Sugar is a common ingredient in our daily lives, finding its way into numerous recipes and beverages. However, when it comes to choosing between brown sugar and white sugar, many people find themselves pondering the differences and benefits of each. While sugar originates from the source, sugarcane or sugar beets, understanding what is brown sugar is crucial. Brown sugar is derived from the sap of palm plants such as aren (Arenga pinnata (Wurmb) Merrill), Kelapa (cocos nucivera), and siwalan (Borassus flabellifer L). They undergo different processing methods that result in distinct characteristics. [1] This article will try to understand the qualities, nutritional profiles, and potential health effects of brown sugar vs. white sugar. By understanding their differences, one can decide which type of sugar is best suited for their needs.
Processing Methods and Appearance
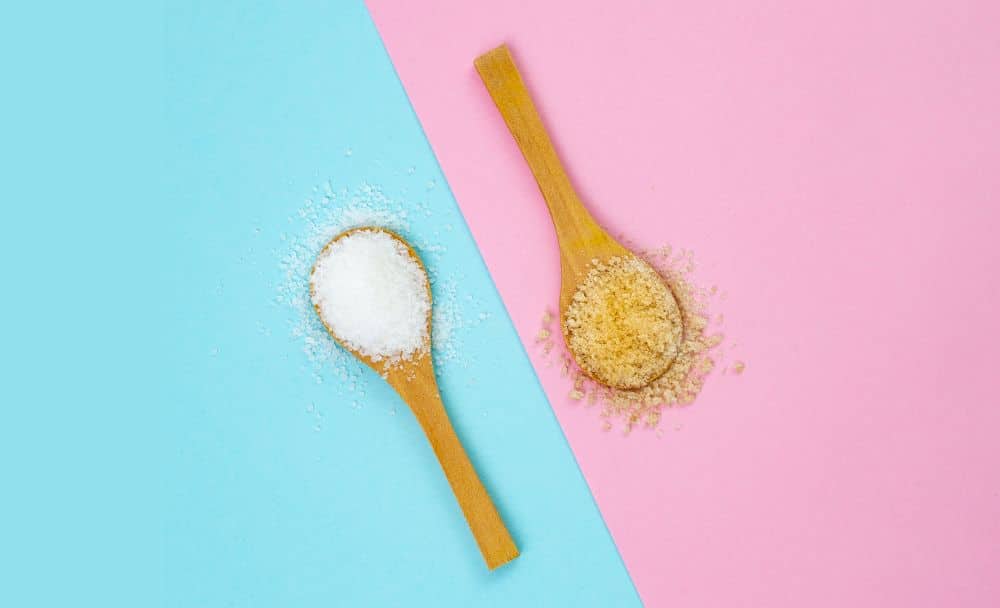
The primary distinction between brown sugar and white sugar lies in their processing methods. White sugar, also referred to as table sugar or granulated sugar, is produced by refining sugarcane or sugar beets to extract sucrose. The refining process involves several steps, including crushing cane stalks or extracting sliced sugar beets with hot water. The resulting solutions are clarified with lime, evaporated to thick syrups, followed by crystallization, after which sugar is recovered. The final syrup is obtained after exhaustive crystallization of sucrose, which leaves the result- a fine-grained, pure white crystal with a uniform texture. [3]
On the other hand, brown sugar is minimally refined and does not undergo a large number of chemical processes. Thus, consumers consider it a more natural substitute than white sugar. During the production of brown sugar, sugarcane juice undergoes minimal processing, leaving behind raw, moist, and dark sugar. Due to its minimum refining process and the absence of chemical products during its production, it can retain most of its iron, calcium, vitamin, and mineral content. The brown sugar can vary in color from light to dark brown and has a moist texture, which can be modified according to the differences in temperature and juice pH during the product processing. [2]
Flavor and Aroma
One key difference between brown sugar vs. white sugar lies in their flavor and aroma profiles. White sugar is known for its neutral taste, providing a sweet and pleasant experience without any distinct flavor. This makes it versatile and suitable for a wide range of culinary applications. [5]
On the other hand, brown sugar meaning refers to a more complex flavor profile. It has a strong caramel aroma largely from the sugarcane and from microbial metabolism and Maillard reaction. The flavor of brown sugar is affected by a variety of factors, such as sugarcane varieties, growing regions, processing methods, storage conditions, and others. The Flavor composition also varies based on the composition and concentration of odor compounds and nutrients in sugarcane from different producing areas. [4]
Nutritional Composition
White sugar chemical structure
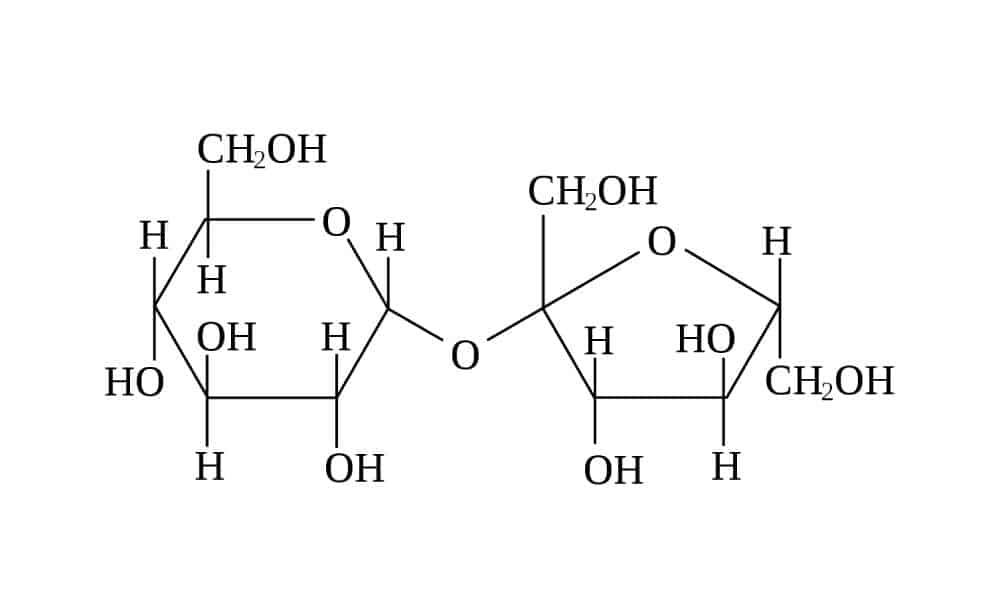
Brown sugar chemical structure
