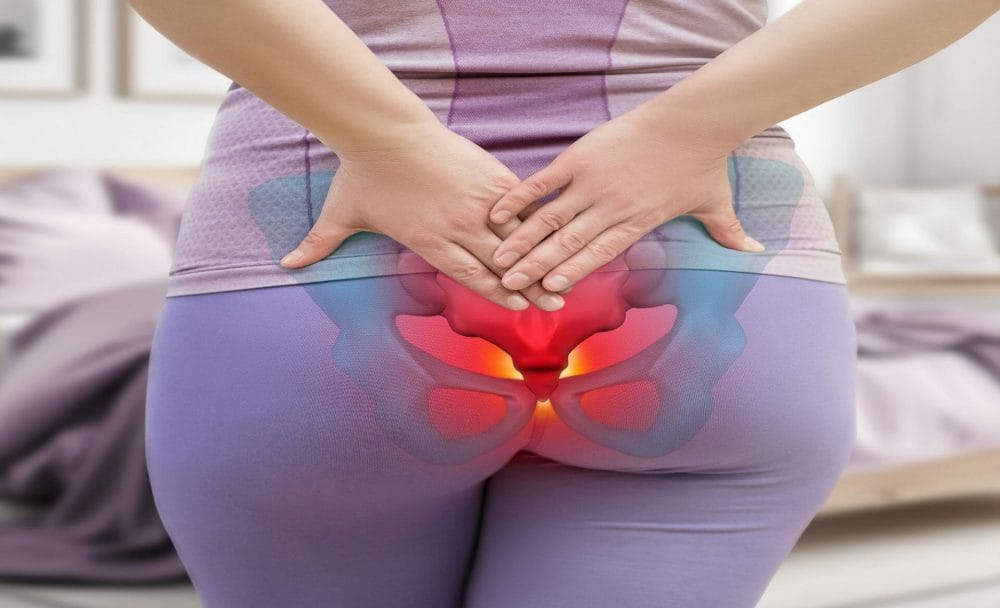
Tailbone pain, medically known as coccydynia, can be a debilitating and uncomfortable condition affecting the coccyx or the tailbone located at the base of the spine. This often overlooked yet vital structure plays a crucial role in supporting our body when sitting and in various other activities. This condition is more commonly observed in women, and individuals who are obese are also at a higher risk. [1]
In Ayurveda, low back pain is referred to as “Katishulam,” “Katigraham,” or “Gridhrasi,” depending on the specific structures involved. Vata dosha is identified as the primary Dosha responsible for the development of low back pain. Consequently, over 90 percent of cases are attributed to Vata-related degeneration. [2]
In this article, we will explore the many facets of tailbone pain, including its overview, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and how to relieve tailbone pain.
Overview of Tailbone Pain
The coccyx, or tailbone, is a small triangle-shaped bone at the spinal column’s base, consisting of three to five fused (joined) vertebrae. While it might seem insignificant, the coccyx functions as an anchor point for several muscles, tendons, and ligaments in the pelvic region. Tailbone pain, or coccydynia, occurs when there is irritation or inflammation in this area. It can range from minor discomfort to pretty severe, debilitating pain. [1]
Causes of Tailbone Pain
Tailbone pain can have various causes, both traumatic and non-traumatic. Common tailbone pain causes include:
Direct Trauma:
The most frequent cause of coccydynia is direct trauma to the tailbone. This can result from a fall, sports injury, or childbirth. Even prolonged sitting on hard surfaces can lead to chronic irritation and pain.
Repetitive Strain:
Activities that involve repetitive strain on the coccyx, such as rowing or cycling, can lead to tailbone pain over time.
