Thyroid disorders are common medical conditions that affect millions of people worldwide, with females being more prone to these issues than males. The highest incidence of thyroid in female occurs during the reproductive years and decreases progressively as the Thyroid patient ages.
The increased susceptibility of females to autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD) can be attributed significantly to the influence of female gonadal hormones and X chromosome inactivation on the thyroid gland and immune system. When the thyroid gland malfunctions, it can lead to a range of thyroid disorders, such as AITD, thyroid goiter, nodule and cancer. [1]
In Ayurveda, the condition of having a swollen thyroid gland is called Galganda. It may produce symptoms like shwasaKashthta (breathlessness), Twak rukshata (Dry skin), smriti alpata (poor memory), Drubalya (Weakness), kesh patana (hair loss). [11] The woman’s menstrual cycle [12] and chances of conception may be affected due to Thyroid disorders.
This article will delve into the Causes of Thyroid in female, exploring genetic and environmental factors contributing to their development.
What are the Causes of Thyroid in Women According to Experts
1. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a prevalent thyroid disorder characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, which produces insufficient thyroid hormones. This condition can have a significant impact on a woman’s overall health and quality of life. The Causes of Thyroid in females can be categorized into several factors, including:
You can also check one of our related posts on – what to eat and avoid in Hypothyroidism
A. Ahar
Having an improper and irregular diet which may include consumption of chicken or Matsya Sevan 3 times in week, Dadhi twice in week, biscuit daily with milk, Dosa, idal, sandwich daily, daily empty stomach water 4-5 glasses per day.
B. Vihar
This may include prolonged seating, Ratri jagran, excessive sex/ masturbation.
C. Manasika nidan:
Here the causes could be Chinta as Vegavrodha causes Vata Vrudhi.
D. Sanprapti Ghatak
This is caused by Dosh of Vata-Kapha, Dushya of Rasa, Rakta, Shukra.
E. Vikalpa Samprapti
Here the Vata Dosha – Sheeta Guna and Kapha Dosha- Manda, Sheeta, Guru are responsible.
F. Samprapti
All hetus in this case are mainly Vata and Kapha Prakopak. Due to hetu-sevan aamuttpatti occurs which causes agnimandya and constipation. Due to hetues first aahar-rasa converts into Aam, which makes vikrut rasa dhatu.
All this further disturbs and produces vikrut dhatu-uttpatti. Excessive sex and masturbation cause direct acts on shukra dhatu and show its symptoms. It also does dhatu kshaya via pratilom gati. [7]
G. Autoimmune Thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s Disease)
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in women. It is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the thyroid gland. Over time, this leads to a gradual decline in thyroid function and is one of the main Causes of Thyroid in females. [2]
H. Ama
In Ayurveda, it is believed that when there is a decline in the proper functioning of Jatharagni and Dhatvagni, which correspond to digestion and metabolism, it results in the accumulation of Ama, which can be likened to advanced glycation end products (AGEP) and other harmful toxins.
Ama, or AGEP, disrupts the normal functioning of the thyroid gland by interacting with thyroid receptors, leading to the malfunction of the thyroid gland and one of the primary Causes of Thyroid in females. [6]
- Vata and Pitta Problems
Hypothyroidism in females can be categorized into five classifications based on its etiology: Vata, Pitta, Kapha, urinary tract infections, and the “goiter” type, characterized by noticeable swelling of the thyroid gland in the neck region.
The “goiter” type is often considered an advanced stage of Kapha-induced hypothyroidism. Improper digestion of food is considered a common underlying factor in all dosha-induced hypothyroidism.
Each dosha-induced hypothyroidism type has its unique characteristics:
Vata-Induced Hypothyroidism: This type has both psychological components, such as mental agitation and stress, and physical components, like excessive physical activity.
Pitta-Induced Hypothyroidism: Hyperthyroidism is predominantly attributed to Pitta dosha.
This classification system helps in understanding the diverse factors contributing to hypothyroidism, from Dosha imbalances to specific causes like urinary tract infections, with the goiter type representing an advanced stage of Kapha-induced hypothyroidism. [8]
Check your Doshas here for free
2. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism; it results from an overactive thyroid gland that produces excessive thyroid hormones. It is attributed to pita only [9] and the condition can be likened to Atyagni, Tikshnagni, or Bhasmaka Roga. [5] Common Causes of Thyroid in female include:
A. Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excessive hormones. It is among the most common Causes of Thyroid in female. [3]
B. Ayurvedic causative factors
These include weak agni, doshaprakopa, Apathyasevana, Chirkaliaushadsevan, Addiction Dushtambu and krimidosha, and Himvataprabhav. [9] Two thyroid hormones, Tri-iodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4), function in the body similar to the Pitta dosha.
Therefore, Bhasmaka Roga can be associated with the lifestyle disorder known as Hyperthyroidism. In this condition, there is an excessive Agni (digestive fire) resembling Atyagni or Tikshnagni, which leads to rapid food digestion and subsequently the consumption of bodily tissues (Dhatu). [5]
3. Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps or growths that can develop within the thyroid gland. While most thyroid nodules are benign, they can cause various thyroid disorders and complications in females. The causes of thyroid nodules include:
A. Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency can lead to the development of thyroid nodules and is one of the main Causes of Thyroid in female. [4]
B. Galaganda
According to Ayurvedic text (Madhav Nidan), Galaganda is characterized by a firm, protruding, and immovable swelling in the neck area. It is also referred to as Ekang Shotha.
Ayurvedic diagnosis categorizes it as Kaphaj Galaganda. One significant observation is that chronic Agnimandya (digestive weakness) and DhatvAgnimandya (tissue metabolism impairment) play a crucial role in the development of Galaganda.
These weaknesses lead to an unhealthy replenishment of Dhatus (bodily tissues), rendering them susceptible to various other health conditions. This susceptibility is reflected in symptoms such as general weakness, lower back pain (Katishula), and chronic rhinitis (Jeerna Pratishyay). [10]
4. Environment and lifestyle
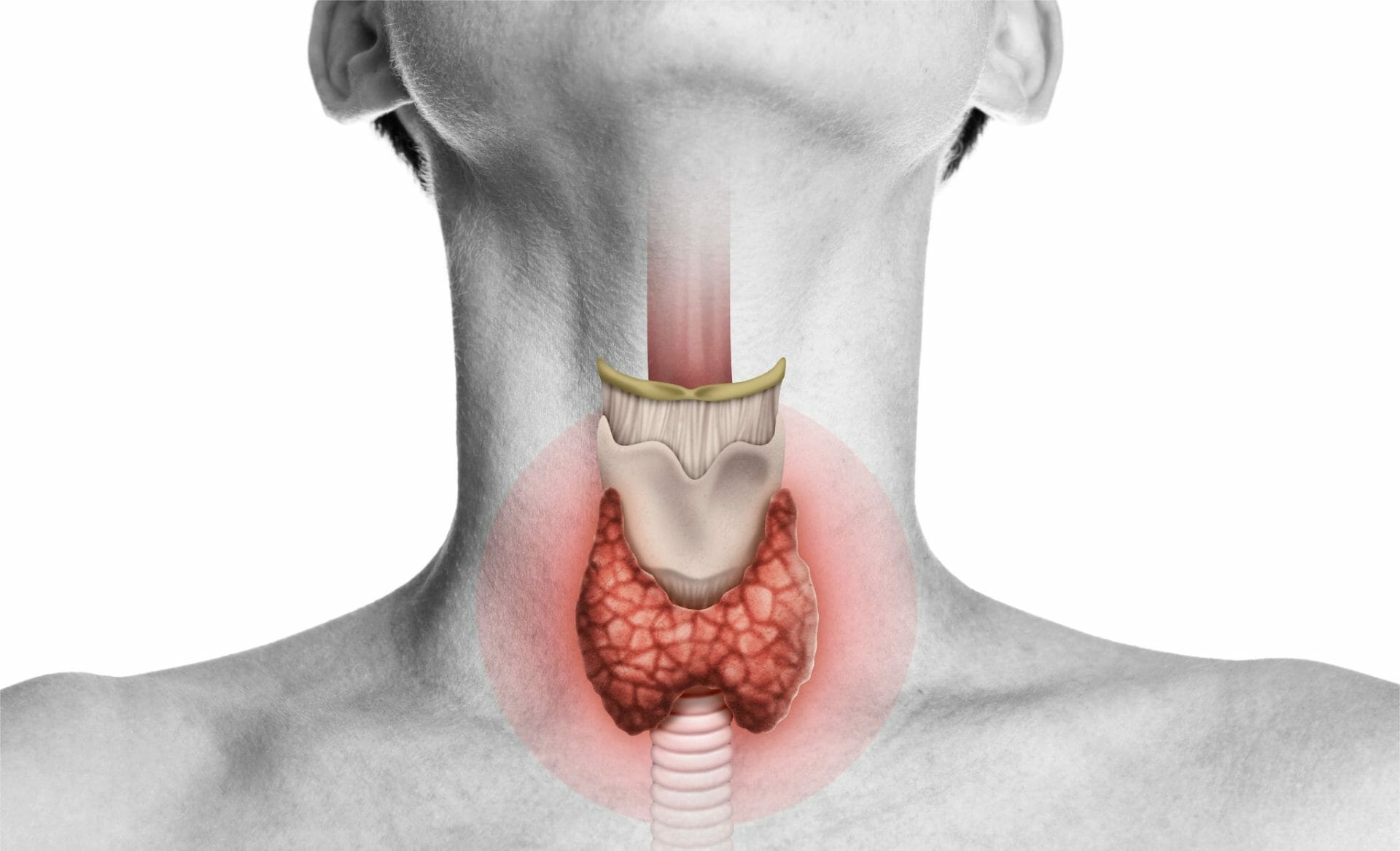
Adhyasana (eating before complete digestion of a previous meal) and Avyayama (a sedentary lifestyle), disrupt the balance of Medavaha Srotasa and Rasavaha Srotasa, which are the microscopic channels responsible for transporting digested food and lipid substances in the body.
This disruption also affects Agni, which is responsible for digestion and metabolism. Consequently, these factors interfere with the normal functioning of the thyroid gland by interacting with thyroid receptors, becoming the Causes of Thyroid in females.
