Bell’s palsy is a condition characterized by sudden muscular weakness or paralysis in the face, usually affecting one side of the face. It occurs due to inflammation and compression of the facial nerve, referred to as the seventh cranial nerve. This nerve controls the muscles responsible for facial expressions, tears, and saliva production. The exact cause of Bell’s palsy is not fully understood, but it is more common in patients with diabetes mellitus and in pregnant females. [1]
According to Ayurveda, Bell’s palsy, or Ardita, also known as Ekayaam is described as a condition wherein the body is primarily affected on one side of the face. Aacharya Arunadatta has clarified that Ardita is caused by an excessive aggravation of the Vata dosha, leading to facial distortion. [4]
This article will delve into Bell’s palsy treatment and prevention strategies for Bell’s palsy. Understanding these aspects is crucial to ensure timely and effective management of the condition and potentially reduce the risk of recurrence.
Treatment Options for Bell’s Palsy
Bell’s palsy treatment primarily aims to reduce inflammation, promote nerve regeneration, and restore normal facial function. Here are the common Bell’s palsy treatment guidelines:
Ayurvedic management:
- Sarvang abhyanga and Mukhabhyanga with Masha taila (Whole body and facial massage with black gram oil):
Black gram oil possesses Vata-Kapha pacifying properties and is an effective Bell’s palsy Ayurvedic treatment for aggravated Vata. Massaging with it, along with sudation, helps to loosen the adhesive doshas, making the subsequent treatment more effective. [4]
- Ksheerbala oil:
Using this oil for massage or Bell’s palsy physiotherapy treatment nourishes the Shleshaka Kapha and stimulates sensory nerve endings, strengthening facial muscles. [4]
- Ksheer Dhomma Swedana (medicated milk steam):
This Bell’s palsy treatment liquefies deranged Doshas and facilitates their expulsion through subsequent Panchakarma procedures.
- Maharasnadi Kashaya:
This Bell’s palsy treatment has a calming effect on Vata and regulates its flow within the body. When taken orally, Ekangaveera Rasa acts as an anabolic agent, revitalizes the body, and acts as a detoxifier. This contributes to improving the speed of recovery in patients with Bell’s palsy.
- Errhine therapy or Nasya Karma with panchedriyewardhana oil:
The oil used primarily pacifies Vata, particularly Vyana, which can alleviate Vata obstruction. The hampered blinking function of the eyelids, caused by the erratic nature of aggravated Vata, is relieved by the stabilizing properties of the oil. The Bell’s palsy treatment may be attributed to a reduced inflammatory response.
- Other therapies:
Moordha Taila (application of this oil to the head), Tarpana (Libation) with medicated oil to the eyes and ears, Nadi Sweda (Tubal sudation), Upanaha Sweda (application of poultice) are also considered the treatment principle of Ardita. [4]
Corticosteroids:
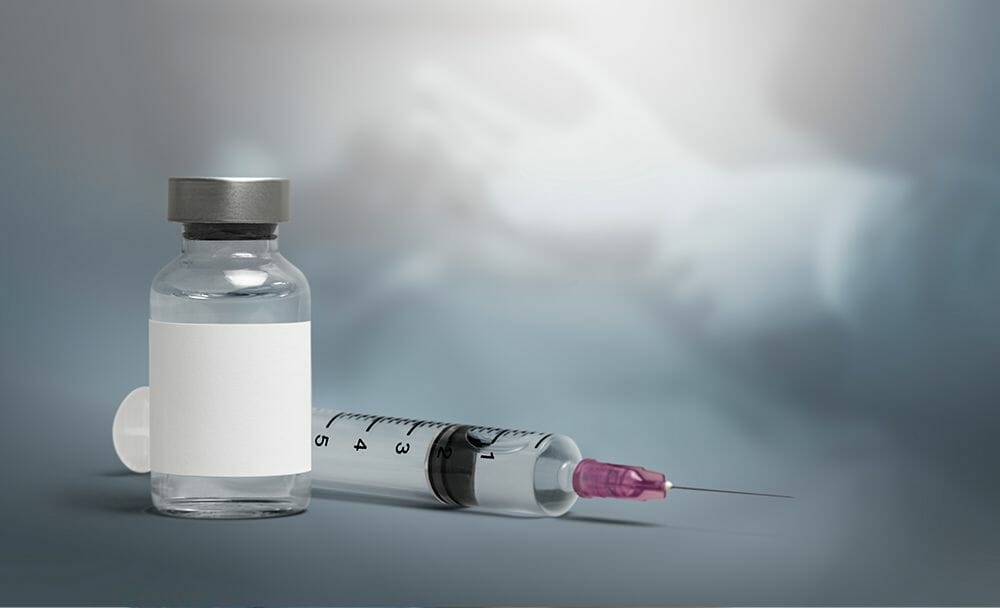
Corticosteroids, like prednisone, are often prescribed to the patient to bring down the inflammation and swelling around the facial nerve. These medications are typically most effective when administered within the first 72 hours of symptom onset. [2]
Antiviral Medications:
Sometimes antiviral medications may be prescribed along with corticosteroids for Bell’s palsy treatment. The goal is to improve the chances of complete recovery, especially for patients with severe facial nerve palsy (House-Brackmann IV or greater). [1]
Bell’s palsy eye treatment:
Bell’s palsy can affect the ability to close the eye on the affected side, leading to potential corneal abrasions and dryness. To prevent this, artificial tears and eye patches can be used to shield the eye and maintain proper lubrication. [1]
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy and Bell’s palsy treatment exercises are necessary to prevent muscle atrophy and maintain muscle tone. Techniques such as facial exercises, massage, mime play, acupuncture, and electrical stimulation can help improve facial muscle strength and mobility. [3]
Biofeedback:
Biofeedback techniques can be employed to aid patients in controlling their facial muscles and improving their ability to make voluntary facial movements. [3]
Surgery:
In rare cases where facial nerve compression is caused by bony abnormalities or tumors, surgical intervention may be considered to relieve pressure on the nerve. [1]
FAQs
• What are the best preventive measures for Bell’s Palsy?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent Bell’s palsy, some measures can be adopted to lessen the risk, complications or severity of the condition. These strategies are particularly relevant for individuals who may be at a higher risk or have experienced Bell’s palsy in the past:
Vaccination against certain viruses, such as the varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox) and influenza, can reduce the risk of developing viral infections that may trigger Bell’s palsy.
Practicing good hand hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can help reduce the transmission of viruses that could cause Bell’s palsy.
Chronic stress has been associated with weakened immune function, which may increase susceptibility to viral infections. Managing stress and tension through relaxation techniques, exercise, and mindfulness can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk of Bell’s palsy.
Eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and getting enough sleep can support a robust immune system and general well-being.
Some studies suggest that exposure to cold temperatures may accelerate the risk of developing Bell’s palsy, especially in individuals already susceptible to the condition. Therefore, staying warm during colder weather may be advisable.
• What is Bell’s palsy during pregnancy treatment?
The most suitable approach for managing the condition is still uncertain and often limited to supportive care. The use of corticosteroids during pregnancy is a matter of debate.
• How can Bell’s palsy recovery be expedited?
Taking oral steroids or antiviral medication within the first few days of onset can increase the likelihood of a complete recovery.
Conclusion
Bell’s palsy is a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life and peace of mind due to the temporary facial paralysis it causes. Timely and appropriate treatment is crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes. Corticosteroids and antiviral medications are the mainstays of Bell’s palsy treatment, and Ayurvedic therapies also play a vital role in rehabilitation.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective only and is not a piece of medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References: