This article is reviewed by Dr. H.M. Chandola
Have you ever encountered a family member or a relative suffering from prostate issues? According to statistics about 50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60, and up to 90% of men older than 80 suffer from some form of prostate problem. But, what is a prostate gland? The prostate gland is an organ that is situated below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. The prostate contributes additional fluid to your semen that nourishes your semen cells and lubricates the urethra [1].
Your prostate may get damaged at some point in life, and there are many types of prostate diseases. In this article, we will take a deeper look at the different stages of prostatomegaly. But before that let us help you understand what prostatomegaly means!
Understanding Prostatomegaly [2]
Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), or prostatomegaly means an abnormally enlarged prostate gland, and is considered as the most common noncancerous tumour in men. As the prostate enlarges it presses against the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thickened and may weaken over a period of time. This leads to the inability of the bladder to empty the contents completely.
Unraveling Prostatomegaly Causes [3,4]
Prostatomegaly in Hindi is known as Mutrashtheela, whose cause is not clear. It may be attributed to factors like genetic predisposition, ageing, and hormonal imbalance in men. As men age the amount of testosterone in the blood declines, while estrogen levels remain the same. These hormones may trigger prostate cell growth. Another reason could be due to the higher levels of DHT in aging men. DHT, also known as dihydrotestosterone, is a male hormone that supports prostate development. Increased levels of DHT can cause the testosterone levels to decline.
Risk factors:
- Men with a family history
- Men who are obese or overweight
- Men with a sedentary (inactive) lifestyle
- Men with erectile dysfunction
According to Ayurveda Apana Vata affects the prostate and weakens the gland leading to prostatomegaly. Vata is one of the three primary Doshas in the body. Imbalance in Vata can cause a problem called Vatashateela [5].
Exploring The Prostatomegaly Symptoms [6]
When the prostate is abnormally enlarged it can block your bladder, leading to the following symptoms:
- Nocturia
The need to wake up at night frequently to pass urine which can negatively impact your quality of sleep.
- Urinary urgency
A feeling when there is an urgent need to urinate and you cannot wait.
- Incomplete emptying
A feeling of bladder fullness even after passing urine.
- Frequency
Passing urine often, about every one to two hours.
- Straining
Trouble starting to pass urine or the need to push or strain while urinating.
Stages of Prostatomegaly [7,8]
Prostatomegaly can be classified into four stages based on the enlargement as determined by a digital rectal exam or imaging tests like an ultrasound or an MRI.
- Stage I
The prostate gland is only slightly enlarged without any significant bladder obstruction, and obvious symptoms.
- Stage II
There is moderate enlargement of the prostate gland with no significant bladder obstruction. However, you may experience mild symptoms like difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream.
- Stage III
The prostate gland may be significantly enlarged with obvious bladder obstruction. You may exhibit severe symptoms like frequent urination, inability to empty the bladder, and urinary incontinence.
- Stage IV
Your prostate gland may be extremely enlarged with severe complications of prostatomegaly like retention of urine, hematuria (blood in urine), recurrent urinary infection, and stone formation in your bladder.
Prostatomegaly Treatment [9,10,11,12]
Treatment for an enlarged prostate gland usually depends on the disease stage and severity of your symptoms.
Stage I: Self-care
- Urinate as soon as you feel the urge. Plan a schedule to urinate every few hours even if you do not feel the need to pee.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and excess fluid consumption, especially at night after dinner. Spread the fluid intake throughout the day.
- Try to avoid cold and sinus medicines that contain decongestants since they may aggravate prostatomegaly symptoms.
- Make sure you exercise regularly.
Stage II: Medication
- Anti-hypertensive medicines like alpha-1 blockers help relax the muscles of the bladder neck and prostate.
- Medications like dutasteride lower the levels of hormones produced by the prostate. This reduces the gland size, increases the urine flow rate, and minimises the prostatomegaly symptoms.
Stage III And IV: Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Procedures like transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) or transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) use heat or radio waves to destroy or remove excess prostate tissue.
- Invasive surgeries like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), and simple prostatectomy that involve surgical excision of the enlarged prostate tissue.