These causative factors also disturb the equilibrium of the three body humors, Vata, Pitta, and Kapha, with Kapha being particularly dominant due to its inherent qualities.
The vitiation of Rasa Dhatu, which encompasses the nutritive substances assimilated in the body, and Meda Dhatu, encompassing adipose tissues and fat contents, results from these causative factors. This imbalance leads to an abnormal supply of nutrients to the thyroid gland and the irregular distribution of fat throughout the body. [6]
FAQs
• Which Dosha is mainly among the Causes of Thyroid in females?
In Ayurveda, it is the imbalance of Pitta Dosha that is primarily associated with thyroid problems. To illustrate, the thyroid gland’s metabolic functions are closely linked to Agni, which represents the fire element and is regulated by Pitta Dosha.
• Which is the chakra that is blocked in the thyroid?
In the context of the body’s energy centers, or chakras, it is the Vishuddha Chakra that resides at the throat area and is intricately linked to the thyroid gland. This chakra governs various aspects, including communication and self-expression, and it plays a significant role in thyroid-related functions, which encompass mental and physical development as well as metabolic regulation.
• Which foods should be avoided in case of thyroid problems?
A person managing hyperthyroidism should be cautious about consuming foods rich in iodine. Limit or avoid iodine-rich foods such as Iodized salt, fish and shellfish, seaweed or kelp, dairy products, iodine supplements, and food items containing red dye among others.
You can also check – Foods to avoid for thyroid patient
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are prevalent in females, affecting their overall health and well-being. While both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of these disorders, women must be aware of their risk factors and Causes of Thyroid in females and seek medical evaluation if they experience symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help mitigate the impact of thyroid disorders on women’s lives and ensure their continued health and vitality.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective and is not medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References
- Thyroid disorders in women
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Review of Factors Contributing to Nodular Goiter and Thyroid Carcinoma
- Review of Hyperthyroidism as per Ayurveda
- Ayurvedic Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
- A Successful Case Study on Ayurvedic Management of Hypothyrodism
- Effective Ayurveda therapy to treat thyroid disorders
- Effective Ayurveda Therapy To Treat : Thyroid Disorders
- Ayurvedic Management of Nontoxic Nodular Goitre with Haemorrhagic Nodules, Calcification and Atypia – A Case Report
- A Successful Case Study on Ayurvedic Management of Hypothyrodism
- Thyroid hormones and menstrual cycle function in a longitudinal cohort of premenopausal women