This article is reviewed by an expert
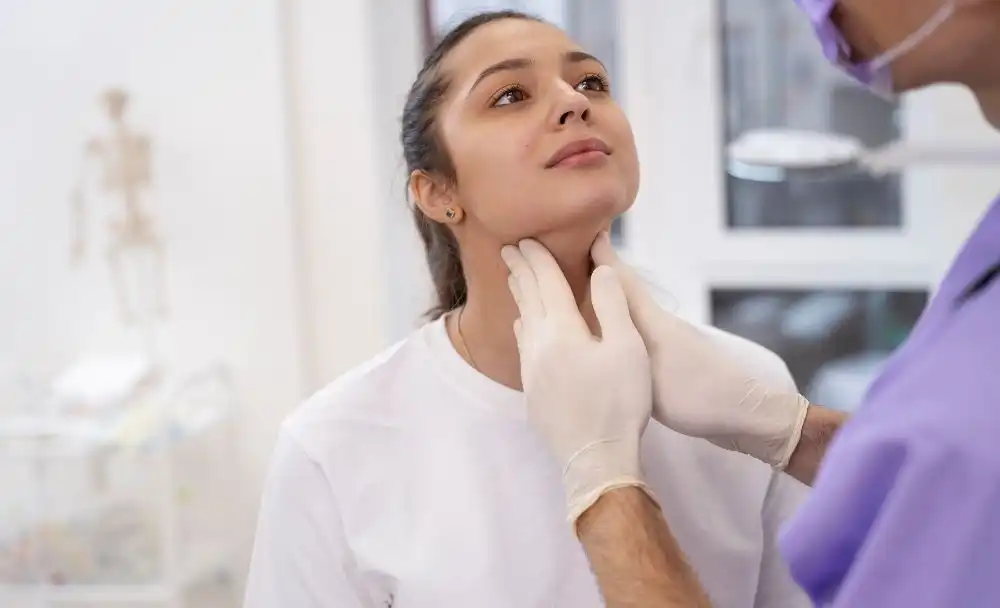
Thyroid disorders are conditions that affect the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ in the front of your neck that produces hormones that regulate your metabolism. There are different types of thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone), hyperthyroidism (high thyroid hormone), goiter (enlarged thyroid), nodules (lumps in the thyroid), thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid) and thyroid cancer. Reports suggest that India has a high burden of thyroid disease, with more than 42 million patients recorded in 2011, while more recent studies point to a hypothyroidism prevalence rate of 11 percent, as compared to 2 percent in the UK 1,2. Tackling this burden requires greater public awareness and efforts to lower the risk of thyroid disorders.
Causes Of Thyroid Disorders
Iodine Deficiency
The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce thyroid hormones. A deficiency or excess of iodine in one’s diet can lead to thyroid problems. In areas where iodine deficiency is prevalent, conditions like goiter (enlarged thyroid gland) or hypothyroidism can occur. Conversely, excessive iodine intake, such as from certain medications or supplements, can cause hyperthyroidism.
Autoimmune Diseases
The most common cause of thyroid disorders is autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) 3. Graves’ disease, on the other hand, causes hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) due to the immune system stimulating the thyroid to produce excess hormones 4.
Certain Medications
Some medications, such as lithium (used to treat bipolar disorder) or amiodarone (used for heart rhythm problems), can affect thyroid function. Additionally, treatments like radioactive iodine therapy, used to treat hyperthyroidism or thyroid cancer, may cause long-term thyroid problems.
Radiation Exposure
Exposure to ionizing radiation, especially during childhood or adolescence, increases the risk of developing thyroid disorders 5. This can occur from medical radiation treatments, radiation therapy for cancer, or exposure to nuclear accidents or fallout.
Nodules
Nodules are abnormal growths of thyroid tissue that can be benign or malignant. Some nodules can produce excess thyroid hormones, causing hyperthyroidism, while others can interfere with the normal function of the thyroid gland, causing hypothyroidism.
