Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary during the menstrual cycle. If the mature egg is fertilized by a sperm, a woman becomes pregnant. Otherwise, the egg disintegrates, and the uterine lining is shed, leading to your period or menstruation. Understanding the importance of ovulation, the period in which it occurs, and the signs that can help predict the ovulation period will vastly help you achieve or avoid pregnancy.
Ayurveda also underlines the importance of ovulation. It is known as Beejotsarga in Ayurveda and is considered an essential element for conception or Garbhadhana. The fertile period in Ayurveda is called Rutu Kala and has been defined as the period wherein the chances to get pregnant are the most.
When Does Ovulation Happen?
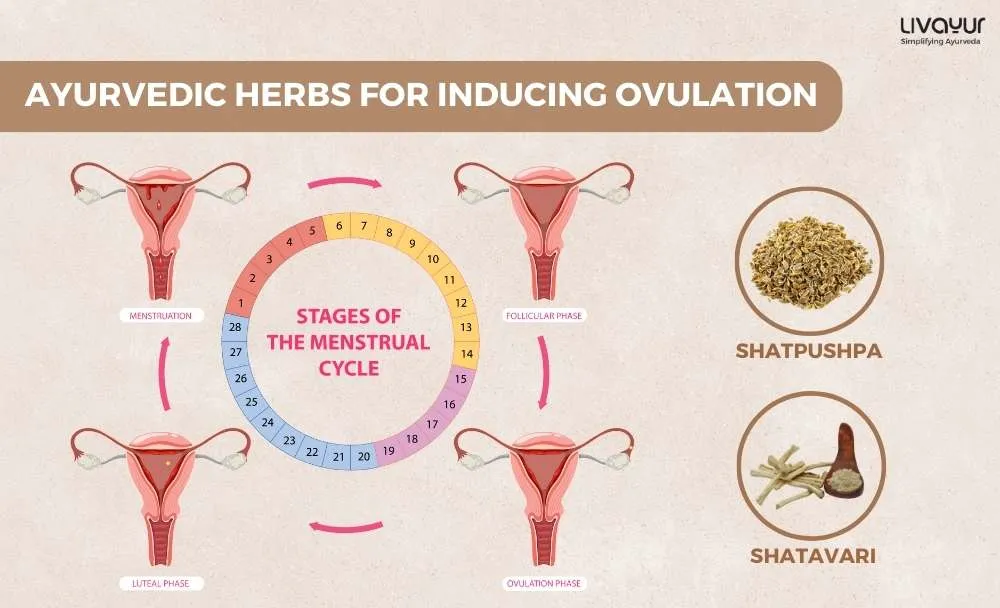
If you have a 28-day menstruation cycle, ovulation will typically take place on day 14. However, the menstruation cycle and the ovulation period vary from person to person. The general rule is that ovulation occurs in the four days before or after the menstruation cycle. It usually lasts for 12-24 hours every month or in every menstruation cycle.
Can You Only Get Pregnant During Ovulation?
The egg can only be fertilized during 12-24 hours of ovulation. However, under ideal conditions, sperms can live in the reproductive tract for up to 5 days. Therefore, if you have sexual intercourse during the days leading to ovulation, you may get pregnant.
What are the Signs of Ovulation?

- Changes in the Cervical Mucus:
Cervical mucus is a fluid discharged from the cervix. Its amount, color, and thickness can help you predict ovulation. Just before ovulation, the estrogen levels increase, and cervical mucus becomes clear and stretchy, with an egg-white consistency. It remains the same during ovulation and starts becoming thicker and cloudy, after ovulation.
- Increase in Libido:
During ovulation, the sexual desire of women increases, and after ovulation has occurred, it drops again. It happens because the levels of testosterone and estrogen rise during ovulation, causing a rise in libido.
- Changes in Cervix:
During ovulation, the cervix rises to a higher level and becomes softer. It also becomes more open and wetter.
- Changes in the Breast:
In many women, breasts become tender, or nipples become sore before or after ovulation due to hormonal changes in the body. Breast tenderness also reflects the potential of pregnancy.
- Changes in the Basal Body Temperature:
Basal body temperature is the lowest temperature that is measured when you are resting. Before ovulation, the BBT is between 97°F (36.1°C) and 97.5°F (36.4°C). After ovulation, it rises by about 0.4°F to 0.8°F due to an increase in the hormone progesterone. You can predict ovulation by taking your BBT every morning.
- Spotting and Bleeding:
Some women may experience slight spotting or bleeding during ovulation. It is called ovulation spotting and usually lasts for a day or two.
- Ovulation Pain:
Some women may also experience pain or cramps during ovulation. Also known as mittelschmerz, it is a one-sided pain in the lower abdomen, depending on which ovary is releasing the egg.
How can Ayurveda Help in Ovulation?

There are many Ayurvedic herbs that can help induce ovulation and promote conception. Shatpushpa and Shatavari are known to be the most effective Ayurvedic herbs for inducing ovulation. They help to increase the endometrial thickness as well as improve menstrual flow. Shilajit is another herb that can boost fertility. Kanchanar Guggulu is also highly effective.
Not only herbs but Ayurvedic therapies such as Panchakarma are also known to improve ovulation in women and promote conception. Basti Karma and Nasya Karma are especially known for boosting fertility.
Takeaway:
Ovulation is an important process of the menstrual cycle. According to Ayurveda, it is the ideal time for conception. Therefore, knowing your ovulation period is extremely important to avoid or achieve pregnancy. The aforementioned signs can vastly help you predict ovulation. Ayurveda also mentions many herbs such as Shatavari, Shilajit, etc. that can help induce ovulation and promote conception.

























1 Comments