Ayurvedic Management [4]
The following Ayurvedic management is helpful in conjunction with conventional treatments for stage I and stage II prostatomegaly :
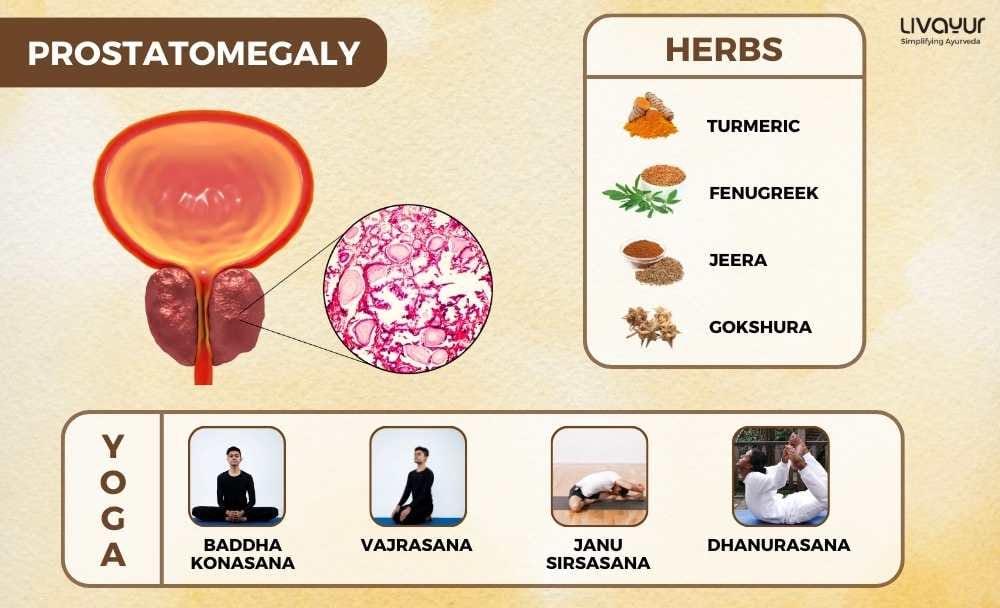
Yoga Asanas
- Baddha Konasana (cobbler pose)
- Virasana (hero pose)
- Supta Padangusthasana (reclining big toe pose)
- Janu Sirsasana (head-to-knee pose)
- Dhanurasana (bow pose)
Ayurvedic Herbs And Medicines
- Haldi (Turmeric)
- Methi (Fenugreek)
- Jeera (cumin)
- Saunf (fennel)
- Gokshura
- Varuna
- Alsi
- Yashada Bhasma
Final Note
Prostatomegaly is an abnormal enlargement of the prostate gland in men. This leads to a cascade of symptoms based on the different stages. Staging is a vital component of disease diagnosis because it is used to guide the treatment plan and predict your prognosis. Prostatomegaly can be classified into four stages which may involve different treatment modalities. Seek medical guidance if you notice any symptoms associated with prostatomegaly.
FAQs
Do women have a prostate gland?
Women do not have an obvious prostate gland. However, they consist of a female version of the prostate gland known as the Skene glands. These are a series of ducts and glands present at the front of the vagina.
Can I live without a prostate?
Yes you can live without a prostate. Your prostate is essential and helpful for reproduction but not needed to survive. However, you may experience side effects like erectile dysfunction.
What are the essential diagnostic tests to confirm prostatomegaly?
Prostatomegaly can be diagnosed through the following:
Blood tests to detect prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
Urodynamic test to analyze the urine flow rate
Digital rectal exam
Biopsy
References
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: An Overview
- Pathophysiology of benign prostate enlargement and lower urinary tract symptoms: Current concepts
- Epidemiology and etiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia and bladder outlet obstruction
- Gokshuradi Vati and Dhanyaka-Gokshura Ghrita Matra Basti in the management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Clinical Evaluation of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The grading and staging of clinical BPH for optimal care
- Staging of benign prostate hyperplasia is helpful in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostate hyperplasia
- Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Various treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia: A current update
- Medical Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Modern best practice in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia in the elderly























