Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition in which the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Diabetes can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness if left untreated or poorly managed. Diabetes can be managed through various approaches, including medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. [1] In this article, we will explore more about diabetes, including the symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options.
Overview of Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is commonly referred to as Madhumeha in Ayurveda. [2]
Diabetes is a chronic illness resulting from inadequate insulin production or ineffective insulin utilization, leading to hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels. This condition can cause significant harm to various systems in the body, including nerves and blood vessels.[1] [3]
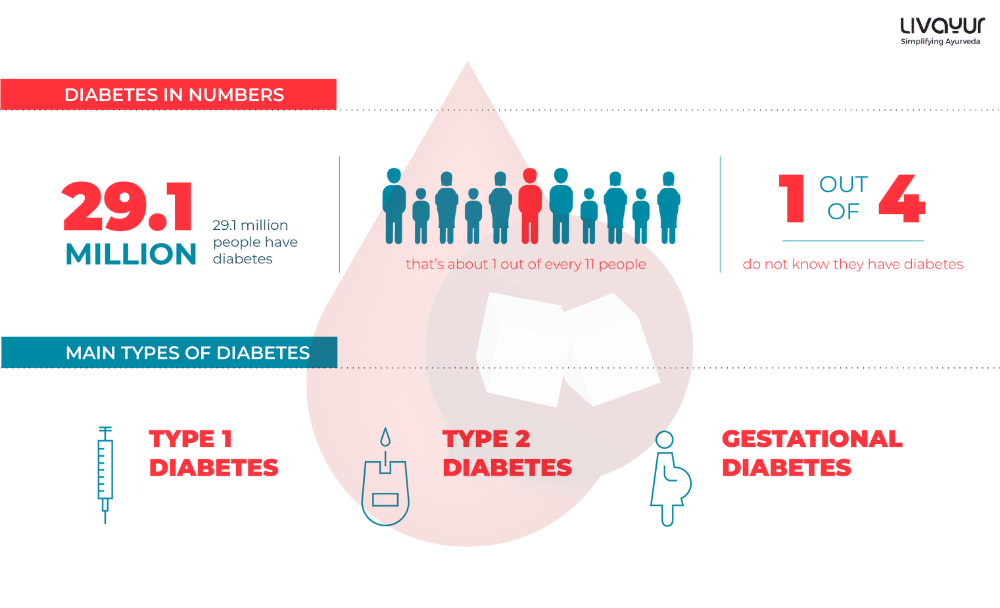
According to data from 2014, 8.5% of adults aged 18 and above suffer from diabetes. In 2019, diabetes was responsible for 1.5 million deaths, with 48% of these deaths occurring in individuals under the age of 70. Diabetes also caused an additional 460,000 deaths due to kidney disease, and hyperglycemia was a contributing factor in approximately 20% of cardiovascular deaths. [3]
Unfortunately, between 2000 and 2019, age-standardized mortality rates related to diabetes increased by 3%. Low- to middle-income countries experienced a 13% increase in diabetes-related mortality rates. In contrast, there was a global decrease of 22% in the probability of dying from one of the four primary noncommunicable diseases (cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes) between the ages of 30 and 70 during the same period. [3]
Diabetes Symptoms
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms associated with diabetes, it is recommended that you consult with your healthcare provider and undergo a blood sugar test: [4]
- Frequent urination, particularly during the night
- Excessive thirst
- Unintentional weight loss
- Insatiable hunger
- Blurry vision
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Fatigue
- Persistent dry skin
- Slow healing of wounds
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Individuals with type 1 diabetes may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. The onset of type 1 diabetes symptoms can occur rapidly, in a matter of weeks or months, and can be severe. Although it typically presents during childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood, type 1 diabetes can manifest at any age. [4]
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes may take several years to surface, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all. Although typically diagnosed in adulthood, an increasing number of children and adolescents are developing type 2 diabetes. Given the elusive nature of symptoms, it is crucial to be aware of the risk factors associated with this condition and seek medical attention if any are present. [4]
Gestational diabetes, a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, often does not present with any noticeable symptoms. Medical professionals recommend screening for gestational diabetes between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. In the event that gestational diabetes is diagnosed, lifestyle modifications can be implemented to safeguard the health of both the mother and the baby. [4]
According to Ayurveda, Madhumeha or diabetes, arises from an imbalance in the three doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), with Vata being the predominant factor. When Vata dominance becomes localized, it can become generalized, affecting the entire body. [2]
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
If an individual has type 1 diabetes, their pancreas fails to produce adequate amounts of insulin or none at all. Insulin plays a crucial role in allowing glucose to enter the body’s cells to provide energy. In the absence of insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream as it cannot enter the cells, resulting in high blood sugar levels. This condition can cause numerous complications and symptoms associated with diabetes. [5]
Formerly known as juvenile or insulin-dependent diabetes, type 1 diabetes usually affects children, teenagers, and young adults. However, it can occur at any age. Type 1 diabetes is less prevalent than type 2 diabetes, with only 5-10% of diabetic individuals having type 1 diabetes. [5]
Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that acts as a key to facilitate the entry of blood sugar into cells for energy production. However, in cases of type 2 diabetes, cells in the body become resistant to insulin, leading to insulin resistance. To counteract this resistance, the pancreas produces more insulin to stimulate cell response. However, over time, the pancreas becomes unable to keep up with the demand, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to prediabetes and ultimately, type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar can cause severe health issues such as heart disease, kidney disease, and vision loss. [6]
Gestational Diabetes

