Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a vital nutrient that aids in several bodily functions. It plays an important part in helping your nervous system function in top shape and in the DNA synthesis. However, some individuals may experience a deficiency of this vitamin, which can lead to a range of symptoms and complications such as macrocytic anemia, and it has also been connected with a spectrum of neuropsychiatric disorders. [1] In this article, we will learn about the various causes, symptoms, complications, and treatment options associated with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can manifest in various ways, and the vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms can vary from person to person. Some B12 deficiency signs and symptoms include:
Fatigue and weakness:
Feeling excessively tired and lacking energy is a common symptom of B12 deficiency. This occurs because B12 is very much needed for red blood cell (RBC)production, and RBC transports oxygen throughout your body. [4]
Neurological problems:
Vitamin B12 is crucial for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Deficiency can lead to symptoms such as numbness or tingling sensation in the hands and feet, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, memory problems, and mood changes. [5]
Digestive issues:
Some individuals with Vitamin B12 deficiency may experience digestive problems such as diarrhea. [5]
Poor appetite:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can result in a loss of appetite and unintended weight loss. [5]
Sore tongue:
Inflammation of the tongue is another common symptom. The tongue may appear swollen, sore, or red. [5]
Mouth ulcers:
Painful ulcers can develop inside the mouth due to Vitamin B12 deficiency. [5]
Other symptoms:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause rapid breathing or shortness of breath, headaches, palpitations, and problems with your vision. [5]
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Several factors can contribute to the development of Vitamin B12 deficiency but they can be broadly distinguished into three categories, nutritional deficiency, malabsorption syndromes, and other gastrointestinal causes. [1] The most common vitamin b12 deficiency causes include:
Inadequate dietary intake:
Certain animal-derived food stuffs such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy naturally contain an adequate amount of Vitamin B12. Vegetarians and vegans who do not consume these foods are at a higher risk of B12 deficiency if they do not obtain the vitamin from other sources, such as Vitamin B12 supplements and fortified foods. [1]
Malabsorption:
Some physiological conditions can interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12 from the food you eat. Examples include pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition that affects the stomach’s ability to produce intrinsic factor, a protein necessary for B12 absorption, and gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease. [1]
Aging:

As individuals age, the ability to absorb vitamin B12 decreases because of the high prevalence of atrophic gastritis–associated food-cobalamin malabsorption, and the increasing prevalence of pernicious anemia with advancing age. This can eventually lead to a higher prevalence of B12 deficiency among older adults. [2]
Certain medications:
Long-term use of certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and anticonvulsants can interfere with B12 absorption. [3]
Other factors:
Other factors such as chronic alcoholism, certain inherited disorders, HIV infection, pancreatic disease, and intestinal diseases can cause Vitamin B12 deficiency. [1]
Complications of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
If left untreated, Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to various complications, including:
Risk of gastric cancer:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can emanate the risk of gastric cancer. [4]
Neurological problems:
Prolonged Vitamin B12 deficiency can result in irreversible neurological deficits and damage. [4]
Autoimmune disorder:
The risk of developing an autoimmune disorder like type 1 diabetes, myasthenia gravis, Hashimoto disease, or rheumatoid arthritis also increases. [4]
Cardiovascular complications:
Vitamin B12 deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke. [4]
Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
The vitamin b12 deficiency treatment usually involves addressing the underlying cause and replenishing the body’s B12 stores. Treatment options include:
Dietary changes:

Start eating foods rich in vitamin B12, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. This can help correct a mild deficiency. For individuals who are vegetarians or vegans, fortified foods or B12 supplements may be necessary as a step towards vitamin b12 deficiency self care. [5]
B12 supplements:
Oral B12 supplements are commonly prescribed to correct the deficiency, especially in cases of a strict vegan diet. In severe cases or when malabsorption is present, B12 injections may be necessary to bypass the digestive system and ensure adequate absorption. [4]
Addressing underlying conditions:
If B12 deficiency is caused by an underlying vitamin b12 deficiency diseases such as anemia treating the underlying condition by including good sources of folate such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and asparagus can help alleviate the deficiency. [5]
Regular monitoring of B12 levels
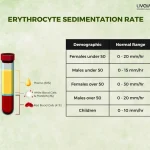
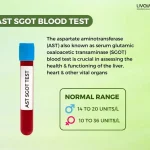
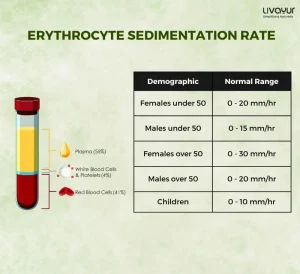
Regular monitoring of B12 levels through blood tests is crucial to assess treatment effectiveness and ensure adequate supplementation. [5]
FAQs
1. What is the best treatment for Vitamin B12 deficiency in Ayurveda?
Dietary Modifications:
Ayurveda emphasizes a balanced diet to maintain optimal health. Incorporate foods rich in vitamin B12 into your diet, such as dairy products, eggs, fish, and meat. However, if you consume a vegetarian or vegan diet, Ayurveda suggests alternative sources such as fermented foods (like idli and dosa), spirulina, and certain seaweeds.
Herbal Supplements:
Ayurvedic herbs can be used as supportive measures to enhance overall health and digestion. Some herbs that are traditionally used to support nutrient absorption and digestion include triphala, brahmi, ginger, and fennel. These herbs may help improve digestion and assimilation of nutrients, indirectly supporting vitamin B12 absorption and act as vitamin b12 deficiency medication.
Panchakarma:
Panchakarma is a therapeutic cleansing process in Ayurveda that aims to remove toxins from the body and restore balance. This process includes various therapies such as oil massages (abhyanga), herbal steam treatments (swedana), and nasal administration of oils (nasya). Panchakarma can help improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and promote overall health, which indirectly supports the body’s ability to utilize vitamin B12.
2. How to raise the Vitamin B12 levels fast?
You can boost the amount of vitamin B12 in your diet by eating more animal products, like meat, seafood, dairy, and eggs. You can also include fortified breakfast cereals which are a great way to get more B12.
3. Which foods are the best Vitamin B12 sources?
Foods such as beef liver, clams, and salmon, are great sources of Vitamin B12.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, neurological problems, pale skin, and digestive issues. It can result from inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption, aging, or certain medications. If left untreated, B12 deficiency in the body can lead to complications such as vitamin b12 deficiency anemia and neurological damage. Treatment typically involves dietary changes, B12 supplementation, and addressing underlying causes. In this article, we have explored the reasons for vitamin b12 deficiency, symptoms, and treatment options to help you out if you ever suspect you have a vitamin B12 deficiency.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is not medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.