Cancerous Tumors
Thyroid cancer is a rare but serious condition that occurs when abnormal cells grow in the thyroid gland. Thyroid cancer can cause symptoms such as a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, or pain

Risk Factors For Thyroid Disorders
- Genetic factors: Some thyroid disorders have a genetic component 6. Certain gene mutations or variations can increase the risk of developing thyroid disorders.
- Age and gender: Thyroid disorders are more common in women, particularly during pregnancy and menopause. Additionally, the risk of developing thyroid disorders tends to increase with age.
- Family history: If you have a close family member with a thyroid disorder, you may be at a higher risk of developing one yourself.
- Stress and certain medical conditions: Chronic stress and some medical conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, type 1 diabetes, or rheumatoid arthritis, may be associated with an increased risk of thyroid disorders.
- Genetic factors: Some thyroid disorders have a genetic component 6. Certain gene mutations or variations can increase the risk of developing thyroid disorders.
- Age and gender: Thyroid disorders are more common in women, particularly during pregnancy and menopause. Additionally, the risk of developing thyroid disorders tends to increase with age.
- Family history: If you have a close family member with a thyroid disorder, you may be at a higher risk of developing one yourself.
- Stress and certain medical conditions: Chronic stress and some medical conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, type 1 diabetes, or rheumatoid arthritis, may be associated with an increased risk of thyroid disorders.
Symptoms Of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disease symptoms can vary greatly depending on the underlying causes, the type of thyroid disorder, as well as other factors such as the gender of the patient. Here is a complete list of thyroid symptoms in the main categories.
Symptoms Of Hyperthyroidism 7
- Nervousness, anxiety, irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Weight loss
- Increased heart rate, palpitations, chest pain
- Tremors, muscle weakness
- Heat intolerance, sweating
- Frequent bowel movements, diarrhea
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
- Eye problems, such as bulging, redness, or irritation
Symptoms Of Hypothyroidism 8
- Fatigue, sluggishness, depression
- Weight gain
- Decreased heart rate, low blood pressure
- Cold intolerance, dry skin, brittle hair and nails
- Constipation
- Muscle aches, joint pain, stiffness
- Swelling of the face, hands, feet, or legs
- Memory problems, difficulty concentrating
Thyroid Symptoms In Women
Some unique features of thyroid symptoms in women include the following 9:
- Irregular menstrual periods or missing periods and early menopause.
- Menstrual changes affect ovulation and can interfere with fertility.
- Women with hypothyroidism report more symptoms than men with hypothyroidism.
- The presence of symptoms is more indicative of hypothyroidism in men than in women.
- The most common symptoms in both genders were tiredness, dry skin, and shortness of breath.
Thyroid Symptoms In Men
Variation in thyroid symptoms in male patients has also been recorded and can include the following 10,11,12:
- Hair loss (not only on the scalp but also on the eyebrows and body)
- Low libido (reduced sex drive)
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Gynecomastia (male breast enlargement)
- Erectile dysfunction (inability to get or maintain an erection)
- Infertility (low sperm count or quality)
Conclusion
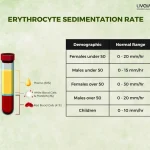
Thyroid disorders can be difficult to diagnose, so if you notice any symptoms, make it a point to talk to your doctor. Simple blood tests and other diagnostic procedures can help with an accurate diagnosis, allowing for more effective treatment that reduces the risk of serious complications.
FAQs
Will iodine supplements prevent thyroid disease?
Iodine is essential for healthy thyroid function but both low or high levels of iodine can cause thyroid problems. Make sure to check with your doctor before taking such supplements.
Can Ayurveda treat symptoms of thyroid in female?
Yes, herbs such as Shatavari are known to help significantly, but any thyroid disorder treatment should first be discussed with your doctor.
Are high thyroid symptoms more serious than low thyroid?
Both high and low levels of thyroid hormone can cause severe symptoms and serious complications. The severity of symptoms can vary among patients depending on various factors.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3169866/
- https://www.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/landia/PIIS2213858714702086.pdf
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/hashimotos-disease
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/graves-disease
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26931197/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459466/
- https://medlineplus.gov/hyperthyroidism.html
- https://medlineplus.gov/hypothyroidism.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25845636/
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(16)00278-6/fulltext
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2058738418775241
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2050052118300593