This article is reviewed by an expert
Are you tired of experiencing excruciating pain and discomfort in your joints? Do you often find yourself wondering about the causes and remedies for gout?
If so, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of gout and its treatment in Ayurveda. Additionally, we will also uncover various home remedies for gout.
What Is Gout (1)?
Gout is a distressing condition that affects the joints. It is characterised by the deposition of urate crystals, causing inflammation and severe pain. This type of arthritis primarily targets the big toe, heel, ankle, and wrist, causing swelling and discomfort.
Types of Gout in Ayurveda & Their Symptoms (1)
According to Acharya Charaka, Vata Rakta, or gout, is categorised into two types: Uttana and Gambhira.
Uttana Vatarakta represents a superficial condition characterised by symptoms such as itching, burning, pain, pricking sensations, joint and skin discolouration as well as joint contraction.
On the other hand, Gambhira Vatarakta represents a deep-seated condition with symptoms including oedema, joint stiffness, hardened joints, pain deep within the body, burning sensations, and suppuration of the joints.
Causes and Pathogenesis of Gout (1)
Gout, or Vata Rakta in Ayurveda, arises from Vata and Rakta vitiation. Etiological factors disturb Rakta and aggravate Vata, creating a cycle of imbalance and Rakta Dushti, resulting in Vatarakta.
Modern science attributes gout to disrupted metabolism, renal issues, and high uric acid levels caused by diet, environment, and genetics. Purine becomes uric acid via xanthine oxidase. Improper metabolism and reduced renal function lead to uric acid deposition in joints, causing gouty arthritis. Purine-rich foods, alcohol, obesity, hypertension, and genetics contribute to gout. Uric acid crystal accumulation triggers gout symptoms.
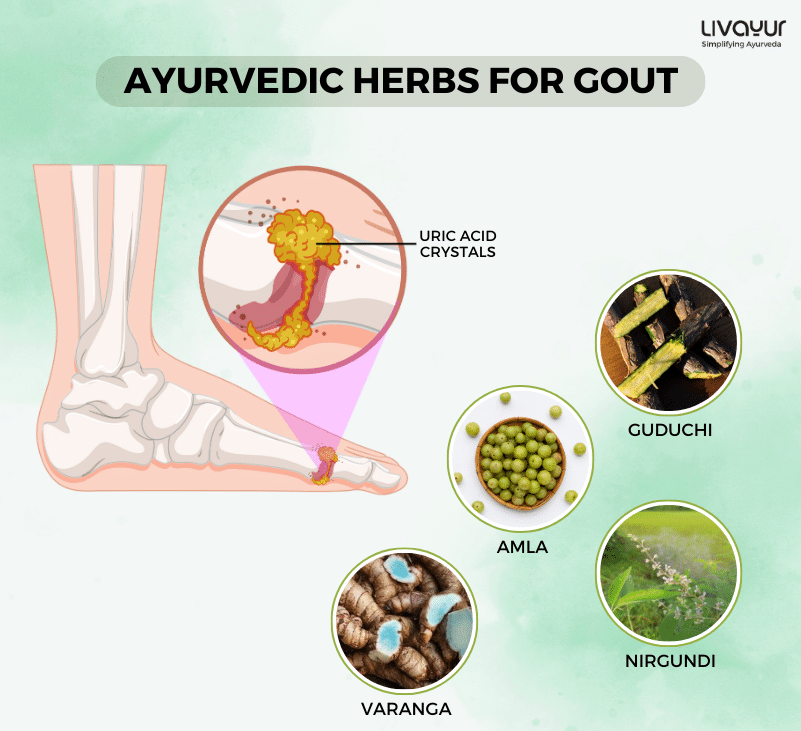
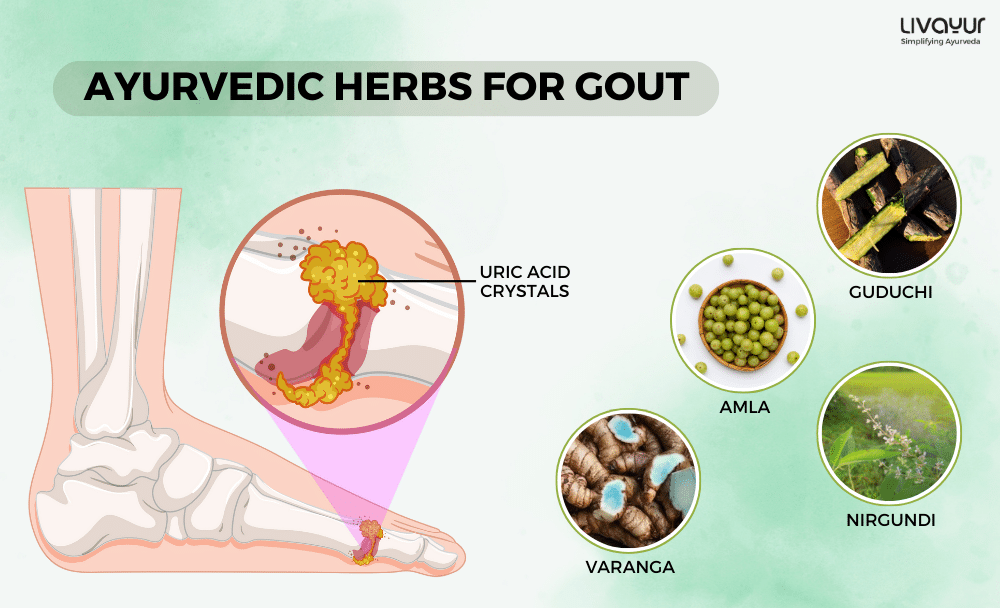
Ayurvedic Herbs for Gout (2)
Guduci (Tinospora cordifolia)
