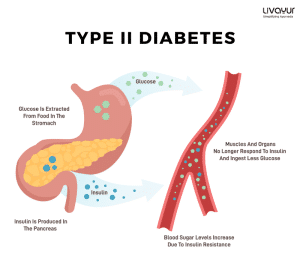
In Ayurveda, dietary choices are significant in managing various health conditions. Among these, diabetes mellitus is a prominent concern in contemporary times, characterized by impaired blood sugar regulation.
While Ayurveda has long advocated for the intrinsic relationship between food and well-being, it prompts us to explore the multifaceted benefits and potential considerations of incorporating watermelon, a widely enjoyed fruit, into the diet of individuals grappling with diabetes.
This article looks at the Ayurvedic perspective on watermelon’s suitability for people with diabetes, offering comprehensive insights to assist those seeking a harmonious balance between health and indulgence.
Watermelon and its sugar content
Watermelon, a delectable summer fruit renowned for its hydrating properties and vibrant sweetness, contains natural sugars that have the potential to influence blood sugar levels. However, the extent of this impact depends on the quantity of watermelon consumed.
To put it into perspective, one cup (equivalent to approximately 152 grams) of diced watermelon contains about 9.42 grams of natural sugar along with 11.5 grams of carbohydrates. While these sugars are natural and differ from the refined sugars often found in processed foods, they can still contribute to fluctuations in blood glucose levels when consumed in excess.
For individuals with diabetes, careful portion control is critical when including watermelon in their dietary regimen. A small serving of watermelon can be a nutritious addition to a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients and hydration. Additionally, consuming moderate amounts of watermelon can satisfy the craving for something sweet while promoting a sense of fullness, thus potentially reducing the temptation to reach for less healthy, high-sugar alternatives.
In this way, mindful consumption of watermelon can be a flavorful and satisfying addition to the diet of those managing diabetes, provided it follows recommended portion sizes and overall carbohydrate intake. [1]
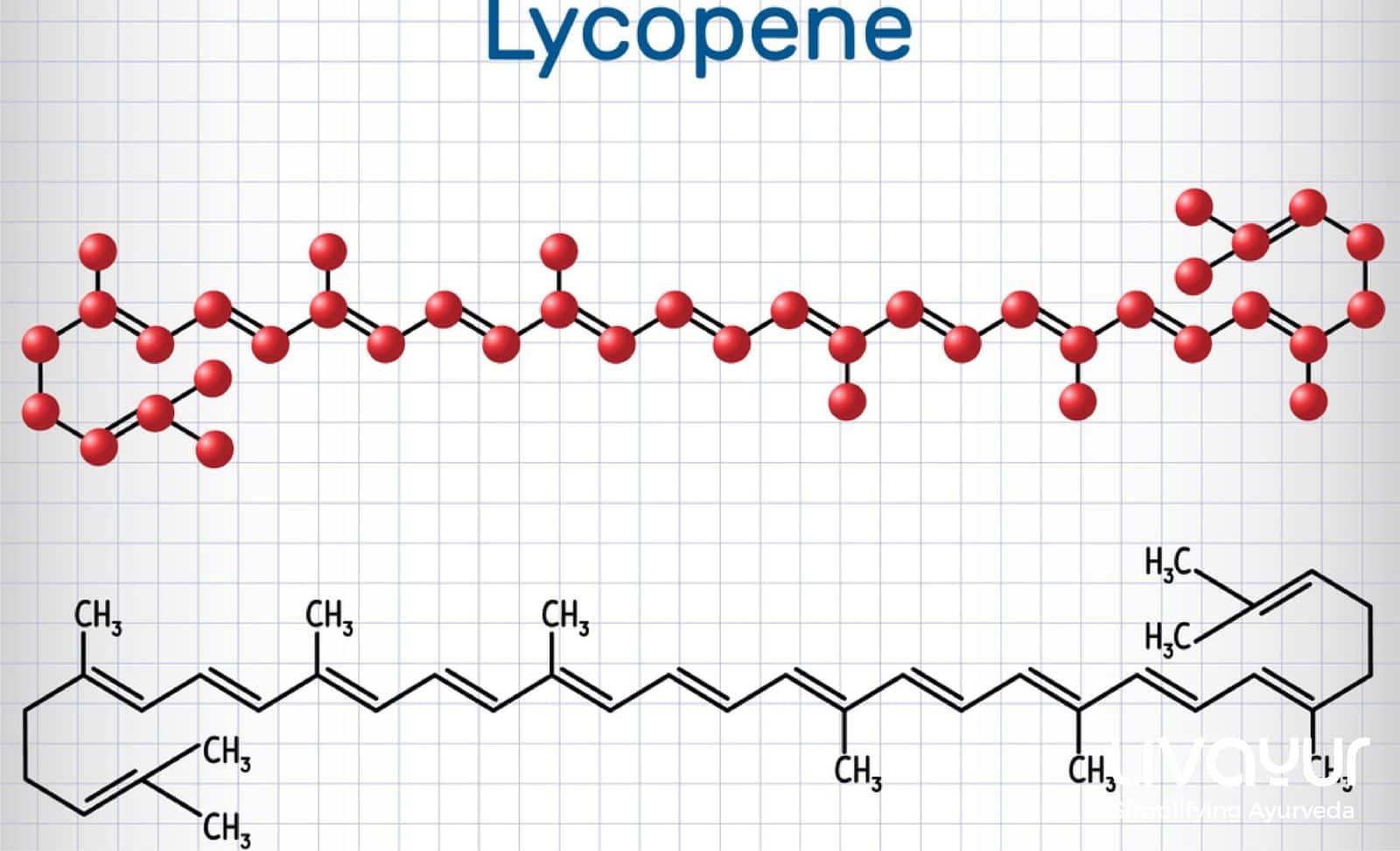
Watermelon’s benefits through lycopene content
There isn’t any specific research directly linking watermelon consumption to the management of diabetes. However, intriguing evidence suggests that including watermelon in your diet may contribute to reducing the risk of some diabetes-related complications. One notable component found in watermelon is lycopene, the natural pigment responsible for the fruit’s characteristic hue.
