
Boswellia serrata, which is also known as Indian frankincense, is a plant extract that has been an integral component in the Ayurvedic science of medicine for thousands of years. Boswellia serrata is also known as Shallaki in Sanskrit and Salai/Salai guggul in Hindi.
Boswellia Serrata Uses And Benefits
- Eases Symptoms of Arthritis
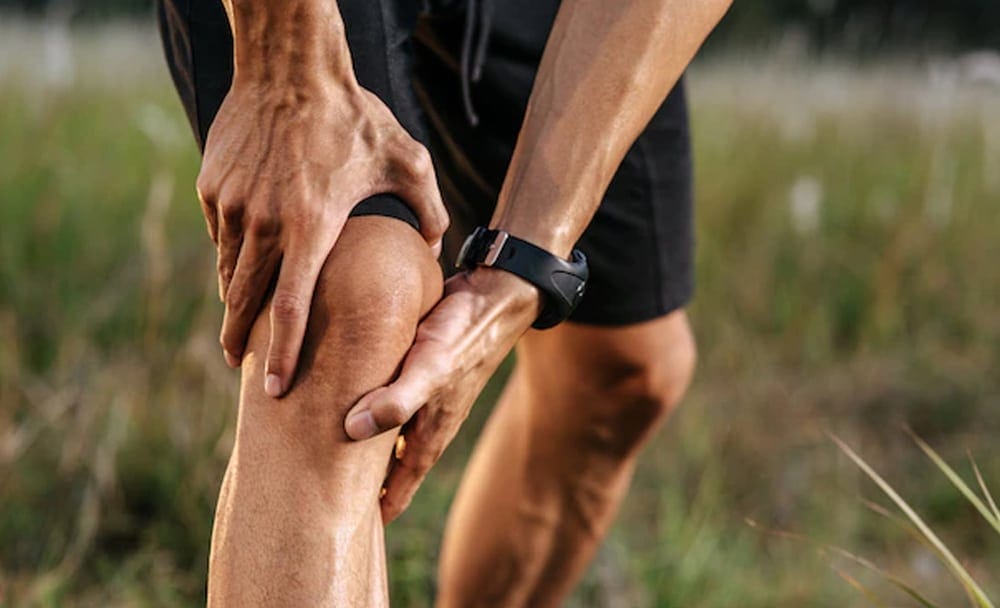

