Eczema is a term commonly used for atopic dermatitis, an itchy skin condition affecting millions worldwide. It can manifest at any age but often begins in infancy or childhood. Eczema is characterized by chronic skin inflammation, leading to uncomfortable symptoms such as dry and itchy patches with a red, bumpy rash. [1] In the context of Ayurveda, the condition is known as “Vicharchika,” and the recommended approach for managing skin disorders is through the use of “Virechana,” which is considered the most effective treatment method. [5] In this write-up, we will delve into the signs and symptoms of eczema, exploring the various aspects of this condition and how to manage it effectively.
Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
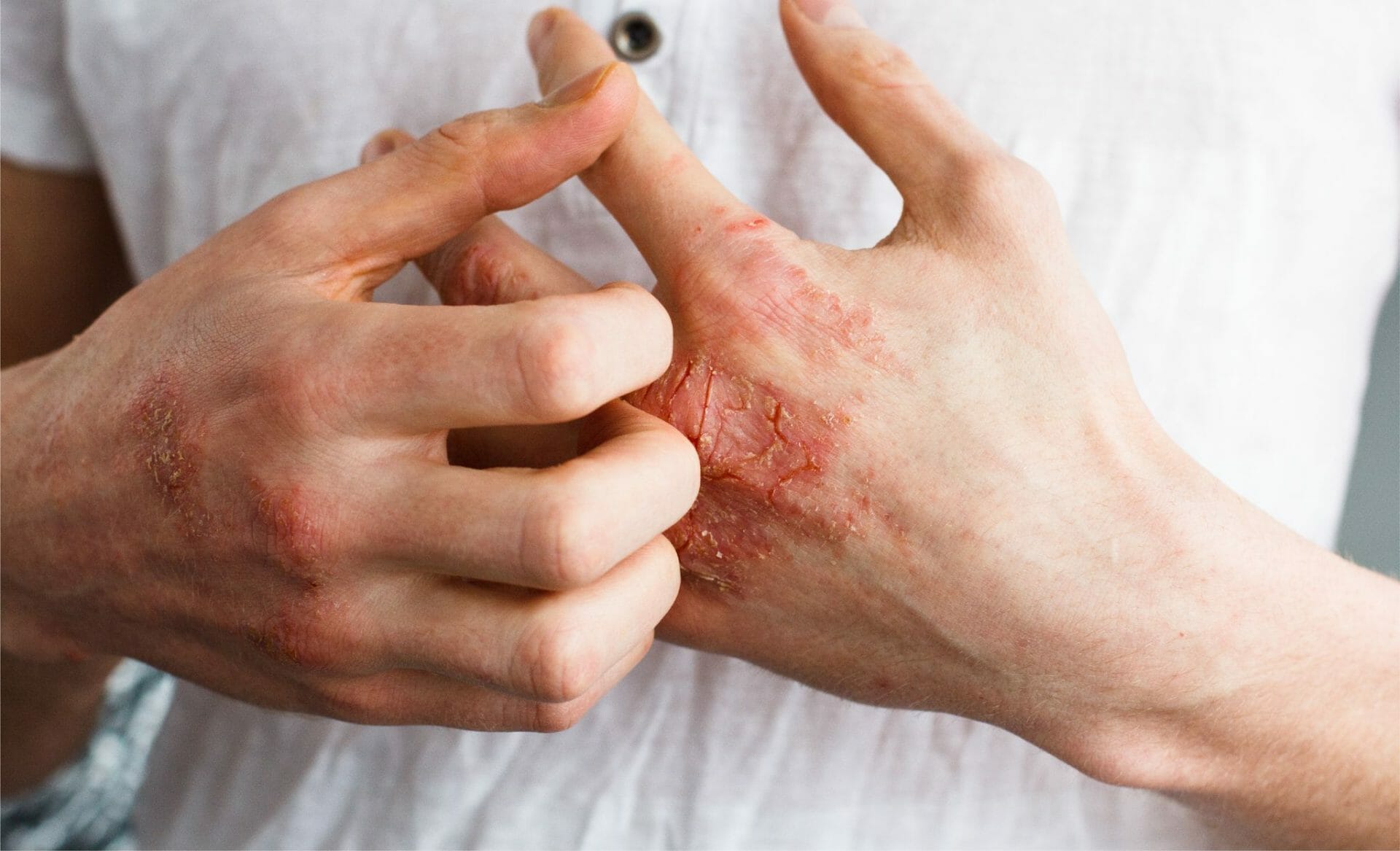
Eczema presents itself with recurring and persistent symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. Commonly, individuals experience dry, itchy skin accompanied by redness, blisters, or sores. The skin may become scaly, indicating extreme dryness with cracking and flaking. Eczema can manifest on any part of the body but often appears on the hands, feet, inner elbows, back of the knees, face, neck, and chest. The intense itching can lead to excessive scratching, resulting in thickened and rough skin. Eczema is a chronic condition, characterized by recurring episodes that can persist for extended periods. [1]
The most evident signs and symptoms of eczema include:
- Denne-Morgan lines (infraorbital skin creases): periorbital darkening, and circumoral pallor, along with symptoms of eczema like Keratosis pilaris, presenting as follicular keratotic papules and papulopustules on the arms and thighs. [2]
- Ichthyosis vulgaris: An autosomal dominant condition characterized by fine scaling, particularly prominent on the lower legs and buttocks are also symptoms of eczema. [2]
- Pityriasis alba: Appears as whitish, round, dry patches with fine scaling. [2]
- Puritic rash: These symptoms of eczema cause itching, the hallmark symptom of eczema. It can be intense and relentless, leading to scratching, which exacerbates the condition. [2]
- Vesicles: In infants, it can affect the entire skin surface except the nappy area and in some cases, symptoms of eczema can be tiny, fluid-filled blisters known as vesicles. [2]
- Red patches: In children, the face is frequently affected with patches of red or inflamed skin, which can be widespread or localized to specific areas. [2]
- Raised bumps: Adolescents commonly experience eczema in the flexures with rashes characterized by symptoms of eczema such as small, raised bumps or papules that may ooze, weep, or crust over when scratched. [2]
- Skin crack: In adults, preferential areas include the hands and nape along with skin crack, especially in areas prone to repeated bending or movement, such as the elbows or knees. [2]
- Erythma: Acute dermatitis is characterized by erythema, edema, vesiculation, oozing, and crusting. [2]
- Edema: The main microscopic features include acanthosis and variable intercellular edema, where the affected skin may become swollen due to inflammation. [2]
- Fissured skin: Chronic dermatitis manifests as leathery thickening of the skin, which becomes dry, scaly, and prone to fissures.[2]
- Orthokeratosis: Microscopy reveals compact orthokeratosis, acanthosis, and collagen arranged in vertical streaks within the papillary dermis. [2]
- Scaly patches: Subacute dermatitis presents with red or brown, scaly patches, and microscopy displays acanthosis and mild spongiosis. [2]
- Lymphocytic infiltrate: All forms of dermatitis and symptoms of eczema exhibit a variable density of lymphocytic infiltrate. [2]
Thickened Skin (Lichenification): chronic scratching can lead to the thickening and hardening of the skin, making it more susceptible to further irritation. [2]
FAQs
• What is the best Treatment of dry eczema, Treatment of facial eczema, Treatment of atopic eczema, Treatment of ear eczema, Treatment of eczema on the legs?
Agnideepaka Aushadhi (appetizer): These oral medications aid digestion and enhance the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. They also help break down and eliminate toxins (Aamapachana), thereby enhancing metabolic activity in the body.
Snehapana (drinking medicated ghee): This initial step involves consuming medicated ghee for a specific duration, usually 5-7 days. This helps eliminate toxins from the body and nourishes the body with essential fats. The process continues until you can take a burp without the smell of ghee and feel hungry.
Sarvang Abhanga (whole body oil massage): This massage is performed three days after Snehapana. It aims to bring toxins from the body’s peripheral regions (Shakha) to the central excretory channels (Koshtha).
Bashpa Swedana (sudation therapy): Sweating is induced to facilitate the elimination of waste and toxins from the body. You have to sit in a steam chamber immediately after the oil massage until they experience proper sweating.
Virechana (purgation): Purgative drugs are administered to induce controlled purgation. This process helps expel toxins from the body through the anal route. If you purge around 16 times, it is considered a moderate purgation.
Samsarjanakrama (post-procedure): After Virechana, a strict bland diet is followed for three days to allow for proper bowel functioning and recovery.
Wound Care: In cases of cellulitis with wounds, daily dressing is carried out using medicated decoction wash, specifically Panchavalkala Kwath Prakshalana. This decoction not only cleanses the wound but also supports the healing process.
This holistic approach in Ayurveda aims to address the condition’s root causes and promote overall well-being by balancing the body’s Doshas (energies) and eliminating toxins. [5]
• What are the symptoms of contact dermatitis?
Symptoms of irritant contact dermatitis may encompass sensations of burning, itching, stinging, soreness, and pain, especially during the initial stages of the condition. In contrast, allergic contact dermatitis is often characterized by a predominant symptom of pruritus or itching. [4]
• What is the best treatment of hand eczema?
Cow ghee is an excellent Ayurvedic ingredient to fight Eczema. Topical application of Ghee, known for its anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antibacterial properties, can relieve itching and skin dryness associated with hand eczema. [6] Combining Mustard Oil (Sarshapa taila) [7] or Coconut oil [8] with a paste of Turmeric [9] or Neem leaves [10] too may be applied topically to relieve eczema symptoms.
Conclusion
Eczema is a common skin condition showing symptoms like chronic inflammation, itching, and various other annoying skin symptoms. While it can be challenging to manage, with the right approach, many individuals with eczema can achieve relief and lead a fulfilling life. Understanding the basic signs and symptoms of eczema, and identifying triggers are crucial steps in effectively managing this condition. With proper care and management, individuals with eczema can experience periods of remission and improved skin health.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is not medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References:
- What Is Eczema?
- The diagnosis and management of atopic dermatitis
- Recent trends in treatment and prevention of eczema
- Contact Dermatitis
- A case discussion on eczema
- An Emerging Approach for Optimization of Cow Ghee as an Ointment Base in Combination With Selected Conventional Bases
- SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS TREATMENT WITH MUSTARD OIL: A CASE REPORT
- The beneficial properties of virgin coconut oil in management of atopic dermatitis
- Potential of Curcumin in Skin Disorders
- Neem in Dermatology: Shedding Light on the Traditional Panacea