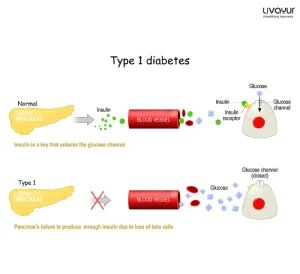
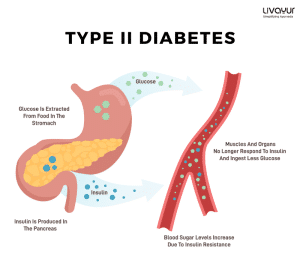
People with diabetes are advised to consume a variety of whole foods including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, lean meats, fish, eggs and low-fat dairy products. These foods provide a balanced intake of macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) that can support overall health and well-being. Vegetables are a particularly important part of any diabetes diet and some vegetables can be particularly helpful. Here are some of the best vegetables for diabetics to add to their diet.
Calorie value of best vegetables for diabetes
| Vegetable name | Calorie content (in Kcal per 100 g) |
| Bitter gourd | 34 |
| Bottle gourd | 15 |
| Cabbage | 25 |
| Spinach | 23 |
| Broccoli | 34 |
| Brussels sprouts | 43 |
| Tomatoes | 18 |
| Eggplant | 25 |
| Carrots | 41 |
| Cauliflower | 25 |
| Cucumbers | 15 |
| Ladyfinger | 365 |
Benefits of eating vegetables for diabetes
Here are some key advantages of incorporating vegetables into the diet of individuals with diabetes.
1. Has low glycemic index
Many vegetables have a low glycemic index. They can cause a steadier rise in blood glucose levels. It helps prevent sudden blood sugar spikes for better glucose control.
2. Offers high fiber content
Fiber regulates blood sugar by slowing down the absorption of sugar and improving insulin sensitivity. Additionally, it can help promote a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management—a crucial aspect of diabetes management.
3. Offers nutrient density
Vegetables include essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients are crucial in supporting health. Some antioxidants found in vegetables may help reduce oxidative stress which can help manage diabetes complications.
4. Promotes weight management
Many vegetables contain low calories and high water content, making them filling without adding excess calories. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for insulin sensitivity and metabolic health.
5. Supports heart health
Diabetes comes with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Vegetables, significantly those rich in potassium and fiber, can positively impact heart health by promoting healthy blood pressure.
Top 12 Super Health Vegetables For Diabetes
1. Karela or Bitter Gourd
Bitter gourd or Karela is known to positively impact type 2 diabetes. The vegetable harbors at least three active components with anti-diabetic attributes: charanti, validated for its blood glucose-lowering impact; vicine; and a polypeptide-p, functioning similarly to insulin. These constituents work in synergy, contributing to the reduction of blood sugar levels. This lectin is believed to be a key factor in the hypoglycemic effect observed after consuming bitter melon.
2. Lauki
Bottle gourd or lauki is regarded as the most secure dietary option for individuals with diabetes. With a glycemic index as low as 15, it stands as one of the lowest GI foods. Lauki is deemed exceptionally safe for diabetes, exerting minimal impact on sugar levels and, conversely, is employed to regulate and manage blood sugar levels.
3. Cabbage
Cabbage can be beneficial for managing diabetes primarily due to its high fiber content. Cabbage also contains essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C and potassium, which support overall health. Furthermore, it has antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
4. Spinach
Spinach features prominently in any list of fruits and vegetables for diabetics because of its nutrient-rich profile. It’s low in calories and carbohydrates while being packed with nutrients including fiber, vitamins A and C, and minerals like magnesium. The high fiber content in spinach aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugars in the bloodstream. Additionally, magnesium is linked to improved insulin sensitivity.
5. Broccoli
Broccoli is one of the best vegetables good for diabetics for a variety of reasons, starting with its low glycemic value, high fiber content, and rich nutritional profile. Its abundant fiber helps control blood sugar by slowing sugar absorption and improving insulin sensitivity. Broccoli is also rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and compounds like sulforaphane, which may enhance blood sugar control.
6. Brussels sprouts
Brussels sprouts are small cruciferous vegetables that have a high content of glucoraphanin, a precursor of sulforaphane. Glucoraphanin can activate the Nrf2 pathway, which can enhance antioxidant defense and reduce inflammation. They are also rich in fiber which helps slow the absorption of sugars in the digestive tract and improves insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, Brussels sprouts are rich in essential nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin K, and antioxidants, which can support overall health and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Explore our related articles on sprouts:
1. 20 Amazing Health Benefits of Eating Sprouts
2. The Best Way of Eating Sprouts According to Ayurveda
7. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are technically fruits but are often considered vegetables. Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that can protect against visual impairment, cardiovascular disease, and some cancers Additionally, tomatoes are a source of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C and potassium, contributing to overall health.
8. Eggplant
Eggplant is a purple vegetable that has a high content of anthocyanins, and flavonoids that have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Eggplant also contains chlorogenic acid, which can inhibit alpha-glucosidase enzyme activity and lower postprandial blood glucose levels. It is one of the top choices of vegetables for diabetic patients.
9. Carrots
Carrots can be a smart choice for individuals with diabetes due to their low glycemic index and high fiber content. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels, and carrots have a relatively low score, making them a favorable option for diabetic individuals. The fiber in carrots slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, helping to prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
10. Cauliflower
Cauliflower is another cruciferous vegetable that has many health benefits for diabetics. Cauliflower is low in carbohydrates but high in fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, and phytochemicals. Cauliflower can be used as a substitute for rice or potatoes to reduce the glycemic load of meals. In fact, research indicates that cauliflower can help prevent hyperglycemia.
11. Cucumbers
Cucumbers can be a beneficial addition to the diet of individuals with diabetes, offering various health advantages. Their low carbohydrate content and minimal impact on blood sugar levels make them a diabetes-friendly choice. The high water content in cucumbers also contributes to hydration, which is essential for overall health and well-being.
12. Ladyfinger
Ladyfinger, also known as okra, can highly benefit individuals with diabetes. It offers both nutritional benefits and potential blood sugar management. It is low in calories and carbohydrates, making it a favorable choice for those looking to regulate blood sugar levels.
Most vegetables are considered healthy and suitable for people with diabetes, so long as they are consumed in moderation and are not processed. For example, starchy vegetables, beets, and carrots, peas, and legumes should be consumed in moderation to avoid blood sugar spikes. However, there are no fresh or home-cooked vegetables for diabetics to avoid. The only types of vegetables to avoid in diabetes are those that are canned or packaged with added sugar or sauces.
Conclusion
Remember that individual responses to foods can vary, so individuals with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels and work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan. Incorporating a variety of vegetables into the diet can contribute to better blood sugar management and overall health. Just make sure to be mindful of overall carbohydrate consumption and make informed choices about portion sizes and preparation methods.
FAQs
1. What are the serving size recommendations for vegetables for diabetes?
Serving size recommendations for vegetables for diabetes vary, but a general guideline is to aim for at least 2.5 to 3 cups of non-starchy vegetables per day.
2. Can I have vegetable juice for diabetes instead of eating vegetables?
While vegetable juice can be a part of a diabetes-friendly diet, whole vegetables are preferred due to their higher fiber content. If consuming vegetable juice, choose 100% vegetable juice without added sugars and consider portion control.
3. What should I keep in mind when choosing vegetables for diabetes?
When choosing vegetables for diabetes, prioritize non-starchy options like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower. Be mindful of portion sizes, and opt for fresh, frozen, or canned vegetables without added sugars or sauces.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and lifestyle perspective. It is for general information and not meant to substitute any medical advice. Please consult your doctor for appropriate medical consultation.
References:
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dinesh-Kumar-378/publication/370128917_Kumar752015BJPR17641/links/6440c393e881690c4be7acd3/Kumar752015BJPR17641.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20116660/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Joao-Dias-36/publication/316631106_Vegetables_Consumption_and_its_Benefits_on_Diabetes/links/5dfe43b292851c8364907bfe/Vegetables-Consumption-and-its-Benefits-on-Diabetes.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5018658/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5758090/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6261473/
- https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/8/2410
- https://ajcn.nutrition.org/article/S0002-9165(23)05840-9/pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9007711/
- USDA FoodData Central. (2021). Cucumber, with peel, raw. Retrieved from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/11052/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170379/nutrients