]
- Pre-school children:
- Difficulty learning nursery rhymes or recognizing rhyming words
- Trouble pronouncing words correctly or persistently confusing similar sounds
- Difficulty learning and remembering the alphabet, numbers, or colors
- Slow development of vocabulary compared to peers
- Difficulty following multi-step instructions or sequences
- Primary school children:
- Persistent struggles with reading, including frequent reading errors
- Difficulty decoding unfamiliar words or sounding them out
- Trouble recognizing sight words or frequently forgetting previously learned words
- Poor spelling and inconsistent spelling patterns
- Difficulty organizing thoughts and expressing ideas in writing
- Challenges with understanding and recalling what was read
- Avoidance or dislike of reading and writing activities
- Teenagers and adults:
- Continual difficulty reading fluently and accurately
- Limited reading comprehension and struggles with understanding complex texts
- Persistent spelling errors, especially with words that do not follow regular spelling rules
- Slow reading speed and avoidance of reading tasks
- Difficulty with time management and organizing thoughts in writing
- Challenges with remembering and following oral instructions
- Low self-esteem related to academic or literacy struggles
What are the causes of dyslexia?
While the exact causes of dyslexia are still being studied, researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development. Let’s explore them in detail: [2]
- Inadequate fixation
Dyslexia may be associated with difficulties in maintaining steady eye fixation while reading. It can lead to problems in tracking lines of text and accurately perceiving individual words.
- Excessively large saccadic amplitudes
Saccades are rapid eye movements allowing us to shift our gaze from one point to another. Individuals with dyslexia may exhibit larger than necessary saccades, making it harder to track text smoothly.
- Reduced ability to recognize a letter sequence
Dyslexia may involve difficulties in perceiving and processing letter sequences. It can affect the ability to recognize words accurately and impede reading fluency.
- Longer required fixation time
People with dyslexia require more time to process visual information, like letters and words. The increased fixation time can contribute to slower reading speed and difficulties with comprehension.
- Longer required speech onset latency
Dyslexia can be due to delays in the onset of speech production. The delay may affect the development of phonological awareness, which is crucial for understanding the sound structure of language and decoding written words.
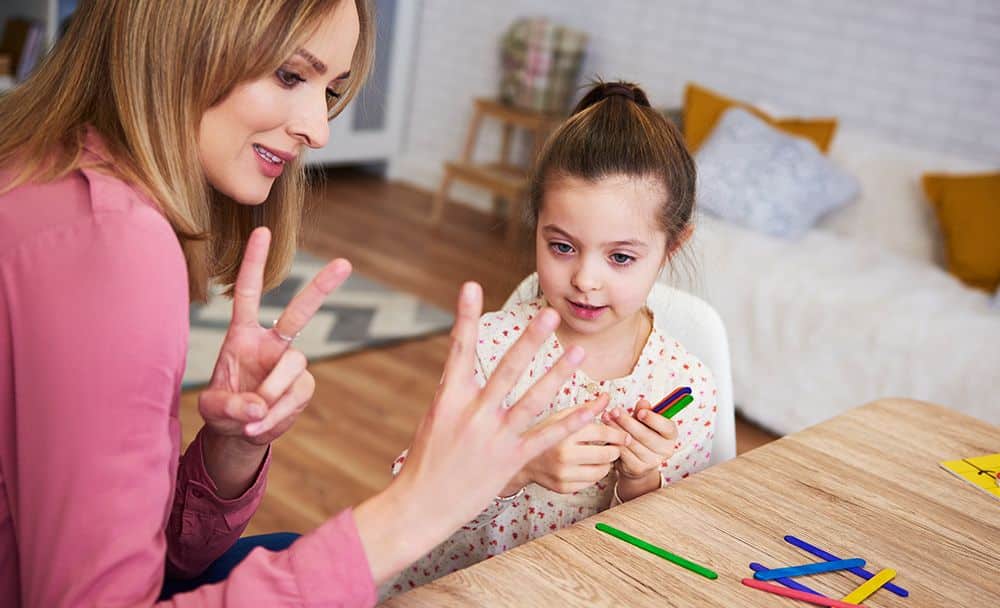

What is the treatment of dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a lifelong condition. However, specialist educational interventions are available to support children. These interventions are most effective when started at a young age. The specific type and extent of intervention required will depend on individual child’s difficulties.
The school will often develop and implement a tailored action plan for the child. It will provide appropriate support within the mainstream educational setting. However, some children may benefit from attending a specialist school that specializes in dyslexia education.
As a parent or caregiver, you can help your child with dyslexia in many ways. Reading to your child and engaging in shared reading experiences can foster a love for books and storytelling. Overlearning, which involves repeated practice and reinforcement of reading skills, can also be beneficial. Encouraging silent reading and making reading enjoyable and fun can help your child develop a positive attitude toward reading.
Technology can be valuable for children with dyslexia. Many find it easier to work with a computer than using traditional pen-and-paper methods. Word processing programs offer features like spell-checkers and autocorrect functions, which can assist with writing tasks.
The advice and techniques used to support children with dyslexia are also applicable to adults. Word processors and electronic organizers can assist with writing and organizing daily activities. A multisensory approach to learning, like recording lectures, can be helpful for adult learners.
In the workplace, it’s important to inform your employer about your dyslexia. They are legally obligated to make reasonable adjustments to accommodate your needs. These adjustments may include providing assistive technology like digital recorders or speech-to-text software and offering verbal instructions instead of written ones. [1]

Dyslexia and Ayurveda
Ayurveda does not specifically address dyslexia as a condition. However, it offers insights and practices that can support brain health and cognitive function. Ayurvedic principles emphasize the importance of a balanced lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate rest. These practices can contribute to optimal brain function and may indirectly benefit individuals with dyslexia.
Ayurvedic herbs and formulations known for their cognitive-enhancing properties, such as Brahmi and Ashwagandha, can help support memory and concentration. However, consulting a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner before incorporating herbs or treatments is crucial. Individualized guidance is necessary for safe and effective use.
FAQs
What is the definition of definition?
Dyslexia is a neurodevelopmental condition in which individuals face reading, writing, and spelling difficulties. It is unrelated to intelligence or cognitive ability and can be due to differences in how the brain processes language.
Is there any dyslexia test?
Yes, there are dyslexia assessments and tests available. Psychologists or educational specialists typically conduct these tests. They involve evaluating reading skills and phonological awareness to determine the presence and severity of dyslexia.
What is dyslexia disease?
Dyslexia is not a disease. It is a learning difference or learning disability that affects the way individuals process language. Dyslexia is not contagious or caused by illness.
What are dyslexia types?
Dyslexia does not have distinct types in the same way that some medical conditions do. However, dyslexia can manifest differently in individuals, leading to variations in symptoms and areas of difficulty. Some individuals may struggle more with reading accuracy, while others may struggle with reading comprehension or written expression.
Conclusion
Dyslexia is a complex learning difference that affects individuals in various ways. It is not a reflection of intelligence or cognitive ability but rather a neurobiological condition that impacts reading, writing, and spelling skills.
While dyslexia is a lifelong challenge, early intervention can make a significant difference in helping individuals navigate their academic and professional journeys. With continued awareness and advocacy, we can empower individuals with dyslexia to reach their full potential.
Disclaimer
The information provided here is not intended to replace professional advice or treatment.
References