Obesity:
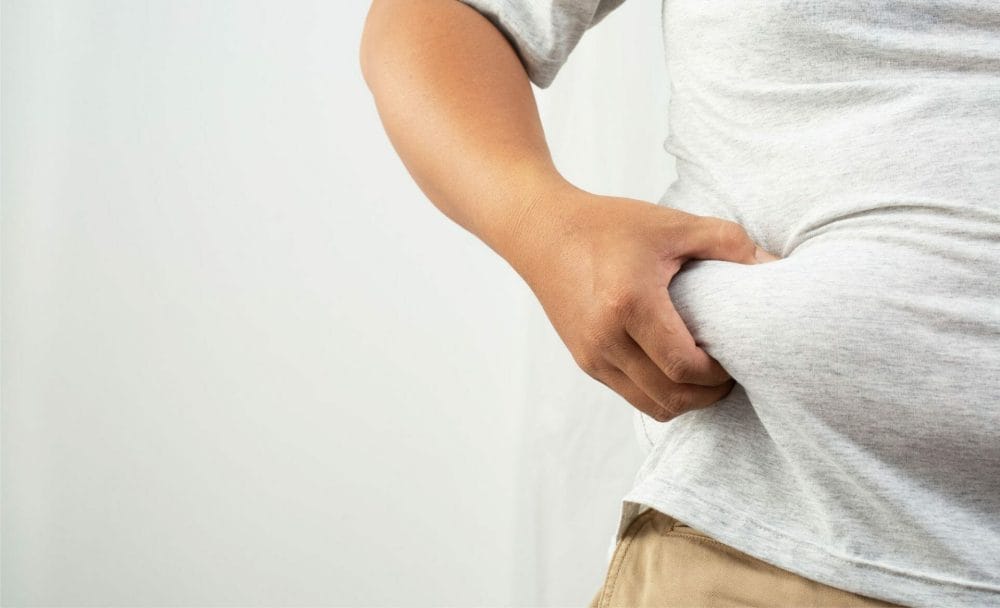
Obesity can trigger tailbone pain as excess weight can cause the coccyx to protrude posteriorly, exacerbating the problem.
Rapid weight loss:
This can also contribute to coccygodynia, as it leads to a loss of natural cushioning.
Infection or Tumor:
In rare cases, infections or tumors in the tailbone area can cause pain. This requires immediate medical attention.
Degenerative Changes:
As people age, the coccyx can undergo degenerative changes, such as arthritis or bone spurs, which may result in pain. [1]
Symptoms of Tailbone Pain
Tailbone pain can manifest in various ways, and its intensity can range from mild discomfort to excruciating pain. Common symptoms include:
- Localized pain in the lower back or buttocks
- Tailbone pain when sitting gets worsened
- Pain during bowel movements
- Discomfort with activities like standing up from a seated position, bending, or lifting heavy objects
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Bruising and swelling in cases of traumatic injury [3]
Treatment Options for Tailbone Pain
Several tailbone pain treatment options are available, ranging from conservative measures to more invasive interventions:
Ayurvedic Management:
There are two distinct treatment approaches employed for tailbone pain relief: shodhana and shamana.
In Shodhana Chikitsa, particular emphasis is placed on Basti therapy, as it directly calms the aggravated Vata Dosha, which is the primary causative factor behind low back pain.
