In the timeless wisdom of Ayurveda, the pursuit of holistic health has always been intertwined with the principles of natural healing and harmonizing the body. In this aspect, the quest for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health extends beyond pharmaceutical interventions, finding resonance in nature’s offerings. The ancient science of Ayurveda emphasizes the significance of balance within the body, a state achieved through the judicious use of herbs, foods, and supplements.
This article looks at the Ayurvedic wisdom to unveil the 12 best natural blood thinners harnessed from the bounteous offerings of the natural world. These time-honored remedies, rooted in Ayurvedic tradition, have the potential to foster cardiovascular vitality and promote well-being through their gentle yet efficacious properties.
What leads to blood clots?
Following Ayurvedic principles, the dynamics of blood clot formation can be due to the imbalance of the three fundamental doshas: vata, pitta, and kapha. Within them, pitta dosha, characterized by its ushna (hot), tiksna (sharp), and katu (pungent) qualities, and vata dosha, characterized by sukshma (subtle) and cala (mobile) qualities, are primarily responsible for regulating bleeding tendencies.
Conversely, Kapha dosha, characterized by its heavy and stable attributes, governs the coagulation process. When these doshas fall out of balance, it can lead to either hypercoagulation or hypo-coagulation, disrupting the delicate equilibrium of blood clotting. In alignment with Ayurvedic principles, restoring harmony among vata, pitta, and kapha facilitates optimal blood circulation and maintains the delicate balance between coagulation and bleeding. [1]
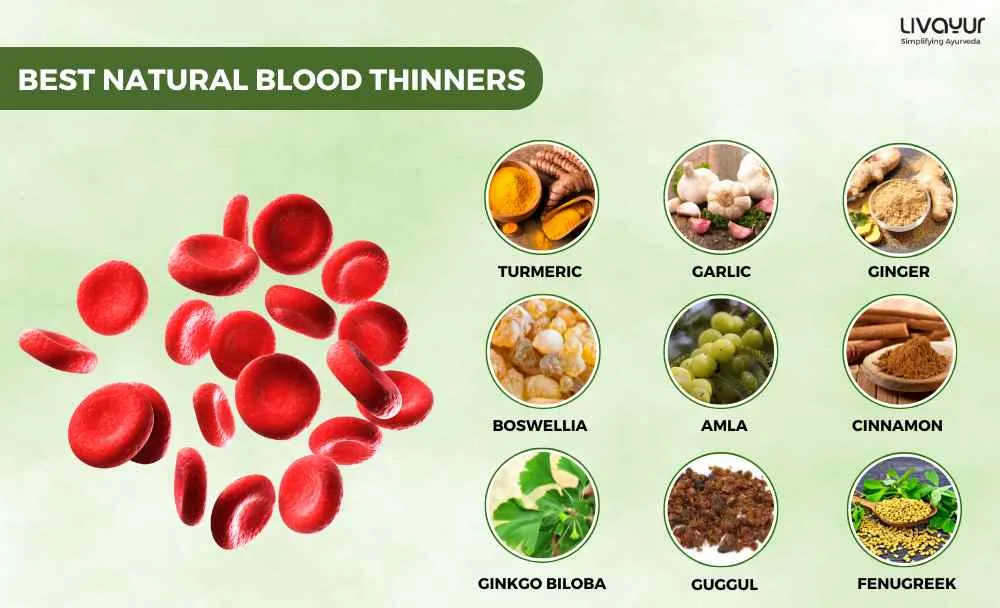
12 best natural blood thinners to consider
Here is a curated list of 12 natural blood thinners derived from the principles of Ayurveda, focusing on dietary choices and supplements.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
Renowned for its potent anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant properties, turmeric is a staple in Ayurvedic medicine. Its active compound, curcumin, helps to prevent blood clot formation. [2]
- Garlic (Allium sativum)
Garlic’s natural blood-thinning abilities can be due to its anti-platelet properties, which reduce the risk of clot formation. [3]

- Ginger (Zingiber officinale)
Ginger enhances digestion and has anti-inflammatory properties that can contribute to improved blood circulation. It also helps prevent blood clots. [4]
- Guggul (Commiphora wightii)
This resinous extract is known for its role in maintaining lipid metabolism, helping to prevent arterial plaque formation, and reducing the risk of clotting. [5]
- Cayenne Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
Its heat-inducing qualities stimulate blood flow and can help prevent the accumulation of blood platelets. [6]
- Boswellia (Boswellia serrata)
Another resin extract, boswellia, possesses anti-inflammatory properties that prevent clot formation and maintain vascular health. [7]
- Indian Gooseberry (Emblica officinalis)
Rich in vitamin C, amla promotes healthy blood vessels and can prevent platelet aggregation. [8]

- Cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum)
Known for its blood-sugar-regulating properties, cinnamon can also contribute to better blood circulation. [9]
- Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
Fenugreek seeds contain compounds that may inhibit blood clot formation and enhance heart health. [10]
- Fish Oil
Omega-3 fatty acids in supplements related to fish oil have natural anticoagulant properties, reducing the risk of clot formation. [14]
- Ginkgo Biloba
Known for enhancing blood flow to the extremities, ginkgo biloba can benefit those seeking to prevent clots. [15]
- Vitamin E
This antioxidant vitamin can help prevent platelet aggregation and is available in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. [16]
FAQs
1. How to thin blood naturally?
Natural blood thinning is possible through dietary choices and lifestyle adjustments. Consuming turmeric, garlic, and ginger, which have natural anticoagulant properties, can help. Staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and exercising can promote natural blood thinning.
2. What are some natural blood thinners in food?
Several foods naturally act as blood thinners. Some examples include turmeric, garlic, ginger, and cayenne pepper. These foods can help prevent excessive blood clotting when incorporated into your diet.
3. How to make blood thin naturally?
To naturally make your blood thinner, focus on dietary choices and lifestyle modifications. Include foods with natural anticoagulant properties like turmeric, ginger, and garlic in your meals. Stay hydrated, maintain an ideal weight, and exercise regularly to support natural blood thinning. Consult a healthcare professional before changing your blood-thinning regimen.
Conclusion
The wisdom of Ayurveda offers a holistic approach to blood thinning that aligns with the principles of balance and well-being. Incorporating natural blood thinners into your diet and lifestyle will help nurture cardiovascular health while respecting your body’s innate intelligence.
However, it is essential to remember that individual health needs may vary. Consultation with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner or healthcare professional is advisable before embarking on any significant dietary or lifestyle changes.
Disclaimer
The information provided here does not intend to replace professional advice or treatment.
References
- CONCEPT OF COAGULATION IN AYURVEDA
- Curcumin, hemostasis, thrombosis, and coagulation
- Consumption of a garlic clove a day could be beneficial in preventing thrombosis
- The Effect of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) on Platelet Aggregation: A Systematic Literature Review
- Pharmacology and Phytochemistry of Oleo-Gum Resin of Commiphora wightii (Guggulu)
- Cayenne – Health Encyclopedia – URMC
- Pretreatment with β-Boswellic Acid Improves Blood Stasis Induced Endothelial Dysfunction: Role of eNOS Activation
- Clinical evaluation of Emblica Officinalis Gatertn (Amla) in healthy human subjects: Health benefits and safety results from a randomized, double-blind, crossover placebo-controlled study
- The Effect of Cinnamon on Glucose of Type II Diabetes Patients
- An in vitro anticoagulant effect of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) in blood samples of normal Sudanese individuals
- An investigation into the stress-relieving and pharmacological actions of an ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract
- Bacopa monnieri
- Revisiting Terminalia arjuna – An Ancient Cardiovascular Drug
- Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation and Warfarin: A Lethal Combination in Traumatic Brain Injury
- Effects of Ginkgo biloba on cerebral blood flow assessed by quantitative MR perfusion imaging: a pilot study
- α-Tocopherol Inhibits Aggregation of Human Platelets by a Protein Kinase C–Dependent Mechanism
























