The aspartate aminotransferase (AST), also known as serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), blood test is a diagnostic tool in clinical medicine. This test is crucial in assessing the health and functioning of the liver, heart, and other vital organs. Measuring the levels of AST in the bloodstream helps healthcare professionals learn about the patient’s physiological state.
This article looks at the AST (SGOT) blood test, exploring high and average range values, their significance, and the clinical implications of interpreting these results. Understanding the intricacies of this diagnostic tool is essential for physicians and patients. It will help support informed medical decision-making and contribute to the effective management of various health conditions.
What is AST?
AST, or aspartate aminotransferase, is a vital enzymatic marker in clinical medicine, often called serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT). This enzyme is primarily synthesized within hepatic cells and serves as one of the two essential liver enzymes. Notably, AST’s clinical significance arises from its role as an indicator of liver cell damage.
In liver injury or disease, the integrity of liver cell membranes may be compromised. It can lead to the release of AST into the bloodstream, resulting in elevated AST levels in blood tests. It is crucial to distinguish AST from ALT, another liver enzyme, as AST does not remain confined to the liver.
It is also present in various tissues throughout the body, including the heart, kidneys, muscles, and brain. Consequently, elevated AST levels can occur due to liver issues and damage to cells in these extrahepatic tissues. The multifaceted distribution of AST underscores its clinical utility as a marker for a broader spectrum of organ health beyond just the liver. [1]
What is an AST (SGOT) blood test?
The AST (SGOT) blood test is a diagnostic tool for assessing liver damage. It revolves around measuring aspartate transaminase (AST), an enzyme released into the bloodstream in response to liver or muscle injury. While AST is predominantly present in the liver and heart, it is worth noting that trace amounts of this enzyme can be present in other muscle tissues.
This test is crucial in clinical practice as it enables healthcare professionals to evaluate the integrity and functioning of the liver by gauging the levels of AST in the bloodstream. Elevated AST levels can indicate liver damage, and the AST blood test serves as a valuable means of diagnosing and monitoring liver-related conditions. [2]
Why is an AST (SGOT) blood test needed?
An AST (SGOT) blood test is necessary when a healthcare provider suspects liver damage in a patient. The diagnostic procedure becomes relevant when individuals exhibit symptoms associated with liver disease, including dark-colored urine, light or clay-colored stool, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), nausea, vomiting, and more.
Additionally, individuals with a family history of liver disease or consuming excessive alcohol may need this test. Furthermore, individuals with underlying medical conditions like diabetes, which may pose a risk to liver health, or those taking medications that can potentially impact liver function may also undergo an AST blood test. [2]
What is the procedure of AST (SGOT) blood test? [3]
The procedure of the AST (SGOT) blood test is pretty standard. This means, that like a regular blood test, this is what can be expected in an AST (SGOT) blood test:
- Visit a medical facility, and schedule an AST (SGOT) blood test after presenting your prescription to them.
- You will be referred to a qualified medical practitioner called a phlebotomist, who will take your blood.
- First, the medical practitioner will use an antiseptic to clean the region, which is often inside your elbow.
- A blood constrictor may be tied above the draw site to enhance the visibility of the veins.
- Blood will be drawn into one or more tubes once a needle is placed into a vein.
- Usually, the procedure goes quickly and painlessly.
Precautions to take while handling the blood sample
- All specimens should be sent to the lab immediately for processing, as they’re potentially infectious and should be treated delicately.
- Separated serum or plasma should not remain at +15°C to +30°C longer than 8 hours.
- If assays are not completed within 8 hours, serum or plasma should be stored at +2°C to +8°C.
- If assays are not completed within 48 hours or the separated sample is to be stored beyond 48 hours, samples should be frozen at –15°C to –20°C.
- Frozen samples should be thawed only once. Analyte deterioration may occur in samples that are repeatedly frozen and thawed.
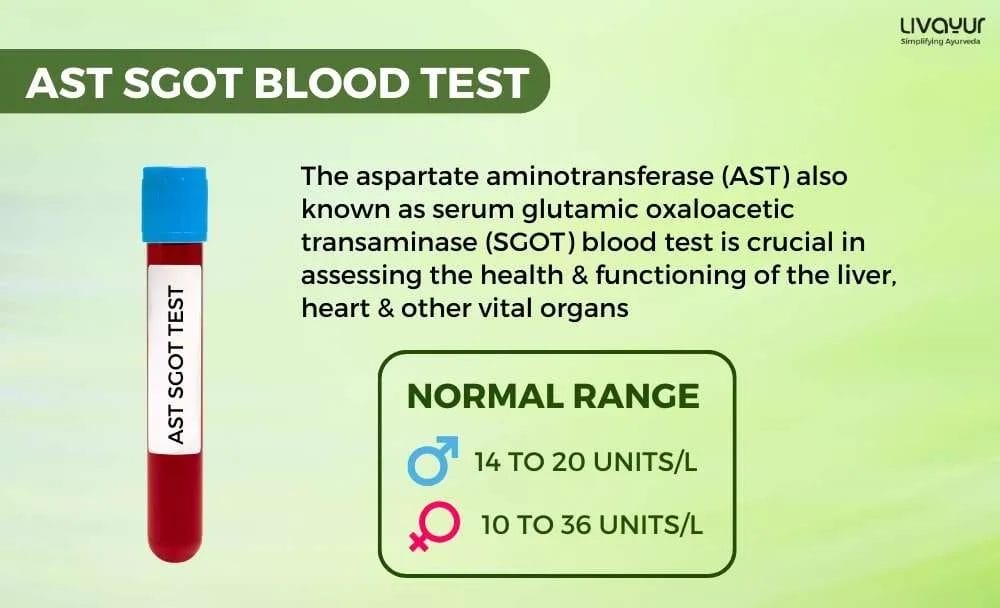
What is the normal and high range for AST (SGOT) blood test?
