Scurvy is a disease that has plagued humans for centuries. It is a result of a deficiency of vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, in the diet. Although scurvy is relatively rare in developed countries today, it can still occur in certain populations or individuals with limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables. [1] [2] In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of scurvy.
Symptoms of Scurvy
The symptoms of scurvy can vary in severity, depending on the duration and extent of the vitamin C deficiency. Some common symptoms include:
Fatigue and weakness
Individuals with scurvy often experience excessive tiredness and a general feeling of weakness. [3] [4] A lack of vitamin C will also affect the immune system, iron absorption, cholesterol metabolism, and other functions.[5] [6]
It is also necessary for synthesizing dopamine [7], norepinephrine, epinephrine, and carnitine, which are required for energy production.
Vitamin C deficiency symptoms can appear after 8-12 weeks. [8] Early signs include a loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue [9], irritability, and lethargy.
Joint and muscle pain
Scurvy can cause pain and tenderness in the joints and muscles. This is due to the weakening of collagen, a protein essential for the health of connective tissues. [3] [4]
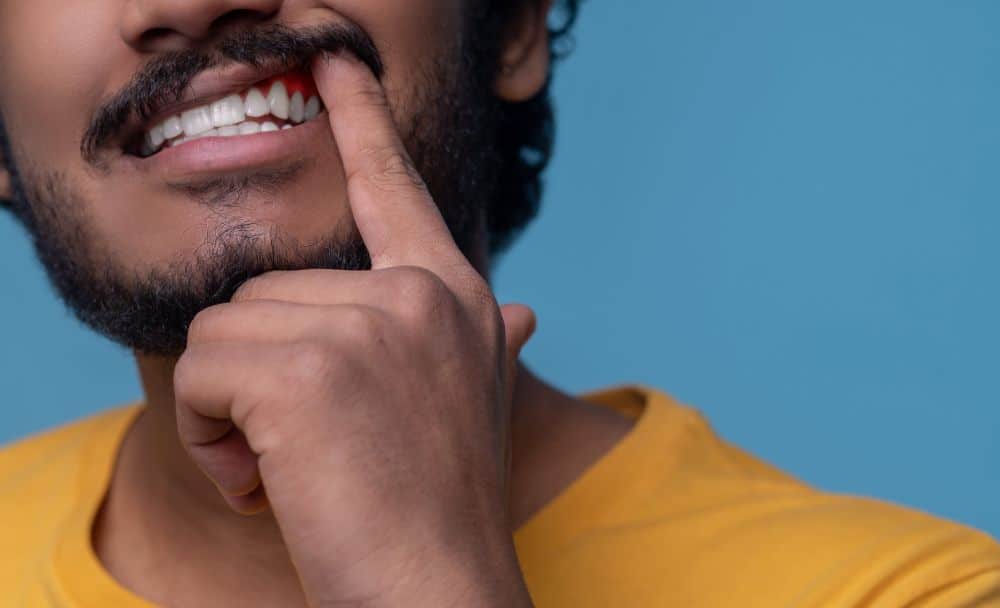
Swollen and bleeding gums
One of the hallmark symptoms of scurvy is gum disease. The gums become swollen, red, and prone to bleeding, especially during brushing or eating. [3] [4]
Easy bruising
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of blood vessels. In its absence, blood vessels become weak, leading to easy bruising and the development of petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin). [3] [4]
Poor wound healing
Scurvy impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds effectively. Minor injuries may take longer to heal and can become infected more easily. [3] [4]
Dry and splitting hair
Lack of vitamin C can cause changes in the hair, making it dry, brittle, and prone to splitting. [3] [4]
Causes of Scurvy
Scurvy primarily occurs due to a deficiency of dietary vitamin C. The human body does not naturally produce or store vitamin C, so it must be obtained through the consumption of foods rich in this essential nutrient. Some common causes of scurvy include:
Poor diet
A diet lacking fresh fruits and vegetables, which are the primary sources of vitamin C, can lead to scurvy. This can be particularly prevalent in populations with limited access to nutritious foods or those who rely heavily on processed or canned foods. [10] [11]
Alcoholism
Alcohol interferes with the absorption and utilization of vitamin C in the body, leading to a higher risk of scurvy among individuals with alcohol addiction. [12] [13]
Malabsorption disorders
Certain medical conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or gastrointestinal surgeries, can impair the absorption of vitamin C from the diet, increasing the likelihood of scurvy. [14] [15]
Diagnosis of Scurvy
Diagnosing scurvy typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional may inquire about dietary habits, symptoms experienced, and conduct a thorough examination. Blood tests can reveal low levels of vitamin C in the body, which further supports the diagnosis. [2] [3]
Treatment of Scurvy
The treatment of scurvy revolves around replenishing the body’s vitamin C stores. This can be achieved through dietary changes and, in some cases, vitamin C supplementation. Treatment options include:
Dietary modifications
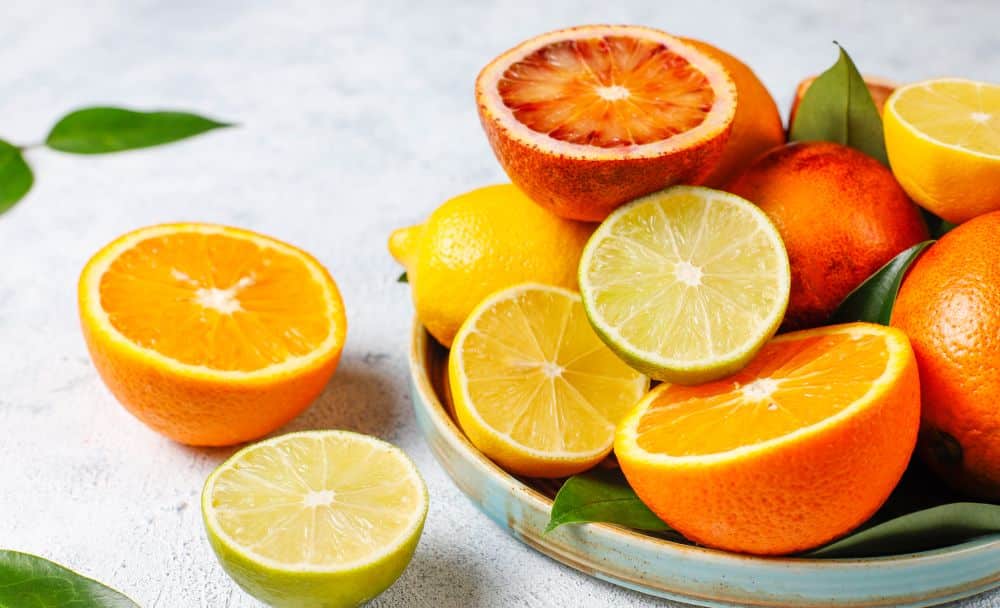
Increasing the intake of vitamin C-rich foods is vital to treating scurvy. Foods such as citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), Amla(Indian Gooseberry), green chillies, strawberries, kiwi, broccoli, bell peppers, and leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamin C. [2] [4]
Vitamin C supplementation
In severe cases or when dietary changes are not sufficient, vitamin C supplements may be prescribed. These supplements can help restore vitamin C levels rapidly. [2] [4] Additionally, Ayurvedic formulations made using Amla like Zandu Chyavanprash, Brahma Rasayan, Amalaki Rasayan, Amla Churna, Zandu Nimbadi Churna and Zandu Panchnimbadi Churna can be effective remedies for the condition.
Follow-up care
After initiating treatment, regular follow-up visits with a healthcare professional are important to monitor the progress and ensure that the vitamin C levels are being adequately replenished. The healthcare provider may also recommend additional measures to address any underlying causes or contributing factors of the deficiency, such as addressing malabsorption issues or providing nutritional counselling.