Gestational diabetes is a medical condition that arises when the body of a pregnant woman is unable to produce sufficient insulin. Pregnancy triggers an increase in hormone production and other bodily changes, including weight gain, that result in reduced efficiency in the use of insulin by the cells in the body. This state is known as insulin resistance, which further aggravates the need for insulin in the body. [7]
Treatments for Diabetes in Modern Medicine
The management of type 1 diabetes usually requires regular insulin injections or using an insulin pump, as well as frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels and counting carbohydrates. In some cases, a pancreas or islet cell transplant may be considered. [5] [8]
On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is mainly treated through lifestyle modifications, and blood sugar monitoring, and may involve taking oral diabetes medications, insulin injections, or a combination of both. [6] [8]
Gestational Diabetes treatment involves regular blood tests to monitor blood sugar levels, being physically active and following a diet prescribed by your doctor. [7]
Ayurvedic Treatment for Diabetes

Ayurveda follows a holistic approach to treating diabetes by identifying the root cause of the illness. Factors like the individual’s lifestyle, diet, environment, etc. are all taken into account before prescribing treatment. The treatment after analysing the patient includes dietary changes, exercises like yoga and meditation and ayurvedic medication and herbs. [2] [9]
Ayurveda recommends a variety of herbs, combinations of herbs, herbomineral preparations, and therapeutic practices (such as Panchakarma, meditation, and yoga exercises) to prevent, reduce symptoms of, and manage diabetes based on the needs of each individual patient in conjunction with conventional treatments on recommendations of doctors. [2]
For centuries, hundreds of Ayurvedic herbs, various herbal preparations, herbomineral preparations, and mineral formulations have been utilized to manage Madhumeha, also known as diabetes. [2]
In the management of diabetes or Madhumeha, the use of Rasayana drugs, such as Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) and Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers), which have immunomodulatory properties, are given emphasis. [2]
Ayurveda has enhanced the effectiveness of antidiabetic therapy through various herbal formulations, Bhasmas (purified metals and minerals that have been calcined), herbomineral preparations, oils, Asava-Aristas (alcoholic tinctures that are self-generated), Ghritas (medicated clarified butter), and Guggulu preparations. [2]
FAQs
1. What are the risk factors for developing diabetes?
Several risk factors increase an individual’s likelihood of developing diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, age, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels.
2. How is diabetes diagnosed?
The most common diagnostic tool used for diabetes is the glycated haemoglobin (A1C) test, which measures the average blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months. Other diagnostic tests include fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
3. Can diabetes be prevented?
Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, as it is an autoimmune condition. However, type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes such as weight loss, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco use.
4. What are the treatment options for diabetes?
Treatment options for diabetes include medication, such as insulin, metformin, and sulfonylureas, lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. In some cases, weight loss surgery may be recommended for individuals with severe obesity.
5. Can diabetes be cured?
There is no known cure for diabetes. However, with proper management and treatment, individuals with diabetes can live healthy lives and prevent or delay complications associated with the condition.
6. Can Diabetes be reversed?
Yes, Diabetes can be reversed, with the right kind of diet, exercise, and healthy lifestyle habits. While along with the guidance of a trained medical practitioner complications associated with the condition can be reversed & managed better.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes is a complex and chronic condition that requires ongoing management and attention. While modern medicine offers effective treatments for managing diabetes, Ayurveda provides a complementary approach that can help address the underlying causes of the disorder. By working closely with their healthcare provider and incorporating both modern medicine and Ayurvedic principles into their treatment plan, individuals with diabetes can achieve better glucose control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only. Kindly seek the assistance of a trained medical practitioner for diagnosis and treatment before incorporating any of the mentioned remedies into your daily routine.
References:
- What is diabetes? | CDC
- Ayurveda in changing scenario of diabetes management for developing safe and effective treatment choices for the future
- Diabetes (who.int)
- Diabetes Symptoms | CDC
- What Is Type 1 Diabetes? | CDC
- Type 2 Diabetes | CDC
- Gestational Diabetes | CDC
- Insulin, Medicines, & Other Diabetes Treatments – NIDDK (nih.gov)
- Therapeutic Role of Yoga in Type 2 Diabetes – PMC (nih.gov)
















Amazing blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m completely confused .. Any recommendations? Bless you!