This article is reviewed by Dr. Jyoti Lakhani
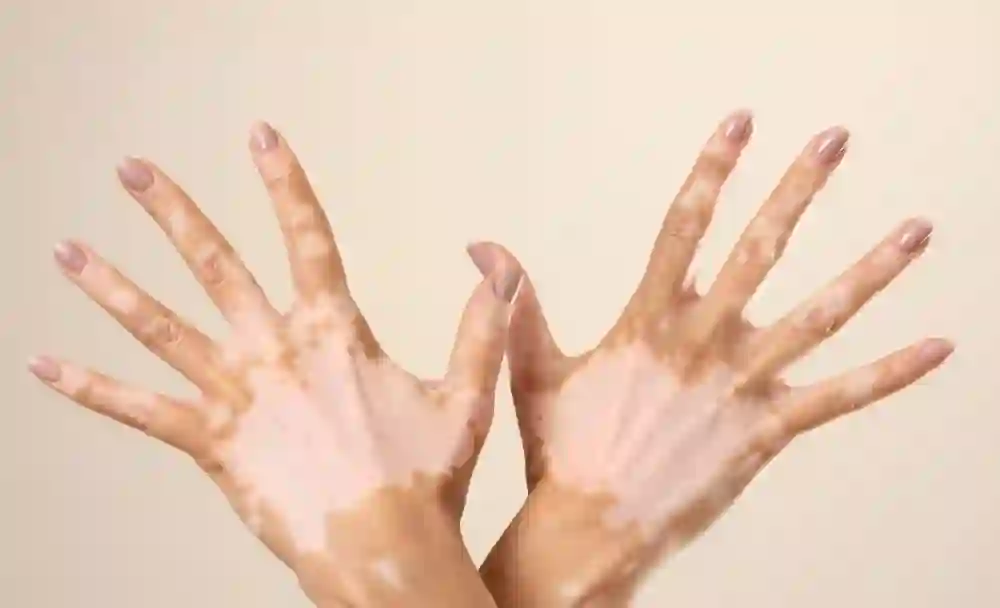

Vitiligo is a chronic skin disorder characterized by the loss of skin pigmentation, leading to the development of white patches on the skin. It affects people of all races and genders and is estimated to affect about 1% of the global population. In this article, we will explore the meaning of vitiligo, its symptoms, causes, available treatments, and more.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a dermatological condition that results in the depigmentation of the skin. It occurs when the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which gives colour to the skin, are destroyed or become dysfunctional. As a result, white or light-coloured patches appear on various parts of the body, including the face, hands, feet, and other areas [1].
Symptoms of Vitiligo
The primary symptom of vitiligo is the presence of depigmented patches on the skin. These patches are usually pale white or light-coloured and can be of varying sizes and shapes. They commonly occur symmetrically, affecting both sides of the body simultaneously. The patches may start small and gradually enlarge over time, or they can remain stable without further progression. In addition to the skin, vitiligo can also affect other areas, such as the hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, and even the inside of the mouth [2].
Causes and Risk Factors of Vitiligo [1]
The exact cause of vitiligo is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to be a multifactorial condition involving a combination of genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors. Some of the proposed causes and risk factors include:
- Autoimmune Factors
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its cells and tissues. In the case of vitiligo, it is thought that the immune system targets and destroys melanocytes, leading to depigmentation.
- Genetic Predisposition
There is evidence to suggest a genetic component in vitiligo, as the condition often runs in families. Certain gene variations have been associated with an increased risk of developing vitiligo.
- Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them, has been implicated in the development of vitiligo. It is believed that increased oxidative stress may contribute to the destruction of melanocytes.
- Environmental Triggers
Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals, sunburn, or emotional stress, may act as triggers for the onset or progression of vitiligo in susceptible individuals.
