This article is reviewed by an expert
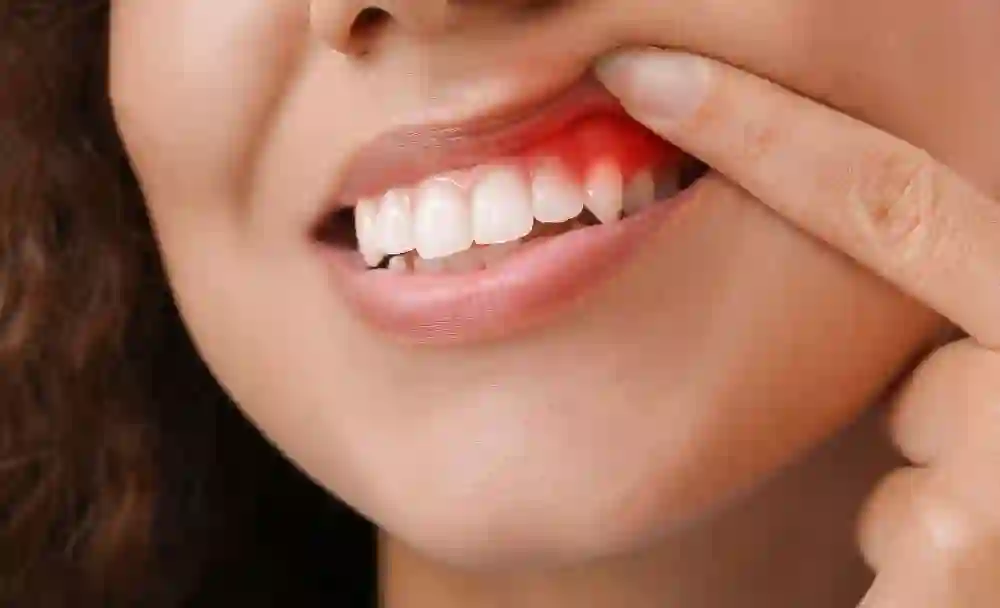

Gingivitis is a common gum disease that involves inflammation of the gums (gingiva). It is usually caused by the build-up of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque is not effectively removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can irritate and infect the gums, leading to gingivitis. Gum inflammation may not seem like a serious threat, but it can give rise to serious complications if ignored. Shockingly, gingivitis is estimated to affect roughly 46 percent of all adults in India 1.
Common Gingivitis Symptoms
Look out for these common gingivitis symptoms to deal with the problem swiftly:
- Swelling and inflammation: The gums appear red, swollen, and may feel tender to touch.
- Bleeding gums: Gums may bleed during brushing, flossing, or even spontaneously.
- Gum recession: The gums may start to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets or gaps between the teeth and gums.
- Bad breath (halitosis): Persistent bad breath can occur due to the presence of bacteria in the mouth.
- Tender or sensitive gums: The gums may feel painful or sensitive when touched or while eating.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis. In periodontitis, the infection can spread beneath the gum line, leading to the destruction of gum tissue and the supporting structures of the teeth. Severe periodontitis is seen in roughly 19 percent of India’s adult population 1.
Causes Of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is mainly caused by bacterial plaque overgrowth around the teeth, which hardens to form a hard-yellowish substance called tartar. This accumulates towards the base of the gums and can lead to the destruction of gingival or gum tissue and inflammation 2. If neglected it can progress to damage the soft tissue and bone structure that supports your teeth, leading to tooth loss.
While gingivitis causes may be hard to control, you can address known risk factors that include 2:
- Tobacco use – both smoked or chewed
- Poor dental hygiene
- Poorly fitted dental appliances or broken fillings
- Crooked teeth
- Conditions like diabetes
- Use of certain medications
- Chemotherapy
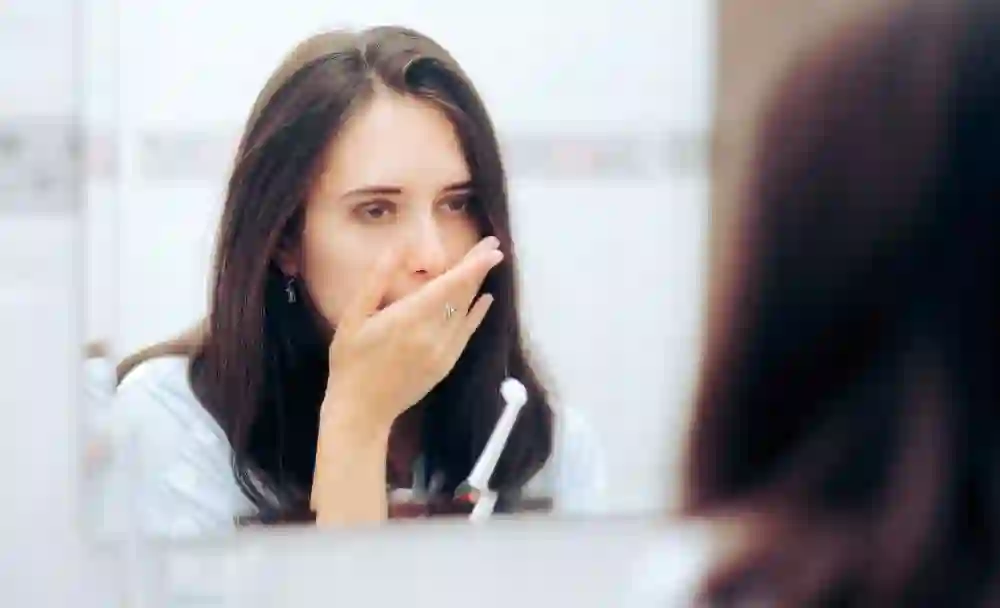

Gingivitis Stages And Progression
Gingivitis is a progressive gum disease that develops in stages. Gingivitis is actually the mildest stage of gum disease and if ignored it progresses to other stages. Gum disease or gingivitis stages include 3:
- Gingivitis: This is reversible with early diagnosis and treatment and is regarded as the earliest stage of gum disease.
- Early Periodontitis: Plaque build-up leads to separation of gums from the teeth leaving space for increased food, bacteria and plaque accumulation that leads to infections and tissue damage.
- Moderate Periodontitis: Symptoms of inflammation become more severe as there is greater loss of supporting bone, loosening of the teeth and further receding of the gums.
- Advanced Periodontitis: In addition to causing tooth loss, this is also characterized with the formation of painful abscesses due to infection that reaches beneath the gums.
Gingivitis Treatment Options
Gingivitis treatment requires a holistic approach that also addresses the underlying causes or risk factors. This means seeking dental treatment and making lifestyle changes. The main options for gingivitis treatment include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning
A dentist will perform a thorough cleaning of your teeth, including scaling and root planing. Scaling involves the removal of plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and below the gumline, while root planing smooths the root surfaces to promote gum tissue reattachment.
- Improved Oral Hygiene
Your dentist or dental hygienist will provide guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques. They may recommend using a soft-bristled toothbrush, an antimicrobial mouthwash, or other oral hygiene products to help control plaque build-up.
- Regular Dental Checks
It is important to schedule regular dental visits for check-ups and professional cleanings. This allows your dentist to monitor your oral health, detect any signs of gingivitis or periodontitis early on, and provide appropriate treatment 5.
- Antibacterial Mouth Rinses
In some cases, your dentist may prescribe or recommend an antibacterial mouth rinse to help reduce bacteria in the mouth and control gum inflammation.
- Medications
In certain situations, your dentist may prescribe antimicrobial medications or oral antibiotics to help control the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Natural Treatments
Salt water mouthwashes and mouthwashes contain herbs with antibacterial properties can help control gingivitis. The Ayurvedic practice of oil pulling has also been shown to reduce signs of gingivitis and plaque formation 6.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a warning sign that you need to pay greater attention to your dental health as the problem is still reversible at this stage. If ignored, gingivitis progresses to periodontal disease, which causes permanent damage to the gums, teeth and supportive structure.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for education and general awareness. It is not intended to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your healthcare professional for any medical information.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7649635/
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001056.htm
- https://www.health.ny.gov/health_care/medicaid/fact_sheets/docs/periodontal/english.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279593/
- https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/conditions/periodontal-disease.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4382606/