This article is reviewed by experts.
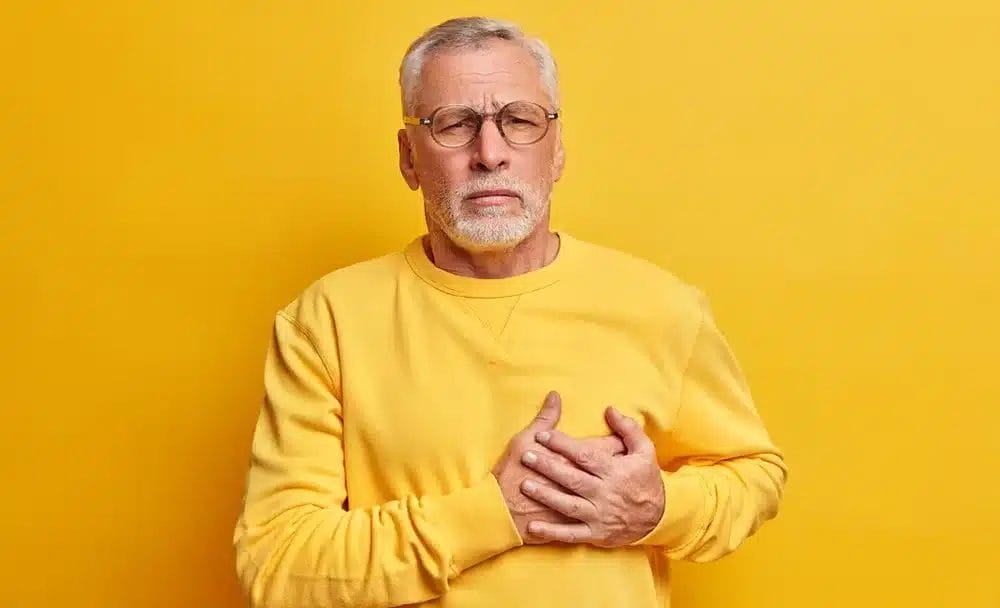

In today’s world, heart attacks are rapidly emerging as a grave health concern. While the problem of heart attacks is commonly associated with older individuals, it can affect people of all ages. Due to busy routines, many individuals tend to neglect their health, gradually paving the way for various health conditions. A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when there is a sudden blockage in one or more coronary arteries, responsible for supplying blood to the heart muscles. This blockage typically results from the buildup of cholesterol, fat, and other substances on the walls of the arteries. When blood flow to a section of the heart muscle is severely reduced or completely cut off, it leads to damage to the heart, resulting in a heart attack.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from person to person, but some common indicators and signs include:
- Chest Pain: The most common symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort. It may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest. This pain can last for several minutes or come and go.
- Pain or Discomfort in Other Upper Body Parts: Pain or discomfort may also radiate to other upper body parts such as the arms (usually the left arm but can also affect the right arm), back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Shortness of Breath: Breathlessness or a feeling of difficulty in breathing is another common symptom, often occurring with or without chest pain.
- Cold Sweating: Sudden cold sweats or profuse, drenching sweats can occur during a heart attack.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea or vomiting, which is particularly common in women.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy can also be an early sign of a heart attack, sometimes occurring alongside other symptoms.
It’s worth noting that not all symptoms of a heart attack appear suddenly and intensely. Some signs can develop gradually, including slow-onset general discomfort or uneasiness. Certain individuals, particularly women, the elderly, or those with diabetes, may experience common symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing these signs, seeking immediate medical assistance is essential. Call emergency services or head to the nearest hospital without delay.
Causes of Heart Attacks
There are several factors that can increase your risk of a heart attack, including:
High Cholesterol Levels: High levels of LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol, also known as “bad cholesterol,” can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries.
- High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the walls of your arteries and increase the accumulation of plaques.
- Smoking: Smoking can harm your blood vessels and accelerate the development of atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at an increased risk of atherosclerosis and heart attacks.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can contribute to various heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Inactive Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can be a risk factor for heart disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming high amounts of saturated and trans fats, refined sugars, and processed foods can promote the development of atherosclerosis.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase the risk of heart attacks.
- Age and Gender: The risk of heart attacks increases with age and is higher for men than premenopausal women. However, after menopause, women’s risk also rises.
- Stress: Prolonged mental stress and certain personality traits can be associated with heart disease risk.
Preventing a Heart Attack

You can reduce your risk of a heart attack by addressing factors that can increase this risk through lifestyle changes. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help prevent heart disease. If you already have coronary artery disease, these changes can also reduce your risk of a heart attack. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption as it can increase the risk of heart disease.
It’s also crucial to seek proper medical care for other health conditions that may elevate your risk of a heart attack. Consult your doctor to determine if taking aspirin can help reduce your risk of blood clot-related heart attacks.
Treatment for a Heart Attack
Upon recognising the symptoms of a heart attack, seeking immediate medical treatment is of utmost importance. Only then can a doctor start your treatment without delay.
- Medications: Following heart-related procedures, various medications may be prescribed to reduce pressure on the heart, control blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, and prevent blood clots.
- Cardiac Procedures: Depending on the severity and condition of your arteries, interventions such as angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery may be recommended.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Undergoing cardiac rehabilitation after a heart attack can improve your health, assist in adopting a healthy lifestyle, and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
- Changes: After a heart attack, making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to a heart-healthy diet can significantly improve heart health.
FAQs
Does what you eat increase the risk of a heart attack?
Yes, certain foods and dietary choices, including high levels of fats, sugar, salt, and others, can increase the risk of a heart attack when consumed in excessive amounts.
Can children have a heart attack too?
Yes, children can experience a heart attack, although it is less common compared to adults. The causes of a heart attack can include various factors, including genetic, dietary, and environmental factors.
Why do heart attacks happen suddenly?
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in the blood vessels. Besides this, several factors in the body can contribute to an increased risk of a heart attack over time, such as the accumulation of plaque in the arteries.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.