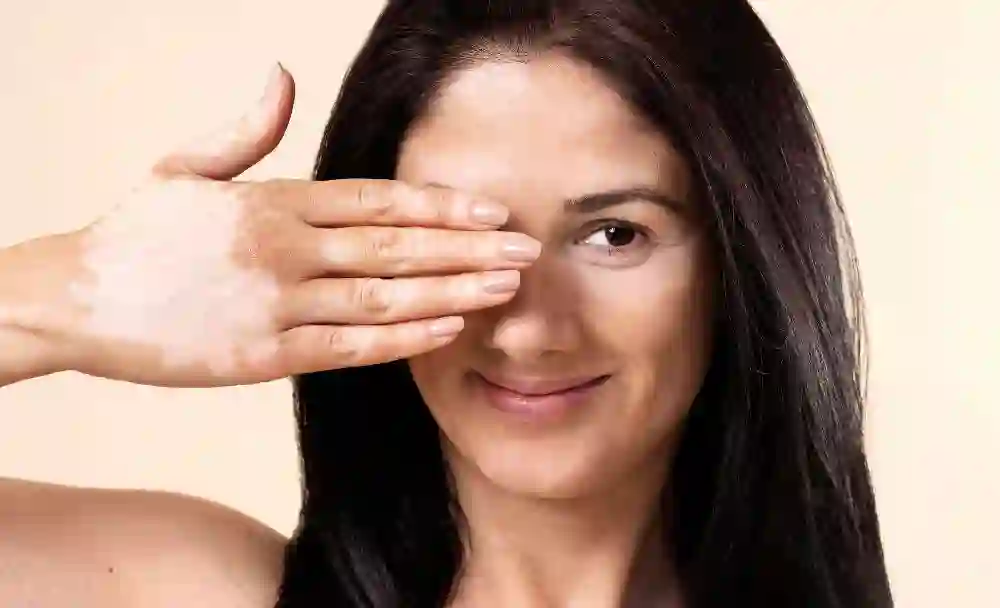

Treatment Options for Vitiligo [3]
While there is no known cure for vitiligo, various treatment options aim to manage the condition and improve the appearance of the affected skin. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the extent of depigmentation, the location of patches, and individual preferences. Some common treatment modalities include:
- Topical Corticosteroids
These medications are applied to the affected skin to help suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation. They can help to repigment the skin in some cases.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
These medications modulate the immune response and can be used in sensitive areas where corticosteroids may not be suitable, such as the face and genitals.
- Psoralen Plus Ultraviolet A (PUVA) Therapy
This therapy involves the administration of a psoralen medication, either topically or orally, followed by exposure to UVA light. Psoralen makes the skin more sensitive to UVA light, which helps stimulate repigmentation by activating melanocytes. This therapy is often recommended for more extensive vitiligo and can be effective in certain cases.
- Narrowband Ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) Therapy
This treatment involves exposure to a specific wavelength of UVB light, which helps stimulate repigmentation of the skin. NB-UVB therapy is a common choice for vitiligo and can be administered in clinics or through handheld devices for home use.
- Excimer Laser
This targeted laser treatment delivers a high-intensity beam of UVB light to specific areas of depigmentation, stimulating repigmentation. Excimer laser therapy is often used for localized vitiligo patches and can be an effective treatment option.
- Surgical Procedures
In cases where other treatments are ineffective, surgical procedures may be considered. These include techniques such as autologous melanocyte transplantation, blister grafting, and tattooing, which aim to repopulate the depigmented areas with melanocytes.
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
In addition to conventional medical treatments, some individuals may explore alternative or complementary approaches for vitiligo management. One such approach is Ayurvedic treatment, an ancient Indian medical system that utilizes herbal remedies, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. However, it is important to note that the scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of these approaches is limited, and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is advised.
Is Vitiligo Contagious?
No, vitiligo is not contagious. It is not caused by any infectious agents and cannot be transmitted from one person to another through direct contact [4].
Prevention and Lifestyle Considerations [5]
While there are no specific strategies to prevent vitiligo, individuals with vitiligo can take certain steps to manage the condition and protect their skin. These include:
- Sun Protection
Protecting the skin from excessive sun exposure is crucial, as sunburn can trigger the spread of vitiligo patches. Wearing sunscreen, and protective clothing, and seeking shade can help minimize the risk of sunburn and further depigmentation.
- Camouflage Techniques
Camouflaging the depigmented areas with cosmetics, such as makeup or self-tanning products, can help improve appearance and boost self-confidence.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by depigmented patches on the skin. While there is no known cure for vitiligo, various treatment options are available to manage the condition and improve the appearance of the affected skin. Individuals with vitiligo need to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their specific case.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for education and general awareness. It is not intended to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your healthcare professional for any medical information.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559149/#:~:text=Vitiligo%20is%20an%20acquired%20pigmentary,abnormalities%20are%20the%20commonest%20one.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/symptoms-causes/syc-20355912
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8170669/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7281839/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355916