Do you want to know the amazing benefits of folic acid? Are you curious to learn how this essential nutrient can contribute to your overall health and well-being? If yes, then you’ve come to the right place. In this article, learn everything you need to know about folic acid, the major folic acid benefits, and potential folic acid side effects.
What is folic acid?
Folic acid is the synthetic form of folate, also known as vitamin B9. Folic acid plays a crucial role in the production of healthy red blood cells. [1] While folate can be obtained from specific foods, folic acid is commonly used in dietary supplements and fortified foods to ensure an adequate intake. Its importance in maintaining overall health makes folic acid an essential nutrient to consider for a balanced diet.
Recommended daily intake values
| Group | Recommended daily dosage |
| Adults | 400 micrograms |
| Adult women who are planning a pregnancy or could become pregnant | 400 to 1,000 micrograms |
| Breastfeeding teens and women | 500 mcg/day |
| Children | |
| 0-6 months | 65 mcg/day |
| 7-12 months | 80 mcg/day |
| 1-3 years | 150 mcg/day |
| 4-8 years | 200 mcg/day |
| 9-13 years | 300 mcg/day |
| 14 years and older | 400 mcg/day |
| Pregnant teens and women | 600 mcg/day |
Folic acid benefits for health [2]
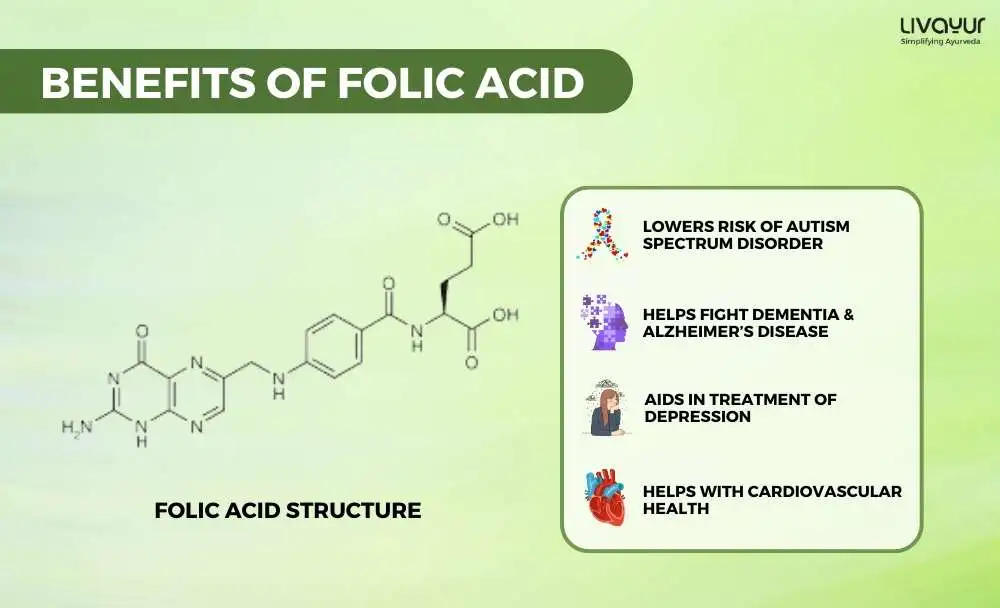
1. Reduces Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) risk
One of the primary folic acid benefits is that its intake shows promise in reducing ASD risk based on observational studies, possibly due to its positive influence on neurodevelopment through DNA methylation.
2. Helps in cancer prevention
Folic acid’s impact on cancer development, through its involvement in DNA replication and cell division in one-carbon metabolism, is its primary benefit. Additionally, higher folate intake appears to inversely correlate with a range of cancers, including colorectal, lung, pancreatic, esophageal, stomach, cervical, ovarian, breast, and bladder, among others.
3. Reduces cardiovascular disease and stroke risk
Yet another of the several folic acid benefits is that in conjunction with B vitamins, it supports homocysteine metabolism, associated with cardiovascular risks. Furthermore, supplementation shows the potential to lower stroke risk by up to 25% and offer cardiovascular protection.
