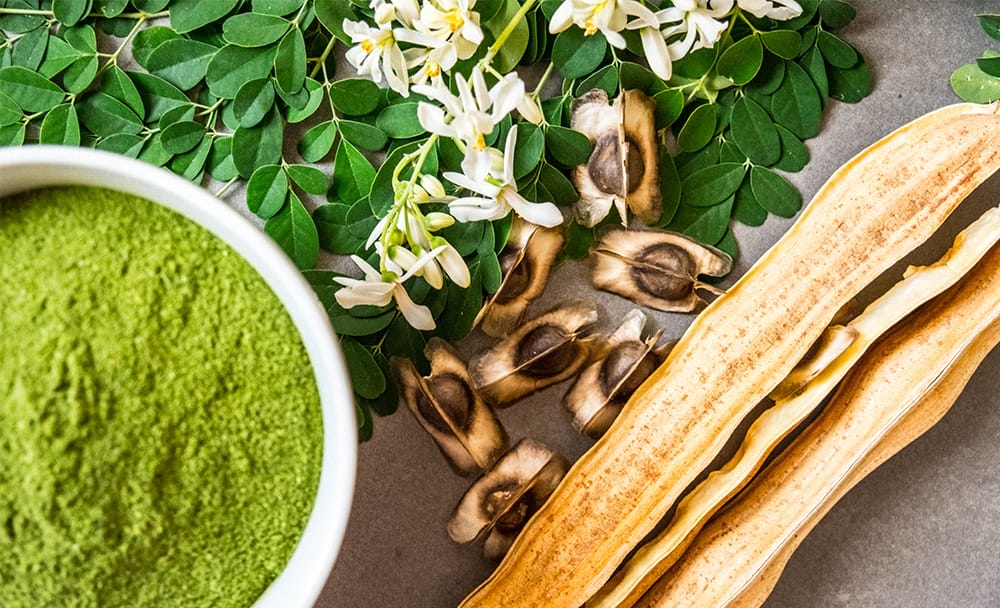
If you have been brought up in an Indian household, chances are that you have grown up eating Moringa or drumstick leaves. It’s a common vegetable in most parts of the country and is also extensively used in Ayurveda for its medicinal value.
One of the most common uses of Moringa in Ayurveda is in the treatment of diabetes and heart diseases.
Let’s find out how exactly Moringa helps treat diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in this article.
Moringa for Diabetes
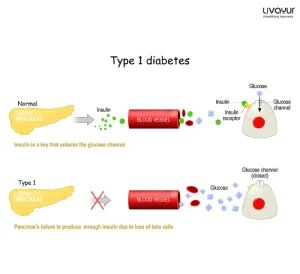
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder. High blood glucose levels in those with diabetes result from the defects in insulin production and insulin action. In addition, long-term hyperglycaemia can cause damage to multiple organs and lead to acute complications, especially involving the heart, eyes, and kidneys. When it comes to mortality related to type 2 diabetes, one of the most predominant factors involve cardiovascular disease.
The Moringa Tree
Moringa oleifera is, by far, the most widely cultivated species when it comes to the genus Moringa. Moreover, the Moringa tree is native to the Indian subcontinent and is edible. Its leaves are extensively used as a vegetable in India. It is an effective remedy to treat malnutrition, and it is used in the science of Ayurveda to combat diabetic complications. Because of the numerous side effects associated with oral hypoglycaemic drugs used to treat diabetes, there is a keen interest on herbal medicines to tackle the same. One popular study evaluated the protective role of the methanol extract of the leaves of Moringa on the hearts of diabetic rats.
Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Disease
Oxidative stress is the primary cause for the development of cardiovascular diseases such as diabetic cardiomyopathy (which is a diabetes-associated heart dysfunction) and congestive heart failure. Several studies have demonstrated that antioxidant therapy plays a key role and a promising function in the prevention of the progress of heart complications caused by diabetes. Thus, it can be concluded that oxidative stress plays a significant role in the progression as well as complications that are associated with diabetes. Therefore, the precise relationship between oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy is being closely studied.
Anti-Hyperglycaemic/Antidiabetic Effects
Numerous compounds present in Moringa leaves may be involved in glucose homeostasis. For instance, isothiocyanates are known to reduce insulin resistance and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Phenolic acids as well as flavonoids directly affect glucose homeostasis, influencing beta-cell function and mass, and augmenting insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Phenolic compounds, tannins, and flavonoids additionally inhibit intestinal sucrase and (to some extent) pancreatic alpha-amylase activity.
The favourable activities of Moringa leaves on the metabolism of carbohydrates have been demonstrated by diverse mechanisms, including prevention and restoration of the integrity and function of beta-cells, increase in insulin activity, and improvement in glucose uptake and utilisation.
Hypoglycaemic and anti-hyperglycaemic activity of the leaves of the Moringa tree may be due to the high presence of terpenoids, which are actively involved in the stimulation of beta-cells and the subsequent production of insulin. In addition, flavonoids have been shown to play a key role when it comes to hypoglycaemic action.
What Are the Benefits of Moringa?
When it comes to the benefits of Moringa, its bioactive compounds confer properties that are associated with prevention and treatment of disease, such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anticancer, antioxidant, cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective. Primary as well as secondary metabolites may additionally be involved when it comes to these applications.
Primary metabolites include proteins, lipids, fibre, and polysaccharides that are involved in physiological functions. Among these, polysaccharides and fibres are the primary compounds that are known to show positive effects on chronic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, among others.
To Sum It All Up:
The Moringa tree (whose scientific name is Moringa oleifera) is native to the Indian subcontinent. Because it is an edible plant, its leaves have been eaten as a vegetable in India. It is used extensively in the science of Ayurveda to combat diabetic complications. Besides being antidiabetic and cardioprotective, the Moringa tree is known to demonstrate anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and hepatoprotective activity. The primary cause for the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure is oxidative stress. Antioxidant properties of the Moringa tree largely prevent the occurrence of diabetic complications, including diabetic cardiomyopathy. Hypoglycaemic as well as anti-hyperglycaemic activity of Moringa can be attributed to the presence of terpenoids, which are primarily involved in the stimulation of the beta-cells and the subsequent secretion of insulin.
Manage Diabetes With The Knowledge Of Ayurveda (Download Ebook)