Shamana Chikitsa methods are recommended in conjunction with Shodana Chikitsa. Guggulu preparations are favored for immediate pain relief, given their notable pain-relieving properties in acute cases. [2]
Trayodasanga Guggulu
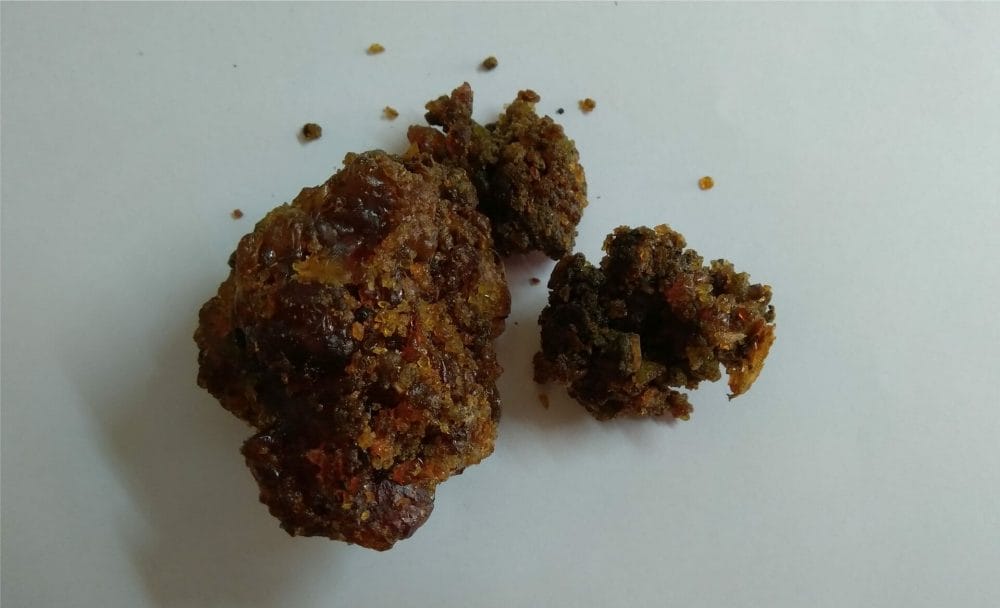

This is a well-renowned medicinal formulation extensively utilized in clinical practice to address low back pain. This medicine is usually available in tablet form. The fundamental component of Trayodasanga Guggulu is guggulu, derived from the resin coming from the Commiphora mukul tree. It has gained widespread recognition in Ayurvedic clinical applications for the management of conditions related to joints and bones. Apart from guggulu, this formulation consists of an additional 13 carefully selected ingredients. [2]
Conservative Treatments:
Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs/medications (NSAIDs) to be taken orally or applied topically, can help manage pain and inflammation. [1]
Physical Therapy: physiotherapy or tailbone pain exercises, which may involve techniques such as TENS (transcutaneous electrical stimulation) and manipulation, is considered as a therapeutic option. [1]
Invasive Treatments:
Injections: In some cases, caudal epidural injections and ganglion impar blocks can reduce inflammation and relieve inflammation. [1]
Psychological Support: In cases where psychological factors contribute to Tailbone pain, counseling or therapy may be recommended to address the emotional aspect of the condition. [1]
FAQs
• How can Tailbone pain be diagnosed?
X-rays and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be ordered to identify structural abnormalities, fractures, or degenerative changes in the coccyx as well as check for inflammation, which suggests hypermobility, and to diagnose tumors. [1]
• Which Taila is good for Tailbone pain?
Eranda Taila is good for low back pain. Use of the oil in Vata disorders, particularly Gridhrasi, Katishula, Pristhashoola, and Sandhishula, is significant. This oil is renowned for its ability to effectively address Vata aggravation due to its properties, including being snigdha (unctuous), guru (heavy), and ushna (warm). It also contains attributes such as tikshna (sharp), sukshma (subtle), katu rasa (pungent taste), and ushna virya (hot potency), which make it beneficial in alleviating Kapha dosha. Furthermore, in situations where Vata vitiation is compounded by Kapha obstruction, Eranda Taila proves to be valuable as it serves the dual purpose of eliminating the obstruction and pacifying Vata. [2]
• What causes tailbone pain without injury?
Repetitive or prolonged stress on the coccyx, such as extended periods of sitting while driving or cycling, can contribute to the condition. Inadequate posture, being either overweight or underweight, and increased flexibility or joint hypermobility in the joint connecting the coccyx to the lower spine can also be contributing factors. [3]
Conclusion
Tailbone pain, or coccydynia, is a distressing condition that can impact an individual’s quality of life. Whether caused by trauma, repetitive strain, or underlying medical issues, tailbone pain should not be ignored. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, which may include conservative measures, physical therapy, or even surgery in severe cases, can help alleviate pain and restore functionality.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is notmedical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References: