Are you drawn to the name ‘Foxtail’? If yes, you must know that Foxtail has nothing to do with the ‘tail of a fox’. It is actually the name given to a millet variety. Foxtail millet, scientifically known as Setaria italica, is one of the oldest cultivated grains in the world, dating back to ancient times. It is a small-seeded grain and belongs to the family Poaceae. Foxtail millet is a staple food crop in many parts of Asia and Africa, especially in India, China, and Nigeria. [1] It is known as Trundhanya [5] or Kanguni in Ayurvedic science and used as food as well as a therapeutic diet in Ayurveda since samhita kala. It has several therapeutic uses including Kustha Vatakarak, Pitta-daha nashak, Bhagna-asthi Sandhan. [4]
It has gained popularity globally in recent years due to its impressive nutritional profile and various health benefits. This article delves into what is foxtail millet, the characteristics of foxtail millet, its nutritional content, foxtail millet benefits for health, culinary foxtail millet uses, other foxtail millet uses and potential foxtail millet side effects.
Foxtail Millet Nutrition Facts
Foxtail millet is a nutrient-dense grain, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. The foxtail millet nutrition content of 100 grams of raw foxtail millet is as follows:
| Calories | 348 kcal |
| Starch | 58.2 g |
| Protein | 12.3 g |
| Fat | 3.3 g |
| Fiber | 13.6 g |
| Ash | 3.7 g |
| Calcium | 53 mg |
| Iron | 4.2 mg |
| Zinc | 2.6 mg |
Properties of foxtail Millet
- Astringent
- Sweet
- Vata-aggravating
- Pitta and Kapha-pacifying
- Dry in nature
- Non-aphrodisiac
- Slightly hot in potency
- Sucks moistness of your body
Other Names of Foxtail Millet across different languages
- Kangni (in Hindi)
- Navane (in Kannada)
- Thinai (in Tamil)
- Kang (in Gujarati and Marathi)
- Korra (Telugu)
- Kaung (in Bengali)
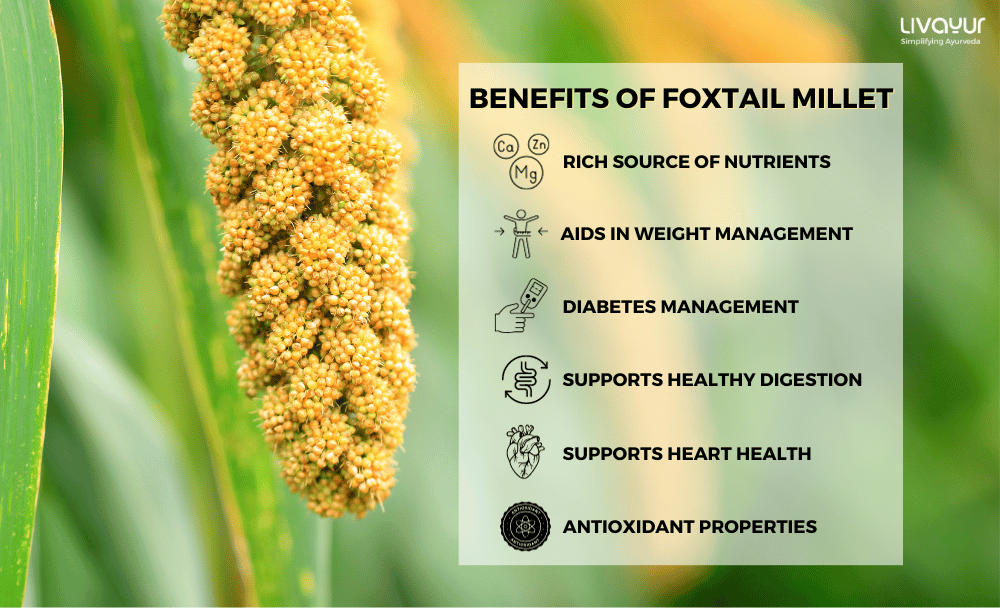
Health Benefits of Foxtail Millet
1. Rich Source of Nutrients
Foxtail millet is a vital source of essential nutrients, such as protein, dietary fiber, digestible starch, and minerals (calcium, iron, and zinc). Including foxtail millet in the diet can help meet daily nutrient requirements. [2]
2. Weight Management
The native resistant starch content of foxtail millet helps promote satiety and reduces hunger, which can aid in weight management and is one of the biggest foxtail millet benefits. [1]
3. Diabetes Management
Foxtail millet glycemic index is low, meaning it causes a slower rise in blood sugar levels compared to other carbohydrate-rich foods. This property makes it suitable for diabetics as it helps in managing blood sugar levels. [3]
4. Digestive Health
The dietary fiber in Foxtail millet supports healthy digestion and prevents constipation by promoting regular bowel movements. [1] According to Ayurveda, it enhances Vata Dosha and balances Pitta and Kapha Dosha. These millets have been mentioned in Ayurvedic texts, specifically in the Nighantu Adarsha, where they are referred to as “Munidhanya.” Rishis and Munis consumed these millets because of their high nutritional value and ease of digestion. [5]
5. Heart Health
Foxtail millet contains essential nutrients, which are vital for keeping the serum cholesterol, and serum triglyceride in check, thereby lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases and maintaining a b and healthy heart. [1]
6. Antioxidant Properties
The presence of various antioxidants in Foxtail millet helps combat oxidative stress and protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. [3]
7. Nutritious option for Celiac patients
Being gluten-free this millet can be a favorable food option for people with Celiac disease.