Prevention of Scurvy
Preventing scurvy is relatively straightforward and primarily involves maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. Here are some essential steps to prevent scurvy:
Eat a vitamin C-rich diet
Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into your daily meals. Citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, bell peppers, broccoli, spinach, and kale are all excellent sources of vitamin C. Aim to consume these foods raw or lightly cooked to retain their maximum nutrient content. [2] [4]
Store and prepare foods properly
Vitamin C is a delicate nutrient that can be easily destroyed by heat, light, and air. To preserve the vitamin C content in foods, store them properly, avoid prolonged exposure to light and air, and minimize cooking time to retain the maximum nutritional value.
Consider supplementation if needed
In some cases, individuals with limited access to fresh produce or those with certain medical conditions may require vitamin C supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if supplementation is necessary and the appropriate dosage.
Be aware of high-risk groups
Certain populations are more susceptible to scurvy, such as infants fed with formula lacking vitamin C, the elderly with limited dietary variety, individuals with alcohol addiction, or those with malabsorption disorders. Extra attention should be given to ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin C in these groups.
Seek medical advice
If you notice persistent symptoms such as fatigue, gum bleeding, or joint pain, seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes.
FAQs
1. Are there any long-term complications of scurvy?
If left untreated, scurvy can lead to severe complications such as anemia, poor wound healing, infections, and even death. However, with timely diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is generally excellent, and most symptoms can be reversed.
2. Is scurvy common today?
Scurvy is relatively rare in developed countries where access to fresh produce is readily available. However, certain populations or individuals with limited access to nutritious foods or specific medical conditions may still be at risk.
3. Is there a connection between scurvy and historical sea voyages?
Yes, scurvy had a significant impact on historical sea voyages and explorations. Sailors and explorers who lacked access to fresh fruits and vegetables suffered greatly from scurvy. The discovery of the link between vitamin C and scurvy prevention revolutionized long-distance travel and led to the implementation of dietary measures to combat scurvy on ships.
4. Does Ayurvedic literature mention scurvy?
Ayurvedic literature does not explicitly mention the term “scurvy.” However, Ayurveda recognizes the importance of a balanced diet and the role of various nutrients in maintaining overall health. Ayurvedic principles emphasize the consumption of fresh and seasonal fruits, vegetables, and herbs, which are rich sources of essential nutrients, including vitamin C.
Conclusion
Scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency, is a condition that can be prevented and treated through dietary measures. Awareness of the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies is crucial to maintaining good health and preventing complications associated with scurvy. By ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin C through a balanced diet, individuals can protect themselves from this historically significant disease and lead healthier lives.
Disclaimer: This Article is for informative purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Kindly contact a medical professional before attempting any treatments mentioned in the article yourself.
References:
- Vitamin C Deficiency – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
- Scurvy – NHS (www.nhs.uk)
- Scurvy Clinical Presentation (archive.org)
- Vitamin C Deficiency – Disorders of Nutrition – MSD Manual Consumer Version (msdmanuals.com)
- Global Vitamin C Status and Prevalence of Deficiency: A Cause for Concern? – PMC
- What causes high cholesterol? (medicalnewstoday.com)
- Dopamine deficiency: Symptoms, causes, and treatment (medicalnewstoday.com)
- Vitamin C Deficiency – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
- What causes fatigue, and how can I treat it? (medicalnewstoday.com)
- Scurvy: A Case Caused by Peculiar Dietary Habits | JAMA Dermatology | JAMA Network
- Scurvy and its prevention and control in major emergencies (who.int)
- Vitamin C and alcohol: a call to action | BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health
- Alcohol Withdrawal: Possible Risk of Latent Scurvy Appearing as Tiredness: A STROBE-Compliant Study – PMC (nih.gov)
- Sailing the ship of life: scurvy and autoimmunity – PMC (nih.gov)
- Scurvy as the tip of the iceberg – ScienceDirect