Type 1 Diabetes is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects millions worldwide. This article offers you the Type 1 diabetes definition, the telltale signs and symptoms to watch out for. We will also examine the underlying Type 1 Diabetes causes that trigger this condition and the risk factors for Type 1 Diabetes. Furthermore, we look at the options to manage this condition. Whether you are seeking to expand your knowledge or have recently been diagnosed, join us as we navigate the intricacies of Type 1 Diabetes.
What is the definition of Type 1 Diabetes?
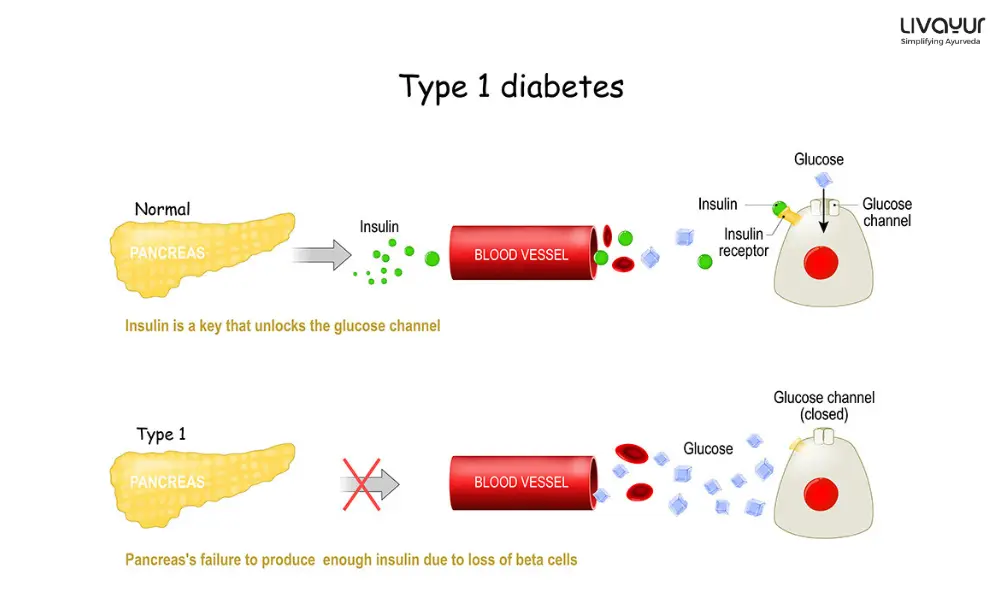
Type 1 Diabetes is also known as juvenile or insulin-dependent Diabetes. It is a chronic metabolic disorder that happens due to the body’s inability to produce sufficient insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and facilitates glucose absorption into cells for energy.
In individuals with such a condition, the immune system mistakenly destroys the beta cells that produce insulin. It leads to a deficiency in insulin production. As a result, glucose cannot enter the cells effectively. It then accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia.
Unlike Type 2 Diabetes, which is usually due to lifestyle factors, Type 1 Diabetes is primarily an autoimmune disease. Managing Type 1 Diabetes requires a lifelong commitment to blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, and a balanced lifestyle. It is essential for individuals and their caregivers to stay well-informed about the condition. [1]
Type 1 Symptoms
Type 1 Diabetes symptoms can be sneaky and may take a while to manifest. However, when they do show up, they can be noticeable. Unlike Type 2 Diabetes, which usually develops gradually, Type 1 Diabetes symptoms can emerge within a relatively short period, ranging from a few weeks to a few months. Once they appear, they can be intense and require immediate attention.
It’s also crucial to note that some symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes can mimic those of other health conditions. So, seeking professional medical advice is always best rather than trying to self-diagnose. If you suspect you might have Type 1 Diabetes, don’t hesitate to visit your doctor and get your blood sugar levels tested. Early detection is crucial, as untreated diabetes can lead to severe, even life-threatening, health problems.
Common Type 1 Diabetes symptoms are given below [3]:
- Excessive thirst or Polydipsia
- Excessive hunger even after eating or Polyphagia
- Frequent urination or Polyuria
- Unnatural fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Sudden, unexplained weight loss
- Dry mouth
- Irritability
- Nausea and stomach upset
- Heavy breathing
- Frequent infections
Being vigilant about these symptoms and taking prompt action can improve the management of Type 1 Diabetes and help individuals lead healthier and more fulfilling lives. [1]
Type 1 Diabetes Causes
The development of Type 1 Diabetes can be due to the following factors. [1] [3]
1. Autoimmune function
In the case of Type 1 Diabetes, the immune system launches an attack on the beta cells of the pancreas. If left unchecked, this autoimmune reaction leads to the destruction of these crucial beta cells, resulting in an insulin deficiency.