The nutritional compositions of white sugar and brown differ slightly. Brown sugar contains a slightly higher mineral content adding to the brown sugar benefits, while white sugar contains traces of vital minerals such as potassium, iron, calcium and magnesium, which are stripped away during the refining process for white sugar. However, the quantities of these minerals in brown sugar are not significant enough to provide substantial health benefits.
It’s important to note that the nutritional differences between brown sugar vs. white sugar are minimal, and their impact on overall health is limited. Both types of sugar are considered added sugars and provide empty calories, devoid of essential nutrients. Excessive consumption of added sugars, regardless of type, can affect the serum levels of BDNF and contribute to insulin resistance and body weight, among other associated diseases.
FAQs
- How are White sugar and brown sugar distinguished when it comes to culinary uses and baking applications?
Both brown sugar and white sugar have their own unique culinary applications. White sugar’s neutrality makes it a staple in many recipes, ranging from baked goods to beverages. It dissolves easily, making it ideal for sweetening coffee or tea. White sugar also plays a crucial role in the creaming method used in baking, helping to incorporate air into the mixture and create light, fluffy textures.
Brown sugar’s distinct flavor and moistness make it a popular choice for certain baked goods, such as cookies, cakes, and muffins. It adds depth and richness to recipes that benefit from a hint of caramel flavor. Brown sugar is also commonly used in recipes that call for a “crunchy” or “crumbly” texture, such as streusel toppings or caramelized coatings.
- How are brown and white sugars different in texture?
Brown sugar tends to be moister than in the brown sugar vs. white sugar comparison due to the residual molasses. Brown sugar benefits are enhanced due to the moisture in it, which can help retain moisture in baked goods, resulting in softer, chewier textures. On the other hand, white sugar’s dry and uniform texture lends itself well to recipes where a light and airy texture is desired, such as meringues or delicate pastries.
- What is the Ayurvedic view on intake of sugar?
It is said in Ayurveda that intake of brown sugar strengthens the body and pacifies Vata while increasing Pitta and Kapha. In the brown sugar vs. white sugar comparison, white sugar, on the other hand, is sweet in taste, heating, and has a stimulating impact on the body leading to an aggravation of all the doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha).
Conclusion
In the brown sugar vs. white sugar debate, the choice ultimately comes down to personal likes and preferences and the desired outcome in your culinary creations. To explain what is brown sugar it offers a more complex flavor and can provide a touch of caramel goodness to your recipes. On the other hand, white sugar’s versatility and neutral taste make it a go-to option for many culinary applications. From a nutritional standpoint, both sugars should be consumed in moderation, as they offer minimal health benefits and can contribute to various health issues when consumed excessively. Whether you opt for brown sugar or white sugar, being mindful of your overall sugar intake is important for maintaining a balanced and healthy diet.
Disclaimer: This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is not medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.