4. Guards against Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease
Enhanced cognitive preservation is a primary benefit, as elevated homocysteine levels, influenced by folic acid, are associated with decreased risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia. Apart from this, supplementing with folic acid can potentially decelerate cognitive decline, particularly among those with insufficient dietary intake of B vitamins.
5. Controls depression
Improved mental well-being stands as one of the primary folic acid benefits, as inadequate folate levels have been connected to depression and less responsive outcomes to antidepressants in certain research. Furthermore, elevated serum folate levels have shown a correlation with reduced depression rates among adults, highlighting the potential for better mental health with sufficient folate levels.
6. Reduces Neural Tube Defects (NTDs) risks
Significant risk reduction of neural tube defects (NTDs) emerges as one of the primary folic acid benefits, as adequate folic acid intake before conception and throughout pregnancy substantially lowers the risk. Moreover, by supporting the closure of the neural tube in early pregnancy, this intake helps prevent malformations in the spine, skull, and brain, further emphasizing its crucial role in prenatal development.
7. Manages high blood pressure issues
Daily oral intake of folic acid for a minimum of 6 weeks exhibits blood pressure reduction in certain individuals with high blood pressure, especially those not using other blood pressure medications.
8. Controls gum enlargement due to Phenytoin
Application of folic acid directly to the gums appears effective in preventing gum enlargement triggered by phenytoin. However, oral consumption of folic acid doesn’t seem to provide similar benefits.
9. Prevents strokes
In regions without folic acid fortification in grain products, taking folic acid supplements can decrease the likelihood of stroke. Conversely, for individuals residing in countries where folic acid is added to grain products, supplements don’t seem to offer the same preventive effects against stroke.
10. Treats Vitiligo skin disorder
In cases of vitiligo, consuming folic acid orally demonstrates potential symptom improvement, particularly in reducing white patch development on the skin.
Folic acid uses [1]
1. Managing Folate Deficiency Anemia
One of the main folic acid uses is that it is employed to treat or prevent folic acid deficiency anemia, ensuring adequate levels of this essential nutrient in the body. [1]
2. Supporting Fetal Development
Benefits of folic acid for women who are pregnant are immense. During pregnancy, folic acid aids in the proper development of the baby’s brain, skull, and spinal cord, reducing the risk of neural tube defects like spina bifida. [1]
3. Mitigating Methotrexate Side Effects
Folic acid uses also include its ability to minimize the adverse effects of methotrexate, a medication used in severe arthritis, Crohn’s disease, or psoriasis treatment, thereby supporting patients undergoing this therapy. [1]
Folic acid deficiency [2]
1. Causes of Folic Acid Deficiency:
Commonly linked to poor dietary intake, alcoholism, and conditions affecting nutrient absorption like malabsorptive disorders (e.g., celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease).
2. Primary Clinical Signs:
Folic acid deficiency primarily presents as megaloblastic anemia, characterized by abnormally large red blood cells. Symptoms include weakness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, headaches, heart palpitations, and shortness of breath.
3. Additional Manifestations:
Other symptoms of folic acid deficiency may encompass soreness of the tongue and oral mucosa, changes in skin and hair pigmentation, gastrointestinal issues, and elevated homocysteine levels.
4. Folate Inadequacy in Alcohol Use Disorder:
Individuals with alcohol use disorder often experience folate inadequacy due to alcohol’s interference with folate absorption and breakdown, worsening the deficiency.
5. Folate Deficiency in Specific Groups:
Women of childbearing age, especially during pregnancy, may face folic acid deficiency. Also, those with malabsorptive disorders absorb less folate, exacerbating the deficiency.
6. Impact of MTHFR Polymorphism:
Individuals with the MTHFR polymorphism exhibit a reduced ability to convert folate, leading to heightened homocysteine levels and an increased risk of neural tube defects.
Who should & who shouldn’t take folic acid [1]?
Folic acid is generally safe for most people. It is especially beneficial for people who have folate deficiency or are at risk of developing it.