Lycopene is responsible for its vibrant color and serves as a potent antioxidant, which may hold critical advantages for individuals concerned about their diabetes management. Lycopene, found in moderate amounts within watermelon, can potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, a condition notably prevalent among adults with diabetes.
Research has shown that adults with diabetes are twice as likely to experience cardiovascular issues compared to those without diabetes. However, there is a silver lining: a nutritious diet rich in fruits and vegetables, like watermelon, and diligent management of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can significantly diminish this heightened risk.
The antioxidant properties of lycopene can play a crucial role in mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, which are pivotal factors in the development of cardiovascular complications. Consequently, while watermelon may not directly manage diabetes, its lycopene content holds promise in supporting overall health and reducing complication risks associated with this chronic condition. [1]
Watermelon’s glycaemic index value
Understanding the glycemic impact of foods is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it directly influences blood sugar levels. Watermelon, often perceived as a sweet fruit, is no exception to this consideration. Watermelon typically possesses a Glycemic Index (GI) of 76. The GI measures how rapidly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels when consumed in isolation. While a GI of 76 may appear relatively high, it’s essential to consider the Glycemic Load (GL) when evaluating the overall effect of a food on blood sugar.
In the case of watermelon, the GL provides a more comprehensive picture of its impact. A 120-gram serving of watermelon carries a modest GL of 5, indicating a relatively low glycemic load. The carbohydrate content of watermelon, which includes natural sugars, gets mitigated by its high water and fiber content. Fiber can slow down the sugar absorption, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels.
For individuals with diabetes, these values suggest that while watermelon may have a moderately high GI, it can be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced meal plan. The low GL and the presence of fiber make watermelon a reasonable choice for those seeking a sweet and hydrating treat without causing drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels. However, as with all foods, portion control is essential, and it is advisable to monitor blood sugar responses to determine how watermelon specifically affects individual glycemic control. [2]
FAQs
1. Is watermelon good for diabetic patients?
Watermelon is a handy dietary choice for diabetic patients. However, it is advisable to consume it in moderation. While watermelon contains natural sugars, it also has a low Glycemic Load (GL), meaning it has a relatively modest impact on blood sugar levels when consumed reasonably. Individuals with diabetes must monitor their portion sizes and how their bodies respond to watermelon. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the best approach for including watermelon in a diabetic meal plan. [1] [2]
2. Can watermelon raise your blood sugar?
Watermelon can cause a temporary increase in blood sugar levels, primarily due to its natural sugar content. It has a relatively high Glycemic Index, which indicates that it can lead to a rapid but short-lived spike in blood glucose when consumed in isolation. However, it’s crucial to consider the Glycemic Load (GL) of watermelon as well, which is relatively low due to its high water and fiber content. When consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced meal, the impact on blood sugar levels can be manageable. [2]
3. How much watermelon should a diabetic eat in a day?
The recommended amount of watermelon for a diabetic individual can vary depending on their overall diet, blood sugar control, and individual responses to the fruit. Generally, it’s advisable to limit the portion size to ensure blood sugar stability. Individuals must monitor their blood glucose levels after consuming watermelon and adjust their portion sizes accordingly. Consulting a healthcare professional is suitable to develop a personalized meal plan that includes watermelon in a way that aligns with an individual’s dietary needs and health goals.
Conclusion
While watermelon boasts a relatively high Glycemic Index (GI), the low Glycemic Load (GL) suggests that its overall impact on blood sugar levels can be manageable when approached mindfully. The key lies in moderation. It is advisable to monitor portion sizes, monitor post-consumption glucose levels, and consider pairing this sweet fruit with a source of protein to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
In making dietary choices, viewing your meals as a holistic composition is prudent, with watermelon being just one part of the puzzle. Consulting with a healthcare professional is invaluable to achieve a comprehensive and tailored approach. They can evaluate your current diet, assess your overall health profile, and offer guidance on incorporating variety and balance into your eating plan.
In pursuing optimal health and diabetes management, an individualized strategy, supported by expert advice, will pave the way for the harmonious integration of watermelon and other nutritious components into your diet. Ultimately, your diet should reflect your unique needs and health goals, ensuring not only the management of diabetes but also your overall well-being.
Disclaimer
The information provided here does not intend to replace professional advice or treatment.
References