Guduchi extracts have demonstrated uricosuric activity, lowering serum uric acid levels. This herb also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, reducing joint swelling. It may be useful in the management of gout and other inflammatory conditions.
Amalaki (Phyllanthus emblica)
Aqueous and alcoholic extracts of Amalaki fruits have shown significant antigout activity. They reduce uric acid and XO enzyme levels and improve kidney function. Additionally, Amalaki exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, further aiding in gout management.
Vidanga (Cinnamomum cassia)
Cassia oil derived from Cinnamomum cassia has been found to possess hypouricemic actions. It decreases urate levels and inhibits xanthine oxidase activity. Cinnamon, including its components like cinnamic aldehyde, is also beneficial for age-related inflammatory conditions.
Nirgundi (Vitex negundo L.)
The leaves, roots, and seeds of Nirgundi have been used in Ayurveda for their Rucapaha (relieves pain), Sothahara (anti-inflammatory), and Amahara (digestive) properties. Studies have shown that the various fractions of Vitex negundo possess antioxidant activity, reduce serum urate levels, and inhibit xanthine oxidase. These properties make it beneficial for gout treatment.
Haritaki (Terminalia chebula. Retz.) and Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellerica (Gaertn.) Roxb.)
These two herbs have been extensively studied for their effects on reducing serum uric acid levels. Clinical trials have shown that both Haritaki and Bibhitaki extracts lead to a significant reduction in serum uric acid levels, making them effective in treating hyperuricemia.

Ayurvedic Therapies for Gout (3)
Ayurveda offers a range of therapeutic approaches for the treatment of gout, focusing on balancing the doshas and promoting overall well-being. The treatment protocol typically begins with Snehana, which involves internal and external oleation to prepare the body for detoxification. Following this, Virechana, a gentle purgation therapy, is recommended using either Sneha Dravyas (oily substances) or Ruksha Virechana (dry purgation). Niruha and Anuvasana Basti (enema) are also advised regularly to cleanse the body.
In cases of Uttana or Ubhayasrita Vatarakta, a combination of therapies is utilised. These include Seka (affusion), Abhyanaga (massage), Pradeha (application of thick ointments), as well as specific dietary modifications and the use of unctuous substances that do not cause a burning sensation.
Some more therapies used in the treatment of gout include:
Rakta-Mokshana
Rakta-Mokshana, or bloodletting therapy, is considered an important treatment for chronic Vatarakta. Prior to Rakta-Mokshana, preparatory measures such as Snehana, Mridu Virechana, and Basti are undertaken. Rakta-Mokshana can be performed using various methods such as Shringa, Jalouka (leech therapy), Suchi (needle therapy), Alabu (cupping), Pracchana (scarification), or Siravedhana (venesection), based on the Dosha imbalance and individual constitution.
Basti
Basti, or enema therapy, is particularly effective for the Vata Pradhana type of Vatarakta. It is considered the treatment of choice for conditions involving symptoms like Basti Shoola (pain in the bladder), Vankshana Shoola (pain in the waist), and Udara Shoola (abdominal pain). Basti is administered using specific oils such as Sukumara Taila, Amritadi Taila, or Pinda Taila.
Bahi Parimarjana Chikitsa
Additional treatments include Bahi Parimarjana Chikitsa, which involves therapies like Avagahana (immersion), Lepa (application of medicinal pastes), and Abhyanga (therapeutic massage). These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and restore balance in Uttana Vatarakta.
Home Remedies for Gout
- Consume nourishing foods such as nuts, vegetables, and fruits while avoiding sour, salty, and pungent foods (1).
- Stay away from carbonated drinks, junk food, alcohol, sugar, and purine-rich foods to prevent gout flare-ups (1).
- Avoid activities that cause mental and physical stress, and be mindful not to exert excessive pressure on the joints. Opt for mild to moderate exercise that induces sweating and helps reduce uric acid levels (1).
- Practice Yoga to relieve Vata, reduce stress and manage gout (1).
- Maintain a healthy weight and steer clear of a sedentary lifestyle (1).
- Add fresh ginger to daily meals or consume ginger water. Ginger is packed with anti-inflammatory properties that can help treat gout effectively (4).
- Drink freshly squeezed lemonade daily to balance uric acid levels and relieve gout pain and swelling (4).
- Soak the affected body part in warm water with Epsom salt to provide instant pain relief, reduce swelling, and prevent gout attacks (4).
- Consume apple cider vinegar mixed with water to help relieve gout pain and inflammation (4).
The Takeaway
Gout is a distressing condition that affects the joints, causing inflammation and severe pain. Ayurveda offers various treatments and therapies to manage gout, focusing on balancing doshas and promoting overall well-being.
Ayurvedic herbs like Guduci, Amalaki, Varanga, Nirgundi, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki have shown efficacy in reducing uric acid levels and alleviating gout symptoms.
Additionally, Ayurvedic therapies such as Snehana, Virechana, Basti, and Rakta-Mokshana can help in detoxification and managing gout.
Alongside these treatments, incorporating home remedies like consuming nourishing foods, practising Yoga, and using natural remedies like ginger, lemonade, Epsom salt, and apple cider vinegar can further aid in gout treatment.
FAQs
What is gout, and how does it affect the joints?
Gout is a condition characterised by the deposition of urate crystals, causing inflammation and severe pain in joints like the big toe, heel, ankle, and wrist.
2. How can Ayurvedic herbs help manage gout?
Ayurvedic herbs like Guduci, Amalaki, Varanga, Nirgundi, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki have demonstrated uric acid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects, making them beneficial in managing gout.
3. What Ayurvedic therapies are recommended for gout treatment?
Ayurveda offers therapies like Snehana, Virechana, Basti, and Rakta-Mokshana to manage gout by balancing Doshas and promoting detoxification. These therapies help alleviate symptoms and restore balance in the body.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.