However, despite being an essential nutrient, folic acid may not be suitable for everyone. Therefore, it’s important to consult with a doctor before starting folic acid supplementation.
The following people should especially take the guidance of a healthcare professional before taking folic acid supplements:
- Individuals who have experienced an allergic reaction to folic acid or any other medication
- Those who have low vitamin B12 levels or pernicious anemia
- Cancer patients
- Patients who are undergoing hemodialysis
- Patients who have a heart stent [1]
Folic acid side effects [2]
While folic acid is generally safe, excessive consumption may cause the following folic acid side effects.
- High folic acid intake may “mask” vitamin B12 deficiency, potentially delaying the detection of neurological consequences until they become irreversible.
- Excessive intake of folic acid has raised concerns about accelerating the progression of preneoplastic lesions, potentially increasing the risk of colorectal and other cancers in susceptible people.
- Intakes of 1,000 mcg or more of folic acid from supplements during the periconceptional period have been associated with lower cognitive development scores in children aged 4–5 years, compared to children whose mothers consumed 400 mcg to 999 mcg.
- Yet another of the various folic acid side effects is that excessive folic acid intake can lead to unmetabolized folic acid in the body, which has been linked to reduced numbers and activity of natural killer cells, potentially affecting the immune system.
Precautions to keep in mind
1. Safe Dosage Limits:
For most individuals, doses up to 1 mg of folic acid daily are likely safe. Higher doses might lead to adverse effects like stomach upset, nausea, diarrhea, irritability, confusion, behavior changes, skin reactions, seizures, and other side effects.
2. L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (L-5-MTHF):
Up to 400 mcg daily of this form is possibly safe for most people, including during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
3. Concerns during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
Recommended daily folic acid intake during pregnancy is 300-400 mcg, with a maximum of 800 mcg (under 18) or 1000 mcg (over 18) unless directed by a healthcare professional.
4. Children’s Dosage:
Safe for children in recommended age-specific amounts, avoiding doses exceeding the upper limits: 300 mcg (1-3 years), 400 mcg (4-8 years), 600 mcg (9-13 years), and 800 mcg (14-18 years).
5. Angioplasty Recovery:
Avoid using folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 post-angioplasty, as they might worsen narrowed arteries.
6. Cancer Risk:
High doses (0.8-1 mg daily) might potentially increase cancer risk, caution advised for individuals with a history of cancer.
7. Seizure Disorder:
Folic acid supplements, especially in high doses, might exacerbate seizures in individuals with seizure disorders.
8. Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Folic acid supplements might improve certain lab tests related to vitamin B12 deficiency, potentially masking the deficiency without treating it, leading to permanent nerve damage if left unaddressed.
Always seek guidance from a healthcare professional, especially if you are taking regular medications, as they can advise on potential interactions and how they might affect your folic acid intake.
FAQs
1. Which are the richest dietary sources of folic acid?
Some of the richest food sources of folic acid are beef liver, broccoli, asparagus, nuts, legumes and eggs.
2. Is it safe to take folic acid with other supplements?
Folic acid is generally safe to take with other supplements. However, it’s always wise to consult with a healthcare professional before combining supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking specific medications.
3. Can I take folic acid if I’m not planning to become pregnant?
Yes, as folic acid also offers other health benefits, like supporting red blood cell production, brain function, heart health, etc. However, you must discuss with your doctor if folic acid supplementation is recommended for you or not. [2]
4. Can folic acid interfere with other medicines?
Yes, folic acid may interfere with certain medications. It’s important to consult with a doctor before starting folic acid supplementation if you are under any medication, including pain relief medications. [1]
5. What are the different forms of folic acid supplements?
The different forms of folic acid supplements include methyltetrahydrofolate, levomefolate, and methylfolate.
Conclusion
Folic acid is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health. From its benefits in preventing neural tube defects and reducing the risk of certain cancers to its impact on cardiovascular health, brain function, and mental well-being, folic acid offers a range of advantages.
However, it’s crucial to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before starting folic acid supplementation, especially if you have specific medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Disclaimer
The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.