8. Manages Blood pressure
According to research, consumption of foxtail millet may show positive results on your blood pressure levels. [7]
9. Offers Nutritional support
For people with micronutrients deficiency, and for those who are underweight, this millet can be a nutritious addition to the diet, eliminating all symptoms of malnutrition.
10. Prevents Gallstone formation
By lowering the bile cholesterol levels and bile acid production, the fiber in foxtail millet may reduce the chances of gallstone formation. [8]
How to use Foxtail Millet
Culinary Foxtail Millet Uses
Due to Foxtail millet’s versatility, it can be incorporated into various dishes. Here are some popular culinary uses:
Porridge
Foxtail millet can be cooked as a porridge, similar to oatmeal, and served with milk or plant-based alternatives and sweeteners like honey or maple syrup.
Baking
Foxtail millet flour can be used in foxtail millet recipes and gluten-free baking to make rusk and cookies.
Breakfast cereals
In many Indian cuisines, foxtail millet is sometimes used to prepare vegetable dalia (porridge), snack foods – sattu (traditional drink), bar, and papad. [2]
Rice Replacement
Cooked Foxtail millet can be used as a rice substitute as it possesses twice the amount of protein compared to rice, providing a diverse range of nutrients and a delightful nutty taste. Moreover, it is highly digestible and non-allergenic, making it a favorable grain option. It is also a good source of essential minerals such as copper and iron. [5]
Other Foxtail Millet Uses
- As a food additive and thickener
- As a Nutritional supplement
- As an Anti-Anemia Supplement
- As a Diet cereal
- As a Baby food supplement
- As a health drink or malt
Foxtail Millet Side effects
- C-glycosylflavones in foxtail millet is a constituent which, according to researchers, may have goitrogenic effects. Constituent may inhibit the production of the thyroid hormone, leading to thyroid gland enlargement or goiter.[6]
- This millet has a low content of fibers and B-Vitamins, and therefore, may not be able to protect you against certain chronic diseases.
- Consuming foxtail millet in huge quantities, and in combination with milk may cause bloating and indigestion for some individuals.
- Although rare, some individuals may be allergic to millet. Allergic reactions may be mild or severe, including symptoms like itching, hives, and difficulty breathing. If allergic reactions occur, medical attention should be sought immediately.
- Like other grains, foxtail millet plants contain phytic acid, which can lead to reduced absorption of certain minerals. To enhance mineral absorption, soaking or sprouting millet before cooking can be beneficial.
Where to buy and price
You can buy foxtail Millet from nearby grocery stores and supermarkets.
If you’re looking for an online option, you can buy the product from online stores like Amazon, Flipkart, JioMart, 1 mg, BigBasket, The Millet Store, IndiaMART, etc.
Average Price of 1 KG foxtail millet may range from Rs 50 to Rs 100. The price actually depends on the quality, brand, location, and packaging.
FAQs
1. Who should refrain from consuming foxtail millets?
Individuals with certain conditions should exercise caution when consuming foxtail millet. While eating foxtail millet in moderate amounts is generally acceptable, specific precautions should be taken in the following situations: Foxtail millet may exacerbate Vataja roga (diseases caused by Vata Dosha imbalance), so those with symptoms such as dry skin, weight loss, or joint pain should be careful when consuming it.
2. Can foxtail Millet be eaten daily?
There is no harm in eating foxtail millet daily, but do not consume foxtail millet recipes the entire day, as it may cause side effects mentioned above. Moreover, a balanced diet consisting of a variety of different foods, including foxtail millet is definitely a healthier choice.
3. Where is foxtail millet grown in India?
In India, cultivation of foxtail Millet takes place in the southern states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
4. What is the key problem faced while cooking foxtail millet?
When cooked, this millet turns very sticky, and even after being cooked in a pressure cooker, foxtail millets do not turn fluffy. Also, this millet variety takes a longer time to be cooked properly.
5. Is Foxtail millet the same as quinoa?
No, foxtail millets and quinoa are two different types of whole grains. Quinoa is loaded with proteins while foxtail millet is devoid of proteins.
Conclusion
Foxtail millet is a highly nutritious grain that offers numerous foxtail millet benefits for health. Its gluten-free nature makes it suitable for individuals with gluten sensitivity, while its low glycemic index makes it a favorable option for diabetics. To experience the power of foxtail millet nutrition, you must add it to your balanced diet. This nutrients-rich millet can contribute to heart health, weight management, and digestive well-being.
Disclaimer:
This article is written from a health and wellness perspective only and is not a piece of medical advice. Kindly seek the help of a certified medical practitioner before initiating any treatment.
References:
- Foxtail millet: Properties, processing, health benefits, and uses
- Assessment of sensory and nutritional attributes of foxtail millet-based food products
- Assessment of sensory and nutritional attributes of foxtail millet-based food products
- Millets: The Indigenous Food Grains
- IMPORTANCE OF MILLETS W.S.R. TO MEDICINAL AND NUTRITIONAL VALUE: A REVIEW
- Antithyroid and goitrogenic effects of millet: role of C-glycosylflavones
- Effect of foxtail millet protein hydrolysates on lowering blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- Nutritional and Health Benefits of Millets