Beta cell destruction can occur over an extended period, ranging from months to even years before any noticeable symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes emerge. The delay in symptom manifestation can make early detection challenging. It shows the importance of regular health check-ups and screenings.
2. Genetics
They are significant in determining an individual’s susceptibility to Type 1 Diabetes. Some people have particular genetic traits passed down from their parents that make them more prone to developing the condition. However, it’s important to note that having these specific genes does not guarantee that a person will inevitably develop Type 1 diabetes.
3. Environmental factors
They, too, can contribute to the development of Type 1 Diabetes. Specific environmental triggers like viral infections can set off the autoimmune response that destroys beta cells.
Type 1 Diabetes Risk Factors
When it comes to Type 1 Diabetes, identifying specific risk factors isn’t as straightforward as it is for prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Nevertheless, research has shed light on some key factors that may increase the possibility of developing this condition, and family history stands out as a significant player.
- Family history is a prominent risk factor for Type 1 Diabetes. If you have a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, with Type 1 Diabetes, your risk of developing the condition may elevate. It’s essential to recognize that while family history can increase the risk, it does not guarantee that an individual with a family history will have this condition. [4]
- Apart from family history, age happens to be another risk factor. There is a tendency among children, teenagers, and young adults to develop Type 1 Diabetes. [4]
Similarly, lacking a family history of the condition does not provide complete immunity. The development of Type 1 Diabetes involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors still being studied. [1]
Complications associated with Type 1 Diabetes [3], [9]
1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis
One should not wait to get treated for Type 1 Diabetes, as uncontrolled high blood sugar levels can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It is a condition where the body produces toxic acids called ketones. DKA can rapidly escalate and become a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.
2. Diabetic Neuropathy
Constant high blood sugar levels can damage the patient’s nerves, leading to loss of sensation and function in many parts of the patient’s body.
3. Diabetic Retinopathy
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels may also damage your eyes leading to poor vision or total blindness.
4. Renal Failure
High blood sugar levels if left untreated may damage your kidneys and lead to renal failure.
5. Heart Attacks and Strokes
Unrestrained blood sugar levels may increase the risk of heart attacks and fatal strokes.
How to diagnose Type 1 Diabetes? [10]
There are several blood tests to determine the occurrence of Type 1 Diabetes. The blood tests listed below are part of the diagnostic procedure.
Blood glucose test
The phlebotomist will collect a blood sample to assess the amount of glucose in your blood. This collection will take place in two ways; one is fasting sugar collection and the second one is after taking food. The latter is the random blood sugar test. If the results show a blood sugar level of 200 mg/dl and beyond, that indicates Diabetes.
Glycosylated hemoglobin test/A1c test
If the results show that a patient has Diabetes the doctor may ask to go for the A1c test. This test will tell the doctor about the patient’s average blood sugar levels over three months.
Autoantibody test
After it is confirmed that the patient has Diabetes, the doctor now tries to determine the type of diabetes the patient has. To do that, the doctor prescribes the autoantibody test. The presence of proteins called autoantibodies in the blood indicates that the diabetes is specifically Type 1 Diabetes and not Type 2 Diabetes.
To rule out the possibilities of Diabetes-related complications such as ketoacidosis and to assess the patient’s overall health, the doctor might prescribe a few more tests such as
Urinalysis
This test is prescribed to check for ketones in the urine of the patient. The volume or number of ketones can make the blood of the patient acidic in nature. This is a life-threatening complication and needs a timely diagnosis.
Arterial blood gas test/ABG test
This test is done to measure the levels of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. The blood is collected from the patient’s artery.
What is the treatment of Type 1 Diabetes?
Managing Type 1 Diabetes is a collaborative effort, primarily led by the individual with support and guidance from healthcare professionals. Unlike some health conditions where treatment is solely in the hands of medical experts, successfully managing Type 1 Diabetes relies on the day-to-day decisions and actions taken by the person living with the condition. Here are some practical ways to manage the disease. [1]
1. Administering insulin
Since the body cannot produce insulin, a related therapy helps regulate blood sugar levels. It involves insulin injections tailored to individual needs. Advances in technology have also introduced insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors. These offer more flexibility and improved glucose control.