The AST (SGOT) blood test offers valuable insights into health by assessing enzyme levels in the bloodstream. The standard reference ranges for AST are typically 14 to 20 units per liter (units/L) for men and 10 to 36 units/L for women. Women tend to exhibit slightly lower AST levels than men, and older adults may have somewhat elevated levels within the normal adult range.
Elevated AST levels beyond these norms may indicate underlying health concerns, including liver disease, muscle injury, heart attack, or pancreatitis. Significantly elevated AST levels may indicate more severe conditions like viral hepatitis and liver damage induced by medications or toxins. The determination of AST levels aids healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. [2]
Diseases that can be tested for with the AST (SGOT) blood test [6]
There has been evidence of the AST enzyme in all examined animal and human tissues. The human brain, liver, stomach mucosa, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and kidneys have all been found to have substantial activity in addition to the heart muscle, which is where the enzyme is most active. Here’s an overview of what can be tested with an AST (SGOT) blood test:
- Certain forms of liver and cardiac disease are diagnosed and treated with the assistance of AST levels. Cells’ cytoplasm and mitochondria both contain AST.
- Serum AST primarily originates from the cytoplasm in minor tissue injury situations, with lower quantities coming from the mitochondria.
- Greater amounts of the mitochondrial enzyme are released in response to severe tissue injury.
- Transaminase levels that are elevated may indicate organ damage, hepatic illness, muscular dystrophy, or myocardial infarction.
Consideration to know about AST (SGOT) blood test
Considering the following aspects when interpreting AST (SGOT) blood test results is crucial. Firstly, it’s important to note that while AST is a valuable marker for liver health, it is not as specific or informative as the ALT (alanine transaminase) level when assessing liver function. Additionally, some individuals diagnosed with hepatitis C may exhibit normal AST levels, making it less reliable as a standalone indicator for liver disease in such cases.
Furthermore, patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis may surprisingly present with normal AST levels, highlighting the limited sensitivity of this test in detecting severe liver pathologies. Therefore, clinical assessments should consider multiple factors, including ALT levels and patient history, to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of liver health. [1]
Ayurvedic interventions for managing healthy liver function
Ayurveda emphasizes maintaining optimal liver health through traditional practices, dietary guidelines, and herbal supplements. Here are some critical Ayurvedic interventions for managing a healthy liver.
1. Panchakarma (detoxification)
Ayurveda recommends periodic detoxification through panchakarma therapies to eliminate accumulated toxins from the body. These therapies, like virechana (therapeutic purgation) and basti (medicated enema), help clean the liver and restore its natural functions. [4]
2. Ahara (diet plan)
Ayurvedic dietary principles play a crucial role in supporting liver health. The concept of “satvika ahara,” which consists of pure vegetarian foods with minimal spices, is ideal for maintaining a healthy liver. Conversely, it is best to avoid “rajasika” (stimulating) and “tamasika” (degrading) foods, as they can disrupt the mind-body equilibrium. Food processing methods (samskara or paka) and proper food combinations are essential considerations in Ayurvedic dietary recommendations. [4]
3. Yoga, dhyana, and vyayama (yogic posture, meditation, and physical exercise)
Incorporating yoga postures (asana), meditation (dhyana), and breathing exercises (pranayama) into daily routines can promote well-being, including liver health. These practices help reduce stress, improve blood circulation, and support the body’s natural healing processes. [4]
4. Herbal supplements
Ayurvedic herbs and products help protect and enhance liver function. Herbs like glycyrrhiza glabra (jasti madhu), bhumi amla (Phyllanthus niruri), Andrographis paniculata (kirata tikta), and curcuma longa (haridra) have hepatoprotective properties. They aid in reducing oxidative stress, promoting virus elimination, inhibiting fibrogenesis, and offering anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects, all of which contribute to liver health. [4]
Risks associated with the AST (SGOT) test [3]
- All the samples taken for the AST (SGOT) test are potentially positive for infections like HIV or Hepatitis B virus. Thus, the specimen should be handled very carefully.
- There is always a little risk involved when there is human intervention in any medical procedure. The person taking out blood samples should be experienced and certified to do so.
- The syringes used for plasma extraction should be clean and hygienic.
FAQs
1. What is the AST (SGOT) normal range?
The normal range for AST (SGOT or Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase) in blood tests is 14 to 20 units per liter (units/L) for men and 10 to 36 units/L for women. [2]
2. What is the normal range of AST ALT ratio?
The normal AST to ALT ratio is approximately <1, but it can vary slightly between individuals. [5]
3. Where is the AST Enzyme active in our body?
The human brain, liver, stomach mucosa, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and kidneys have all been found to have substantial activity in addition to the heart muscle, which is where the enzyme is most active.
Conclusion
The AST (SGOT) blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool in assessing liver health. Understanding the normal reference ranges for AST and its nuanced interpretation is essential for healthcare providers and patients. It is important to recognize that while AST is valuable, consider it with other clinical data, including ALT levels and medical history, for a comprehensive evaluation.
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle incorporating a wholesome diet, regular exercise, and stress-reduction practices like yoga can contribute to liver health. Furthermore, the judicious use of Ayurvedic herbal supplements may offer additional support. For personalized guidance, consult with Ayurvedic practitioners. Adopting these measures and staying informed about liver health will help you safeguard and ensure the longevity of this vital organ.
Disclaimer
The information provided here does not intend to replace professional advice or treatment.