Boswellia has been traditionally used to effectively manage pain that is associated with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, tendonitis, and bursitis. Other uses that are not related to pain include ulcerative colitis, asthma, dyspepsia, sore throat, allergic rhinitis, pimples, syphilis, and even cancer. There exists preliminary evidence that consuming an oral extract of Indian frankincense may help in reducing the symptoms of osteoarthritis such as knee pain as well as swelling. That said, more evidence is required for the use of Boswellia in both these conditions.
- Acts As A Potent Anti-Inflammatory Agent
Traditional medicine that uses extracts derived from the Boswellia plant has long been used to combat the symptoms of asthma. These extracts contain amino acids, resin, phenols, polysaccharides, terpenes, and β-boswellic acid, which is the primary active anti-inflammatory component. Extracts of the plant or β-boswellic acid has demonstrated the ability to inhibit hypersensitivity reactions through regulation of both humoral and cellular immune systems.
- Treats Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
The Boswellia serrata plant, which is native to India, is an Ayurvedic herb that is used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Boswellic acid, which is the primary constituent of Boswellia, is believed to effectively contribute to a majority of herbal and pharmacologic activities.
- Is Used as an Incense
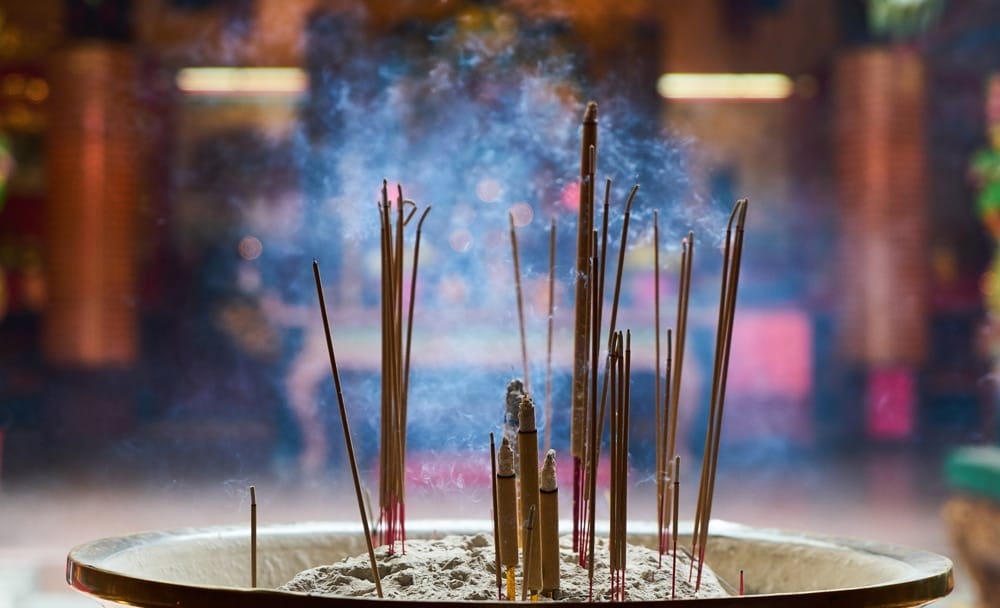

The resins derived from the plant have played a pivotal role as adhesives, active ingredients for cosmetic preparations, fragrances in everyday rituals and religious ceremonies, coating materials, and for its diverse curative powers. In ancient times, Hindus, Persians, Babylonians, Romans, Greeks, and the Chinese have used natural resins majorly for embalming and for its incense when it comes to cultural functions. These civilisations are of the firm belief that when these materials (such as the resin derived from the Boswellia plant) come into contact with fire, the resulting smoke and fragrance not only please the gods but also soothe the individual’s soul. Burning of these resins had become an essential component when it comes to their cultural life. This is one of the many Boswellia benefits. The fresh gum obtained from the plant is hot with a pleasant flavour and a tad bitter in taste. All along, the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians have used it as a prized incense, fumigant, and as a multipurpose aromatic. It is commonly used to prepare incense powder and sticks.
- Other Diverse Uses
Boswellia is a gummy resin that finds mention in traditional Ayurvedic as well as Unani texts as a highly efficacious remedy in the treatment of dysentery, diarrhoea, boils, ringworm, skin and blood disorders, fevers (antipyretic), mouth sores, cardiovascular disease, bronchitis, bad throat, cough, vaginal discharges, hair loss, haemorrhoids, stimulation of the liver, and irregular menses.
How to use Boswellia?
Boswellia is usually consumed as a tablet, capsule, or decoction of the bark orally. The recommended dosage is eventually based on historical practice or, alternatively, available trials. Presently, it is not quite clear what is the right dose when it comes to balancing safety and efficacy. The manufacturing of products varies among diverse produces, thus making it much more challenging to standardise the dosage. It is vital to note that a majority of the trials used diverse products made by several different manufacturers; hence, clinical effects may not necessarily be comparable.
On A Final Note
Boswellia serrata, is a plant that is native to India and is also known as Shallaki in Sanskrit and Salai or Salai guggul in Hindi. Another name for the plant is Indian frankincense. Boswellia has been used for thousands of years in the ancient science of Ayurveda. Earlier civilisations such as the Greeks and Romans used this gummy resin as an incense for cultural and religious purposes. Besides, the plant is well known for its anti-inflammatory, antiarthritic, analgesic, antihyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective agent.




















1 Comments
Comments are closed.