2. Regular blood sugar checks
Monitoring blood sugar levels helps make informed decisions about insulin dosages, food choices, and physical activity. It ensures blood sugar remains within target ranges.
3. Healthy eating habits
Working with a registered dietitian can provide valuable guidance in creating a balanced meal plan. Consistently making nutritious food choices helps control blood sugar levels and maintain overall health.
4. Physical activity
It benefits general health and plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Regular exercise helps the body make use of insulin better, contributing to better blood sugar control. Finding activities you enjoy and can incorporate into your daily routine is essential. [7]
5. Managing other health factors
It includes keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check. Uncontrolled blood pressure and cholesterol can increase the risk of diabetes-related complications. [8] Managing these aspects through lifestyle changes and medication is vital.
Ayurveda and Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is a complicated condition requiring conventional medical management. However, some individuals may seek complementary approaches like Ayurveda to support their health. In Ayurveda, the emphasis is on balancing the body, mind, and spirit to promote harmony and prevent disease. Although Ayurveda does not claim to cure Type 1 Diabetes, it may offer the following strategies to help manage the condition effectively and improve quality of life.
1. Personalized dietary recommendations
Ayurvedic practitioners may suggest foods and herbs that can help support blood sugar regulation and improve digestion. For example, Indian medicinal plants like sugar apple, Davana, Supari, and Chukkander are well known for their anti-diabetic benefits. [2]
2. Stress management
Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Ayurvedic practices like meditation and yoga can aid in reducing stress and promoting relaxation. [5] [6]
3. Individualized lifestyle recommendations
It may include suggestions on sleep patterns, daily routines, and exercise tailored to an individual’s unique Dosha.
While Ayurveda can complement conventional Diabetes management, it’s essential to consult with an Ayurvedic practitioner and a healthcare professional specializing in diabetes to ensure the safe and effective integration of treatments. Communication between the two practitioners is crucial to creating a well-rounded and coordinated approach to managing Type 1 Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Prevention
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disorder and cannot be prevented. However, you can take certain steps to avoid the complications. The steps include
- Monitoring your blood sugar levels every day
- Following your doctor’s advice and recommendations strictly
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Exercising regularly
- Staying away from alcohol and smoking
- Staying away from fast foods, high sugar, and high carb diets
- Take your insulin shots timely
- Consuming a lot of fresh vegetables
FAQs
1. What is the Type 1 Diabetes cure?
As of now, Type 1 Diabetes is incurable. It requires lifelong management through insulin therapy and other measures to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
2. What is the medicine for Type 1 Diabetes?
The primary medicine is insulin. Other medications may work in combination with insulin to manage blood sugar levels.
3. Is Type 1 Diabetes genetic?
Yes, there is a genetic component to Type 1 Diabetes. Having a family history of the condition can increase the risk. However, not everyone with a genetic link will develop the disease. [3]
4. What type of food should the patients with Type 1 Diabetes consume?
Patients with Type 1 Diabetes should consume a high-fiber diet low in glycemic index. [11]
5. How can insulin be administered to a patient of Type 1 Diabetes?
Insulin may be given to the patient in the form of insulin shots, insulin pills, insulin pen, and insulin pump. [3]
Conclusion
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes is essential for those living with the condition and their caregivers. While there is no cure for Type 1 Diabetes, self-care practices can improve the quality of life for individuals managing this chronic condition. Complementary approaches like Ayurveda may offer supportive strategies to enhance overall well-being.
Open communication with healthcare professionals and maintaining a positive outlook are vital components of effective Diabetes management. With diligence and empowered decision-making, those living with Type 1 Diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while navigating the challenges of the condition.
Disclaimer
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective only and is not a piece of medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References
- What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
- Indian Herbs and Herbal Drugs Used for the Treatment of Diabetes. 25 April 2007
- Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
- RISK FACTORS FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES
- Stress and Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Clinical Outcome
- ROLE OF YOGA AND MEDITATION TO REDUCE STRESS AMONG ADOLESCENTS: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
- Type 1 Diabetes and Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents
- Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension
- Complication of Diabetes Mellitus
- CLASSIFICATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES
- Role and importance of high fiber in diabetes management in India