This article is reviewed by an expert
Drinking water is essential for our overall health and well-being, but did you know that the temperature of the water you consume can also make a difference?
Lukewarm water is considered most beneficial for your health. It offers numerous benefits that can positively impact digestion, detoxification processes, and overall bodily functions (1).
Let’s have a look at the key benefits of drinking lukewarm water in detail in this article.
What Is Lukewarm Water?
Lukewarm water refers to water that is neither too hot nor too cold. It is typically around room temperature but slightly warmer.
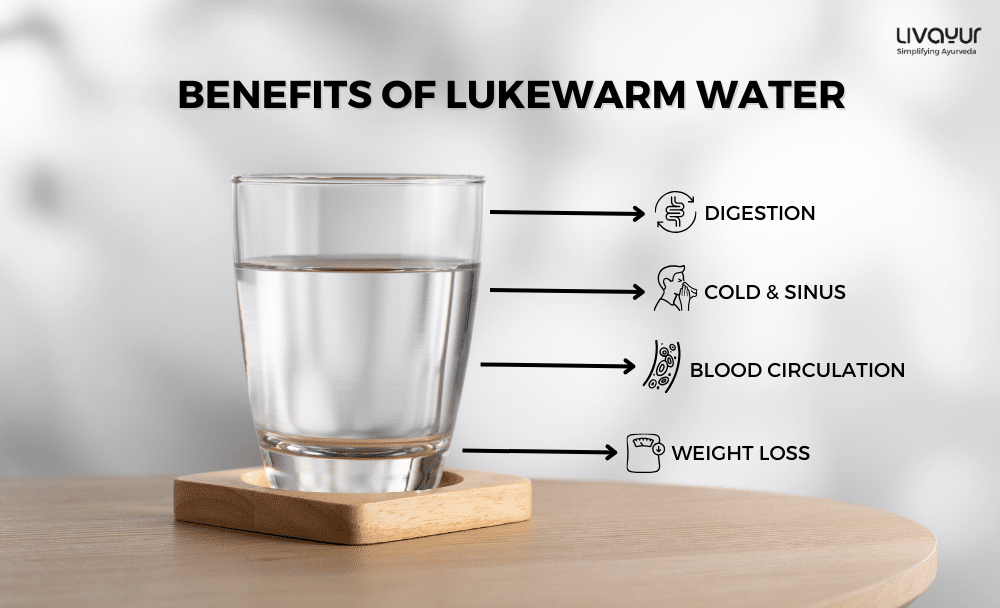
Benefits of Lukewarm Water (1)
Digestion
Primary Benefits: Lukewarm water helps break down food faster, thereby supporting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Secondary Benefits: In addition, lukewarm water also aids in intestinal movement, reducing bloating, abdominal pain, and discomfort.
Detoxification
Primary Benefits: Lukewarm water helps raise body temperature, causing sweating that, in turn, expels toxins from the body.
Secondary Benefits: By aiding in detoxification, lukewarm water also helps reduce the risk of premature ageing.
Blood Circulation
Primary Benefits: Lukewarm water acts as a vasodilator, expanding blood vessels and improving circulation.
Secondary Benefits: Improved circulation can further help muscles relax and reduce pain.
Weight Loss
Primary Benefits: Drinking lukewarm water increases feelings of fullness, reducing the urge to overeat, thereby contributing to weight loss.
Secondary Benefits: Lukewarm water also improves metabolism, making the body absorb nutrients better and flush out waste.
Cold & Sinus
Primary Benefits: Lukewarm water helps move mucus more quickly, encouraging coughing and nose-blowing to be more effective.
Secondary Benefits: Lukewarm water can hence help alleviate nasal congestion and relieve cold.
Menstrual Cramps
Primary Benefits: Lukewarm water can increase blood circulation, which in turn helps relax the uterine muscles.
Secondary Benefits: This aids in relieving menstrual cramps and improving comfort during menstruation.
Why Should You Not Drink Cold Water (1)?

Restricted Digestion and Hindered Hydration
When you consume cold beverages, your blood vessels shrink, leading to restricted digestion and hindered absorption of nutrients. Instead of focusing on digesting food and absorbing essential nutrients to create energy, your body expends energy to regulate its temperature. This can potentially result in water loss and reduced hydration.
Decreased Immune System Function
Drinking cold water after a meal can create excess mucus in your body, which may decrease immune system function. This can make you more susceptible to catching colds and other illnesses. Opting for warmer or room-temperature water can help support a stronger immune system.
Impaired Fat Digestion
If you consume cold water while eating or immediately after a meal, the temperature of the water can solidify the fats from the food you’ve just eaten. This makes it harder for your body to digest these unwanted fats, potentially leading to digestive discomfort and inefficient fat metabolism.
Ayurvedic View of Lukewarm Water (1)
In Ayurveda, the absorption of water by the body is believed to vary depending on its temperature. According to Ayurvedic principles, regular water takes approximately 6 hours to be absorbed, whereas boiled water is absorbed in half that time. Boiled water is also associated with enhanced Agni or the digestive fire.
However, it is to be noted that Ayurveda does not promote the consumption of hot boiled water. Instead, it suggests boiling water for ten minutes but then drinking it at room temperature. Reheating is not required.
The Healthiest Methods to Drink Lukewarm Water (1)
To maximise the potential benefits of lukewarm water, it’s important to incorporate it into your daily routine in a healthy and strategic manner. Here are some recommended methods for consuming lukewarm water:
- Drink one or two glasses of lukewarm water early in the morning, right after waking up, to kickstart your system and hydrate your body before anything else.
- Have a glass of lukewarm water at least 15-30 minutes before your meals. This helps prepare your digestive system and support better nutrient absorption.
- Aim to consume at least three glasses of lukewarm water during the day to maintain hydration levels and promote optimal bodily functions.
- In the evening, aim to have at least two glasses of lukewarm water, and ideally, four glasses if possible. This helps maintain hydration and supports the body’s natural processes.
- Before going to bed, have a glass of lukewarm water to stay hydrated throughout the night and support the body’s overnight processes.
The Final Takeaway (1)
Drinking lukewarm water offers a range of health benefits, particularly when consumed in the appropriate manner. It promotes digestion, aids in body detoxification, improves circulation, supports weight loss efforts, reduces pain and even relieves colds and improves sinus health.
On the other hand, drinking cold water may hinder digestion, impair hydration, decrease immune system function, and interfere with fat digestion.
Ayurveda also emphasises the importance of lukewarm water. It says lukewarm water can help stimulate digestive fire.
FAQs
- What is the ideal temperature for lukewarm water?
Lukewarm water is typically around room temperature, slightly warmer than cold water. It should feel comfortably warm when consumed, but not hot enough to cause discomfort.
- Can lukewarm water aid in weight loss?
Yes, drinking lukewarm water can contribute to weight loss. It increases feelings of fullness, reduces overeating, and improves metabolism, allowing the body to absorb nutrients better and eliminate waste more efficiently.
- Can you drink lukewarm water during exercise?
Yes, drinking lukewarm water during exercise can help maintain hydration levels and support bodily functions. However, it is important to drink water at a temperature that feels comfortable for you and does not cause any discomfort.
Disclaimer: This article is written from a health and lifestyle perspective. It is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.